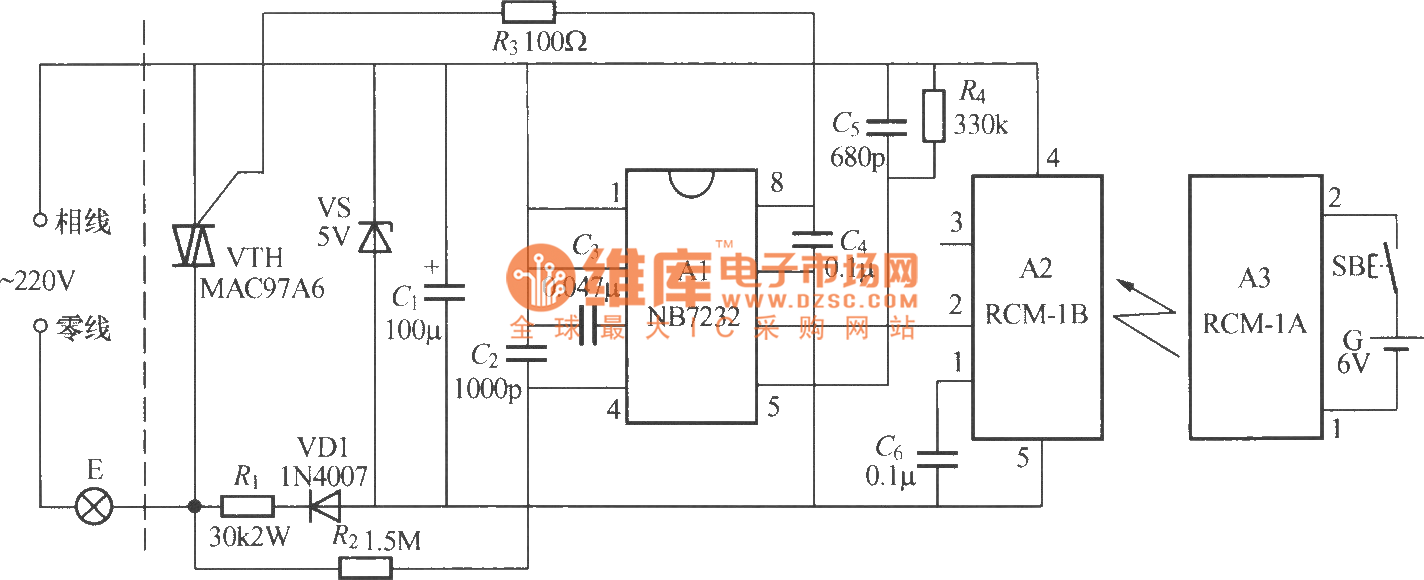
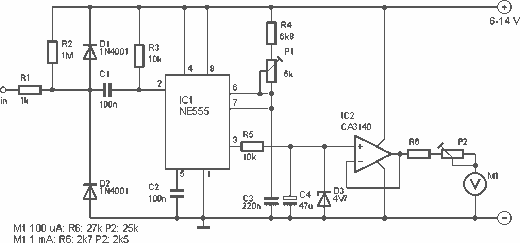
Timer circuit with 106 fixed preset time
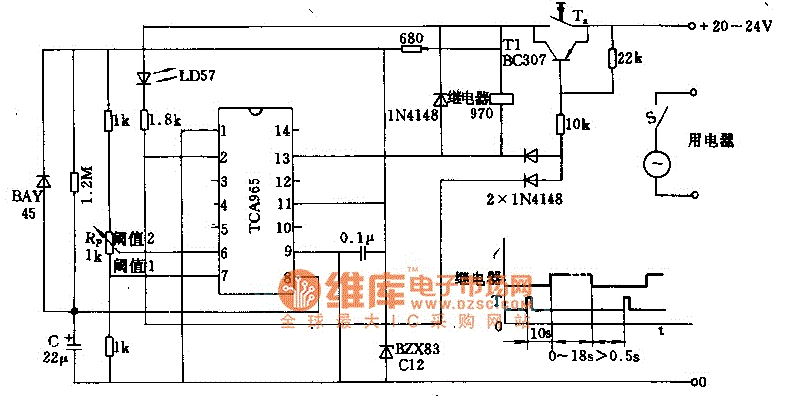
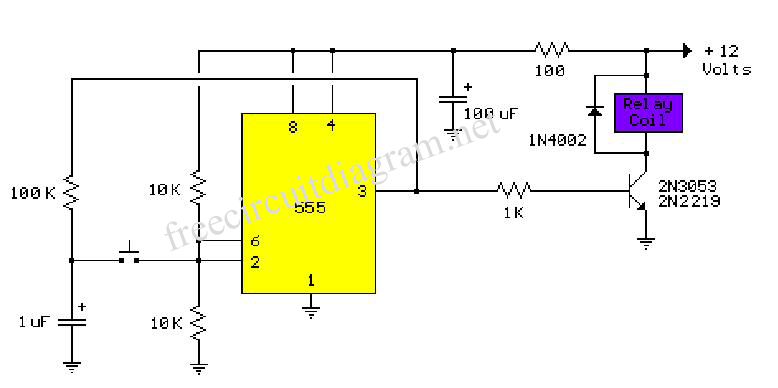
The foot 13 between valve value 1 and valve value 2 will draw the transistor base current. If the relay releases, after a recovery time of 0.5 seconds, pressing the key will initiate the switching process again. The timer is composed of a window discriminator TCA965. After pressing the key Ta, the decision time capacitor C will charge, allowing transistor T1 to receive base current.
