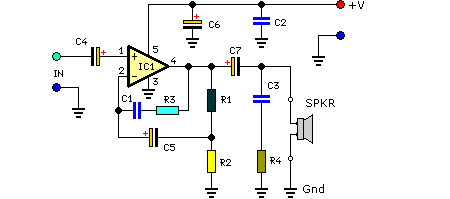
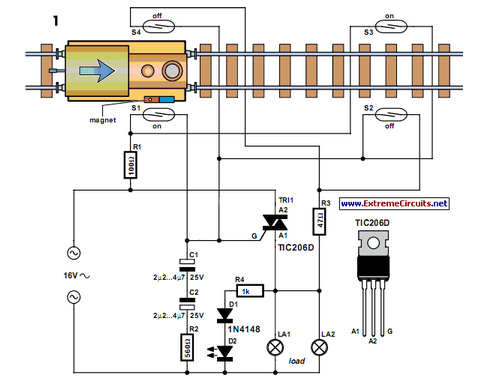
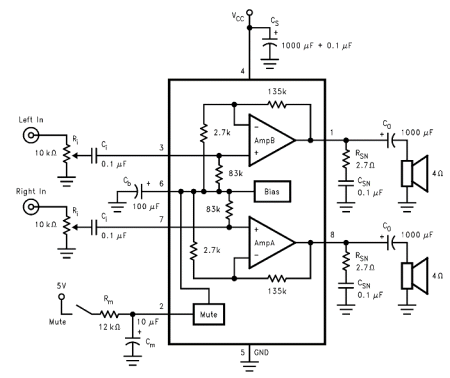
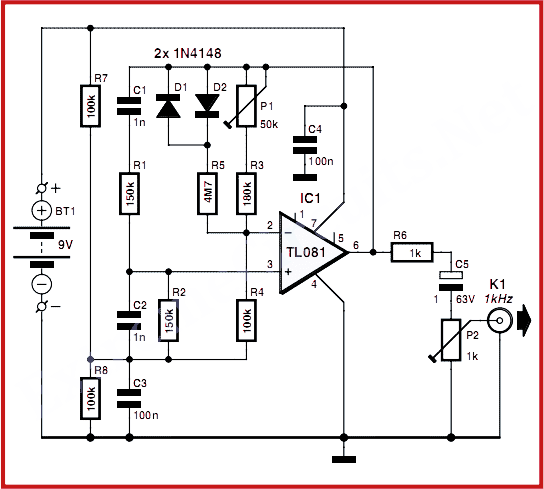
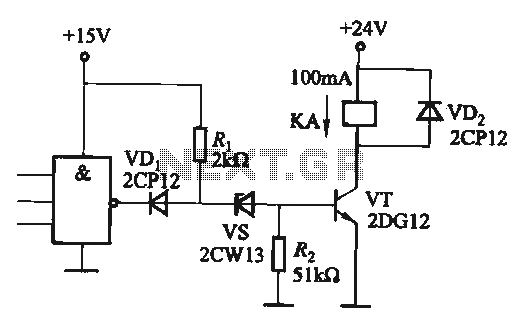
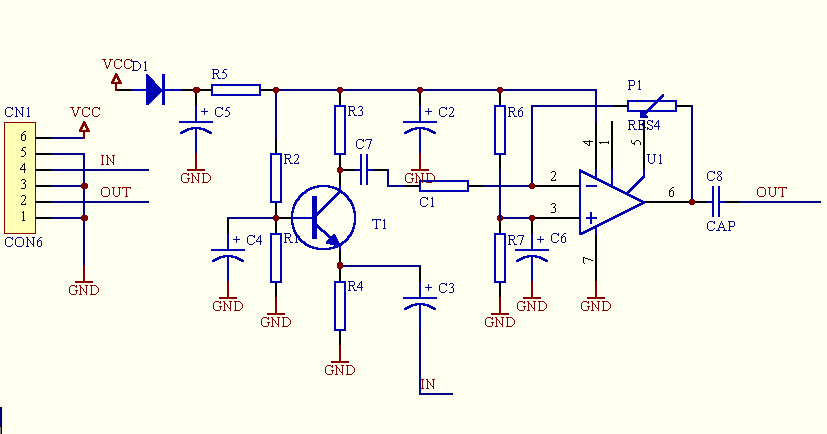
Precision Measurement without Ground Offsets Using Differential Amplifier Input to A/D ADC
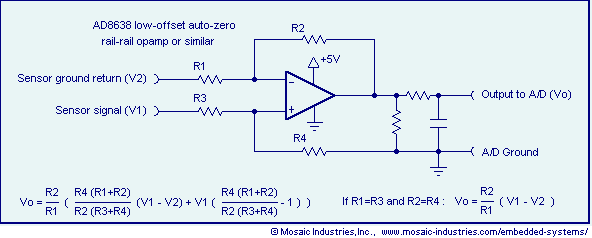
Ground loop offset errors and ground noise are eliminated by a differential amplifier or instrumentation amplifier before the analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. The differential input amplifier addresses ground loop errors, allowing for precise measurement of non-isolated sensors. A simple operational amplifier (op-amp) circuit effectively removes ground loop errors, while an op-amp schematic is utilized to eliminate ground noise.
