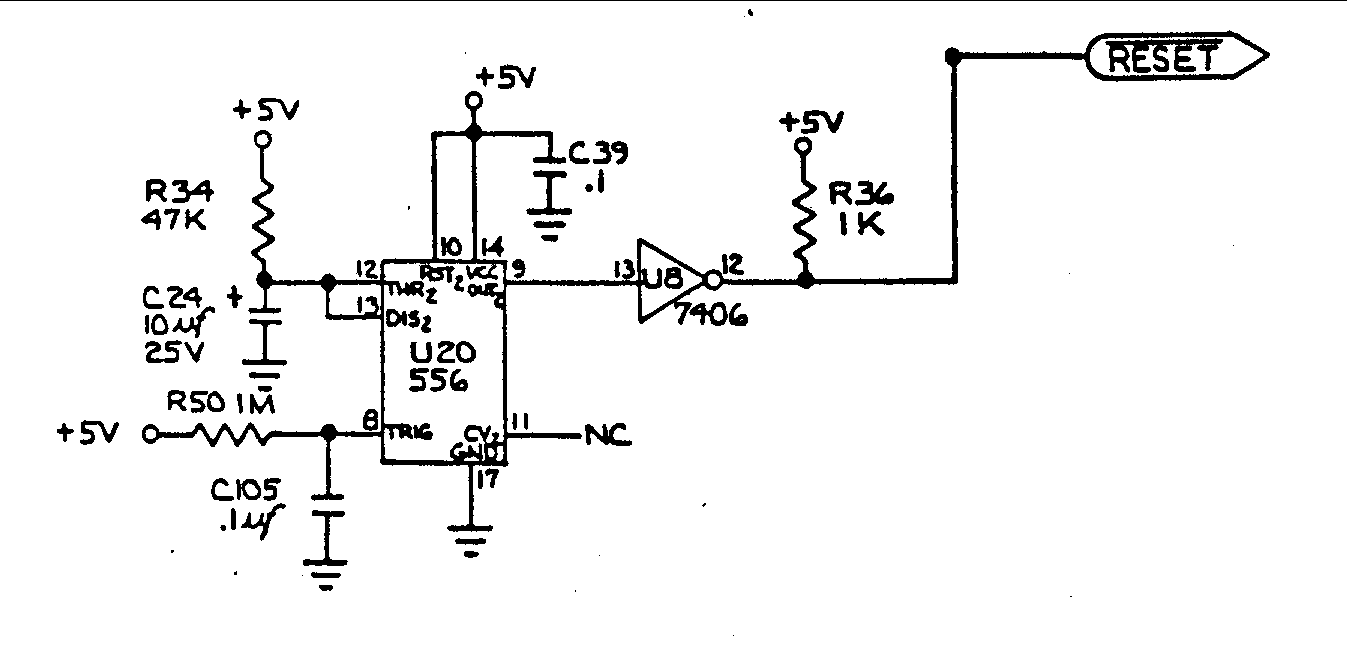
Power-on reset

This type of reset pulse is ideally provided by this circuit. Due to the high input impedance of the Schmitt trigger, long reset pulse durations can be achieved without the excess dissipation that occurs when both output devices are active simultaneously, as seen in a standard gate device (B).
A reset pulse is commonly necessary during power-on in a digital system.
The described circuit utilizes a Schmitt trigger to generate a reset pulse, which is critical for initializing digital systems upon power-up. The Schmitt trigger's high input impedance allows it to maintain a stable output state for an extended period, ensuring that the reset pulse duration is sufficient for the system to stabilize. This is particularly beneficial in applications where prolonged reset times are required to allow all components to power up correctly and reach their operational states.
The configuration of the Schmitt trigger in this circuit prevents simultaneous activation of output devices, which can lead to increased power dissipation. In contrast to traditional gate devices, where both outputs may be driven high, leading to potential short circuits and inefficiencies, the Schmitt trigger ensures that only one output is active at a time. This design choice not only enhances the reliability of the reset pulse but also contributes to overall energy efficiency.
In practical applications, the reset pulse generated by this circuit can be utilized in microcontroller systems, digital signal processors, and other digital logic circuits where a defined startup sequence is crucial. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components such as capacitors to fine-tune the pulse width, or resistors to adjust the trigger thresholds, allowing for tailored performance based on specific system requirements.
Overall, the use of a Schmitt trigger for producing reset pulses represents a robust solution for managing power-on sequences in digital electronics, ensuring reliable operation while minimizing power loss. This type of reset pulse is ideally provided by this circuit. Because of the high input impedance of the Schmitt trigger, long reset pulse times may be achieved without the excess dissipation that results when both output devices are on simultaneously, as in an ordinary gate device (B). A reset pulse is often required at power-on in a digital system.
A reset pulse is commonly necessary during power-on in a digital system.
The described circuit utilizes a Schmitt trigger to generate a reset pulse, which is critical for initializing digital systems upon power-up. The Schmitt trigger's high input impedance allows it to maintain a stable output state for an extended period, ensuring that the reset pulse duration is sufficient for the system to stabilize. This is particularly beneficial in applications where prolonged reset times are required to allow all components to power up correctly and reach their operational states.
The configuration of the Schmitt trigger in this circuit prevents simultaneous activation of output devices, which can lead to increased power dissipation. In contrast to traditional gate devices, where both outputs may be driven high, leading to potential short circuits and inefficiencies, the Schmitt trigger ensures that only one output is active at a time. This design choice not only enhances the reliability of the reset pulse but also contributes to overall energy efficiency.
In practical applications, the reset pulse generated by this circuit can be utilized in microcontroller systems, digital signal processors, and other digital logic circuits where a defined startup sequence is crucial. The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components such as capacitors to fine-tune the pulse width, or resistors to adjust the trigger thresholds, allowing for tailored performance based on specific system requirements.
Overall, the use of a Schmitt trigger for producing reset pulses represents a robust solution for managing power-on sequences in digital electronics, ensuring reliable operation while minimizing power loss. This type of reset pulse is ideally provided by this circuit. Because of the high input impedance of the Schmitt trigger, long reset pulse times may be achieved without the excess dissipation that results when both output devices are on simultaneously, as in an ordinary gate device (B). A reset pulse is often required at power-on in a digital system.