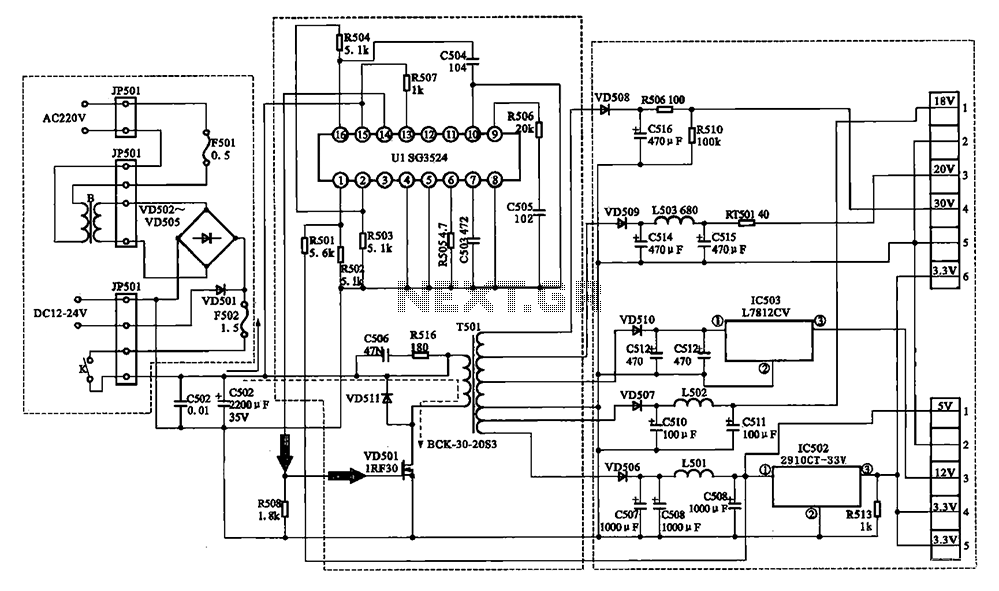
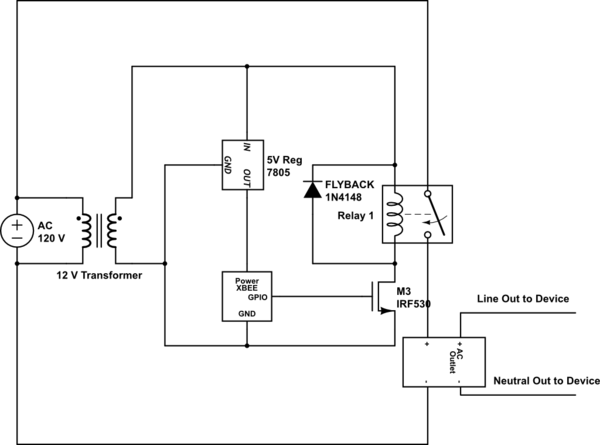
Power Mosfet Inverter
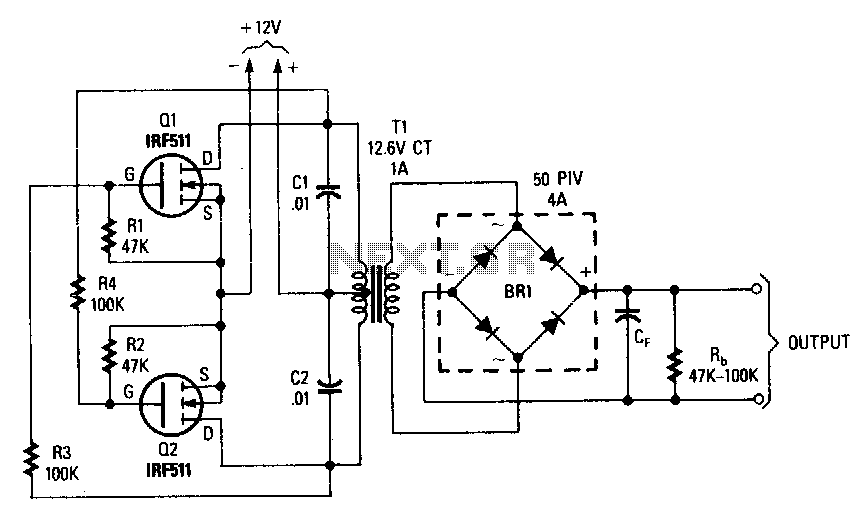
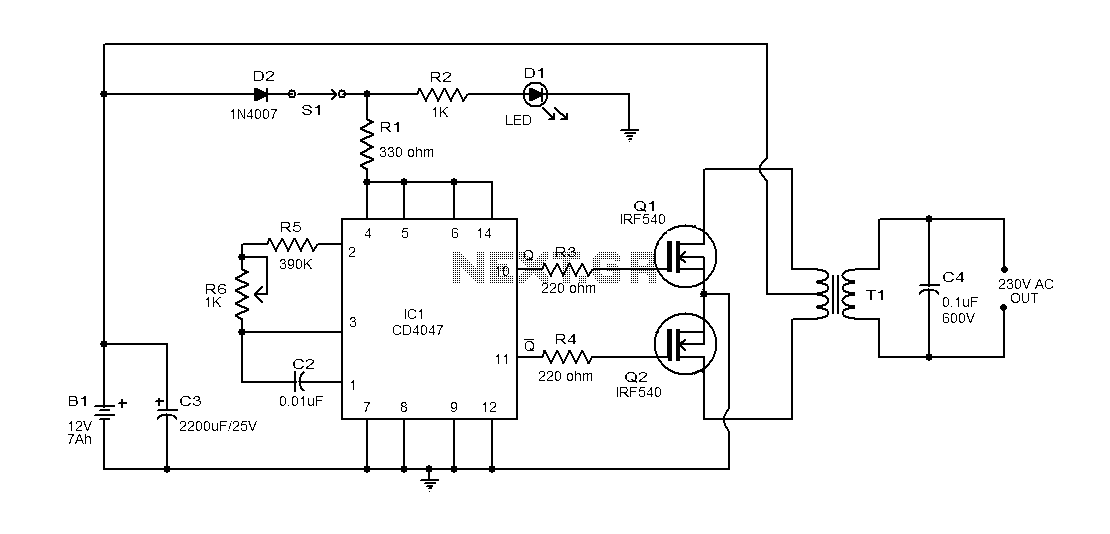
This inverter can deliver high-voltage AC or DC, with a rectifier and filter, up to several hundred volts. The secondary and primary of T1, a 12.6 to 440 V power transformer, respectively, are reversed; e.g., the primary becomes the secondary and the secondary becomes the primary. Transistors Q1 and Q2 can be any power FET. Be sure to heat sink Q1 and Q2. Capacitors C1 and C2 are used as spike suppressors.
The inverter circuit described is designed to convert low-voltage DC into high-voltage AC or DC, suitable for various applications requiring high voltage output. The key components include a power transformer (T1), which is configured with its primary and secondary windings reversed. This configuration allows for flexibility in voltage transformation, enabling the inverter to operate effectively within a range of 12.6 to 440 volts.
Transistors Q1 and Q2, which are specified as power FETs (Field Effect Transistors), play a crucial role in switching the current through the transformer. The selection of appropriate FETs is critical for ensuring that the inverter can handle the required power levels without overheating or failing. Adequate heat sinking for Q1 and Q2 is essential to maintain operational stability and prevent thermal runaway, as these components will dissipate significant heat during operation.
Capacitors C1 and C2 serve as spike suppressors in the circuit. Their primary function is to mitigate voltage spikes that can occur during the switching process of the FETs. These spikes can potentially damage sensitive components or lead to erratic behavior in the inverter. By placing C1 and C2 in parallel with the FETs, the circuit is protected from transient voltages, enhancing reliability and longevity.
The overall design emphasizes the importance of thermal management and transient suppression to achieve a robust inverter capable of safely delivering high-voltage outputs. Proper layout and component selection are critical to ensure efficient operation and reliable performance in various applications.This inverter can deliver .high-voltage ac or de, with a rectifier and filter, up to several hundred volts. The secondary and primary of T1-a 12.6 to 440 V power transformer, respectively-are reversed; e.g., the primary becomes the secondary and the secondary becomes the primary.