The described circuit includes a relay mechanism controlled by a transistor switch, where the activation of the relay is contingent on the charging of a capacitor and the subsequent pressing of a key. The TCA965 window discriminator functions as a critical timing component, ensuring accurate delay intervals for the relay operation.
In this configuration, the capacitor C is charged through a resistor network upon pressing the key Ta. The charging time is dictated by the RC time constant, which is essential for determining how quickly the voltage across the capacitor reaches the threshold necessary to turn on transistor T1. Once the voltage is sufficient, T1 activates, allowing current to flow through the relay coil, thereby engaging the relay contacts.
The recovery time of 0.5 seconds is an important parameter, as it prevents immediate retriggering of the relay after it has been released. This delay is implemented to ensure stable operation and to avoid potential bouncing issues that could arise from mechanical relay contacts.
The schematic would typically illustrate the connections between the TCA965, the capacitor, resistors, and the transistor T1, along with the relay. The input from the key Ta would be shown as a momentary switch that, when pressed, completes the circuit and begins the charging process of capacitor C. The output side would display the relay contacts, indicating the load that is controlled by the relay.
In summary, this circuit effectively utilizes a combination of a window discriminator, a capacitor, and a transistor to control a relay with a specified recovery time, ensuring reliable operation in response to user input.The foot 13 between valve value 1 and valve value 2 will suck the transistor base current. If relay releases, after recovery time 0.5s, to press key then it will start to switch process again. The timer is composed ofwindow discriminator TCA965 to. After pressing the key Ta, decision time capacitance C will charge. transistor T1 obtains base curren.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit includes a relay mechanism controlled by a transistor switch, where the activation of the relay is contingent on the charging of a capacitor and the subsequent pressing of a key. The TCA965 window discriminator functions as a critical timing component, ensuring accurate delay intervals for the relay operation.
In this configuration, the capacitor C is charged through a resistor network upon pressing the key Ta. The charging time is dictated by the RC time constant, which is essential for determining how quickly the voltage across the capacitor reaches the threshold necessary to turn on transistor T1. Once the voltage is sufficient, T1 activates, allowing current to flow through the relay coil, thereby engaging the relay contacts.
The recovery time of 0.5 seconds is an important parameter, as it prevents immediate retriggering of the relay after it has been released. This delay is implemented to ensure stable operation and to avoid potential bouncing issues that could arise from mechanical relay contacts.
The schematic would typically illustrate the connections between the TCA965, the capacitor, resistors, and the transistor T1, along with the relay. The input from the key Ta would be shown as a momentary switch that, when pressed, completes the circuit and begins the charging process of capacitor C. The output side would display the relay contacts, indicating the load that is controlled by the relay.
In summary, this circuit effectively utilizes a combination of a window discriminator, a capacitor, and a transistor to control a relay with a specified recovery time, ensuring reliable operation in response to user input.The foot 13 between valve value 1 and valve value 2 will suck the transistor base current. If relay releases, after recovery time 0.5s, to press key then it will start to switch process again. The timer is composed ofwindow discriminator TCA965 to. After pressing the key Ta, decision time capacitance C will charge. transistor T1 obtains base curren.. 🔗 External reference