In electronic systems, ground loop offset errors and ground noise can significantly impact the accuracy of measurements, particularly in applications involving non-isolated sensors. To mitigate these issues, a differential amplifier or instrumentation amplifier is employed prior to the A/D conversion process. This approach leverages the differential input characteristics of these amplifiers to reject common-mode signals, which are often the source of ground loop errors.
The differential amplifier configuration typically consists of two input terminals that receive the signal from the sensor and a reference ground. By amplifying the difference between these two inputs while rejecting any signals that are common to both, the differential amplifier effectively eliminates the influence of ground loops. This feature is crucial for maintaining measurement integrity in environments where multiple devices share a common ground.
Instrumentation amplifiers, which are a specialized form of differential amplifiers, provide additional benefits such as higher input impedance and better common-mode rejection ratios (CMRR). These attributes make instrumentation amplifiers particularly suitable for precise measurements in medical devices, industrial sensors, and other applications where accuracy is paramount.
In simpler applications, a basic op-amp circuit can also be designed to remove ground loop errors. This circuit typically includes feedback mechanisms that stabilize the output and enhance the accuracy of the measurement. The schematic for this op-amp configuration may include resistors and capacitors to set the gain and bandwidth, ensuring that the circuit operates effectively in the desired frequency range.
Overall, the implementation of differential or instrumentation amplifiers, along with carefully designed op-amp circuits, plays a critical role in achieving reliable and accurate signal processing in electronic measurement systems. By addressing ground loop errors and noise, these amplifiers enable high-quality data acquisition necessary for modern electronic applications.Ground loop offset errors and ground noise are removed by a differential amplifier or instrumentation amplifier prior to A/D analog to digital conversion. The differential input amplifier mitigates ground loop errors. Precision measurement of non-isolated sensors. Simple op-amp circuit removes ground loop errors. Op-amp schematic removes ground noise.. 🔗 External reference
In electronic systems, ground loop offset errors and ground noise can significantly impact the accuracy of measurements, particularly in applications involving non-isolated sensors. To mitigate these issues, a differential amplifier or instrumentation amplifier is employed prior to the A/D conversion process. This approach leverages the differential input characteristics of these amplifiers to reject common-mode signals, which are often the source of ground loop errors.
The differential amplifier configuration typically consists of two input terminals that receive the signal from the sensor and a reference ground. By amplifying the difference between these two inputs while rejecting any signals that are common to both, the differential amplifier effectively eliminates the influence of ground loops. This feature is crucial for maintaining measurement integrity in environments where multiple devices share a common ground.
Instrumentation amplifiers, which are a specialized form of differential amplifiers, provide additional benefits such as higher input impedance and better common-mode rejection ratios (CMRR). These attributes make instrumentation amplifiers particularly suitable for precise measurements in medical devices, industrial sensors, and other applications where accuracy is paramount.
In simpler applications, a basic op-amp circuit can also be designed to remove ground loop errors. This circuit typically includes feedback mechanisms that stabilize the output and enhance the accuracy of the measurement. The schematic for this op-amp configuration may include resistors and capacitors to set the gain and bandwidth, ensuring that the circuit operates effectively in the desired frequency range.
Overall, the implementation of differential or instrumentation amplifiers, along with carefully designed op-amp circuits, plays a critical role in achieving reliable and accurate signal processing in electronic measurement systems. By addressing ground loop errors and noise, these amplifiers enable high-quality data acquisition necessary for modern electronic applications.Ground loop offset errors and ground noise are removed by a differential amplifier or instrumentation amplifier prior to A/D analog to digital conversion. The differential input amplifier mitigates ground loop errors. Precision measurement of non-isolated sensors. Simple op-amp circuit removes ground loop errors. Op-amp schematic removes ground noise.. 🔗 External reference