Transistors Q1 and Q2 can be any power FET.
The inverter circuit described is designed to convert low-voltage DC into high-voltage AC or DC, suitable for various applications requiring high voltage output. The key components include a power transformer (T1), which is configured with its primary and secondary windings reversed. This configuration allows for flexibility in voltage transformation, enabling the inverter to operate effectively within a range of 12.6 to 440 volts.
Transistors Q1 and Q2, which are specified as power FETs (Field Effect Transistors), play a crucial role in switching the current through the transformer. The selection of appropriate FETs is critical for ensuring that the inverter can handle the required power levels without overheating or failing. Adequate heat sinking for Q1 and Q2 is essential to maintain operational stability and prevent thermal runaway, as these components will dissipate significant heat during operation.
Capacitors C1 and C2 serve as spike suppressors in the circuit. Their primary function is to mitigate voltage spikes that can occur during the switching process of the FETs. These spikes can potentially damage sensitive components or lead to erratic behavior in the inverter. By placing C1 and C2 in parallel with the FETs, the circuit is protected from transient voltages, enhancing reliability and longevity.
The overall design emphasizes the importance of thermal management and transient suppression to achieve a robust inverter capable of safely delivering high-voltage outputs. Proper layout and component selection are critical to ensure efficient operation and reliable performance in various applications.This inverter can deliver .high-voltage ac or de, with a rectifier and filter, up to several hundred volts. The secondary and primary of T1-a 12.6 to 440 V power transformer, respectively-are reversed; e.g., the primary becomes the secondary and the secondary becomes the primary.
Transistors Q1 and Q2 can be any power FET.
Be sure to heat sink Q1 and Q2. Capacitors C1 and C2 are used as spike suppressors.