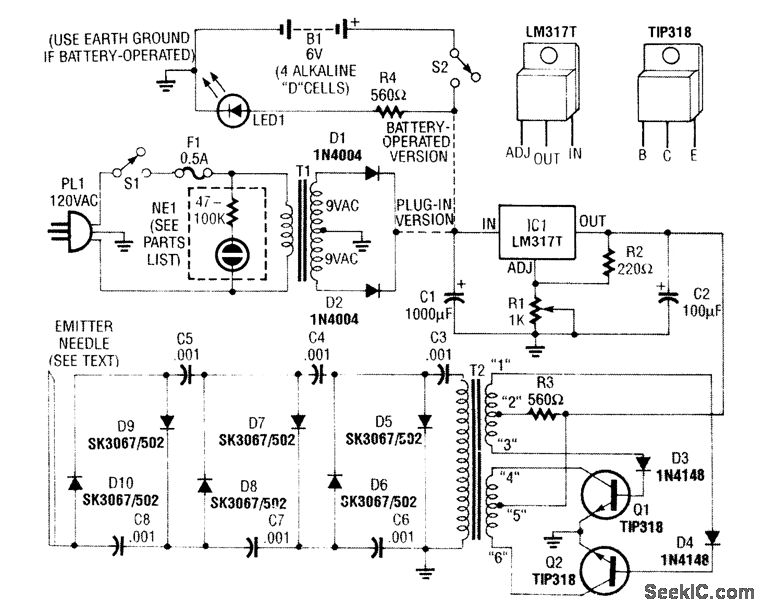
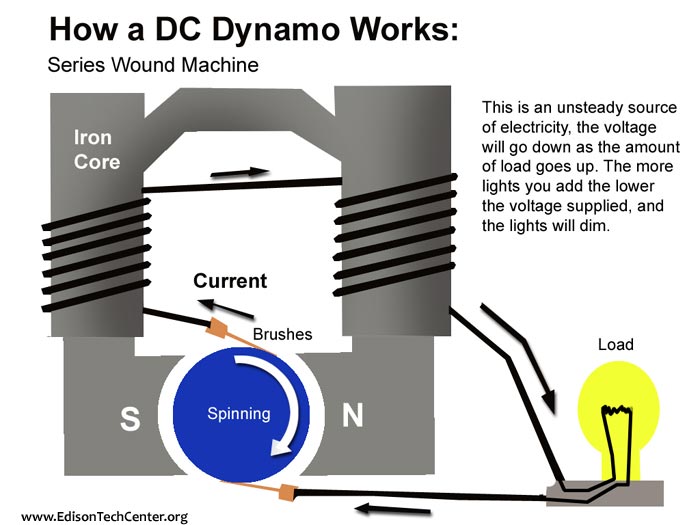
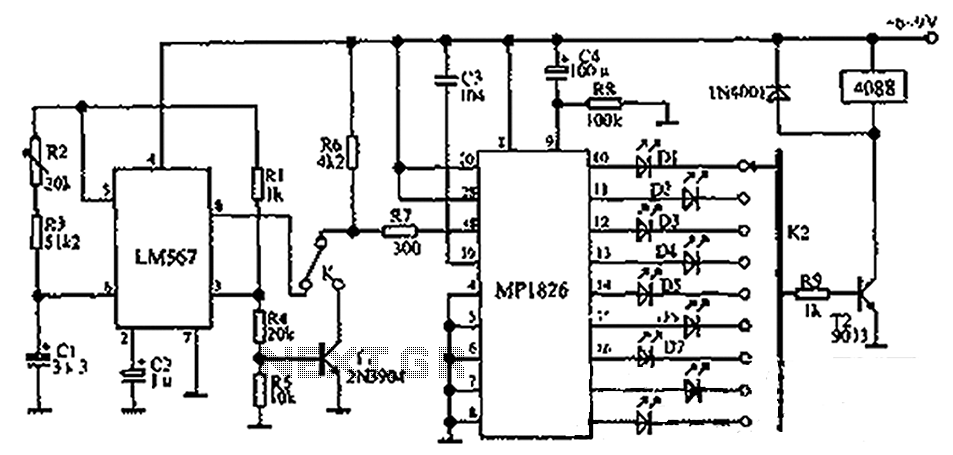
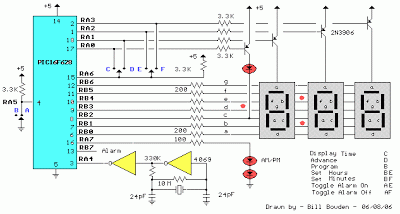
Precision clock generator
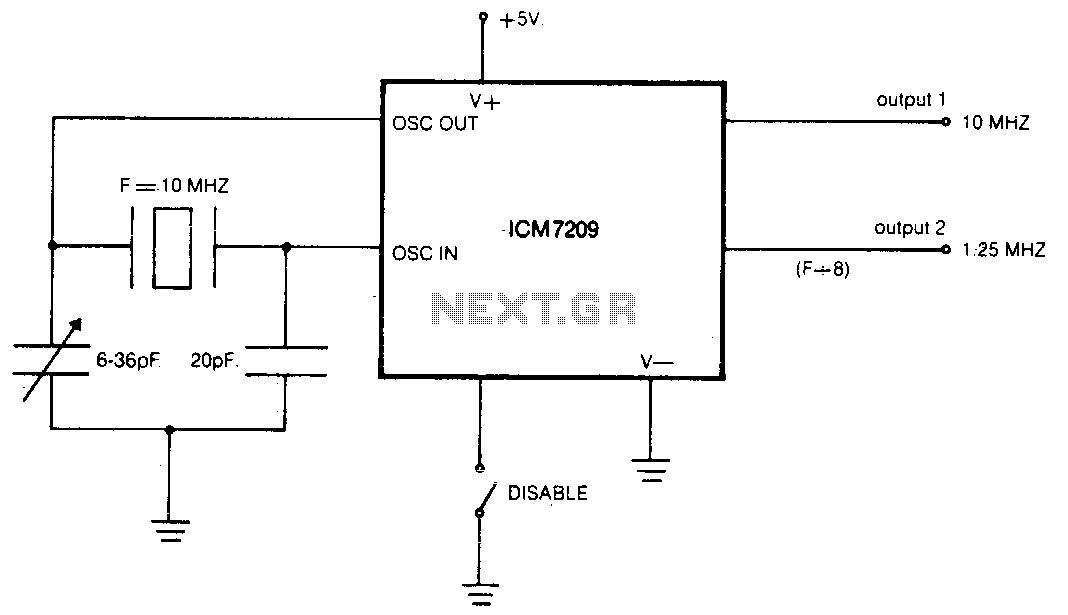
The CMOS IC directly drives five TTL loads from either of two buffered outputs. The device operates at up to 10 MHz and is compatible with bipolar, MOS, and CMOS technologies.
The CMOS integrated circuit (IC) is designed to interface with a variety of digital logic families, specifically targeting TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) loads. It provides two buffered outputs, enabling the connection of up to five TTL devices. This capability is beneficial in applications where multiple loads need to be driven from a single IC, thereby simplifying circuit design and minimizing component count.
Operating at frequencies up to 10 MHz, this CMOS IC is suitable for high-speed digital applications. Its compatibility with bipolar, MOS, and CMOS technologies allows for versatile integration into existing systems, facilitating seamless communication between different logic families. The buffered outputs ensure that signal integrity is maintained, reducing the likelihood of signal degradation that can occur when driving multiple loads directly from an unbuffered output.
In practical applications, this IC can be utilized in various digital circuits, including data communication interfaces, logic level shifting, and signal conditioning tasks. Its ability to drive TTL loads makes it particularly advantageous in legacy systems where TTL logic levels are prevalent. The design considerations for this IC include power consumption, propagation delay, and output drive strength, all of which contribute to its performance in high-speed digital environments. Overall, the CMOS IC serves as a robust solution for interfacing between different logic families while maintaining operational efficiency and reliability.The CMOS IC directly drives 5 TTL loads from either of 2 buffered outputs The device operates to 10 MHz and is bipolar, MOS, and CMOS compatible.
The CMOS integrated circuit (IC) is designed to interface with a variety of digital logic families, specifically targeting TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) loads. It provides two buffered outputs, enabling the connection of up to five TTL devices. This capability is beneficial in applications where multiple loads need to be driven from a single IC, thereby simplifying circuit design and minimizing component count.
Operating at frequencies up to 10 MHz, this CMOS IC is suitable for high-speed digital applications. Its compatibility with bipolar, MOS, and CMOS technologies allows for versatile integration into existing systems, facilitating seamless communication between different logic families. The buffered outputs ensure that signal integrity is maintained, reducing the likelihood of signal degradation that can occur when driving multiple loads directly from an unbuffered output.
In practical applications, this IC can be utilized in various digital circuits, including data communication interfaces, logic level shifting, and signal conditioning tasks. Its ability to drive TTL loads makes it particularly advantageous in legacy systems where TTL logic levels are prevalent. The design considerations for this IC include power consumption, propagation delay, and output drive strength, all of which contribute to its performance in high-speed digital environments. Overall, the CMOS IC serves as a robust solution for interfacing between different logic families while maintaining operational efficiency and reliability.The CMOS IC directly drives 5 TTL loads from either of 2 buffered outputs The device operates to 10 MHz and is bipolar, MOS, and CMOS compatible.