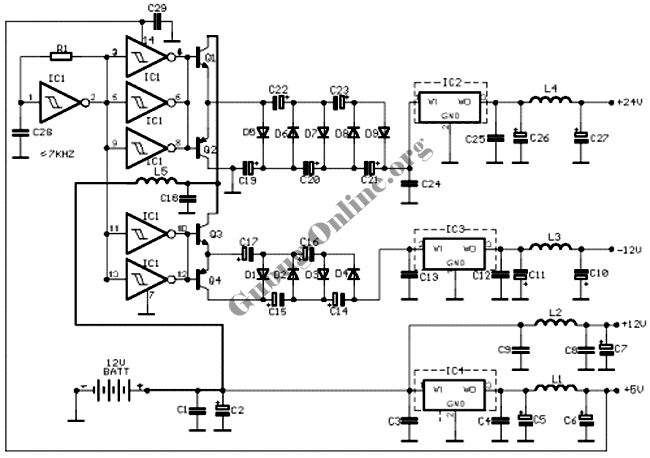
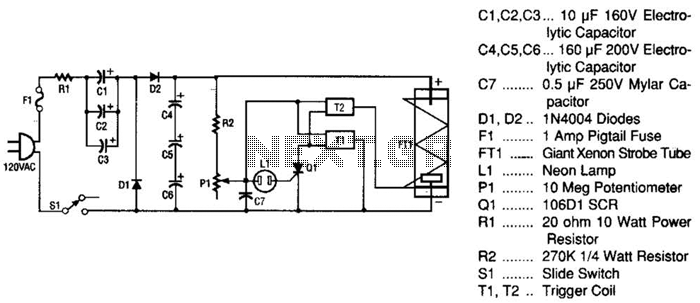
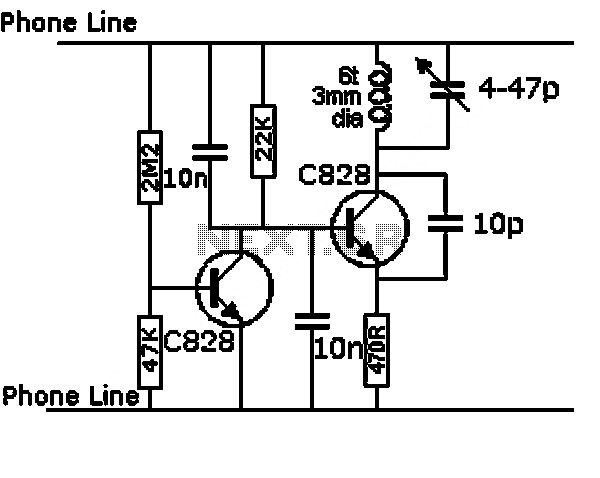
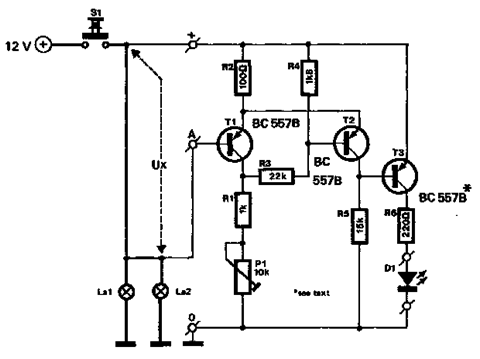
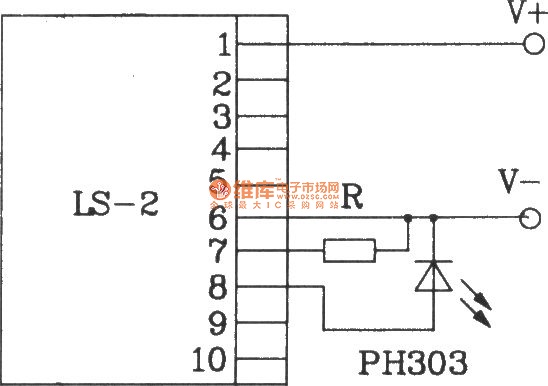
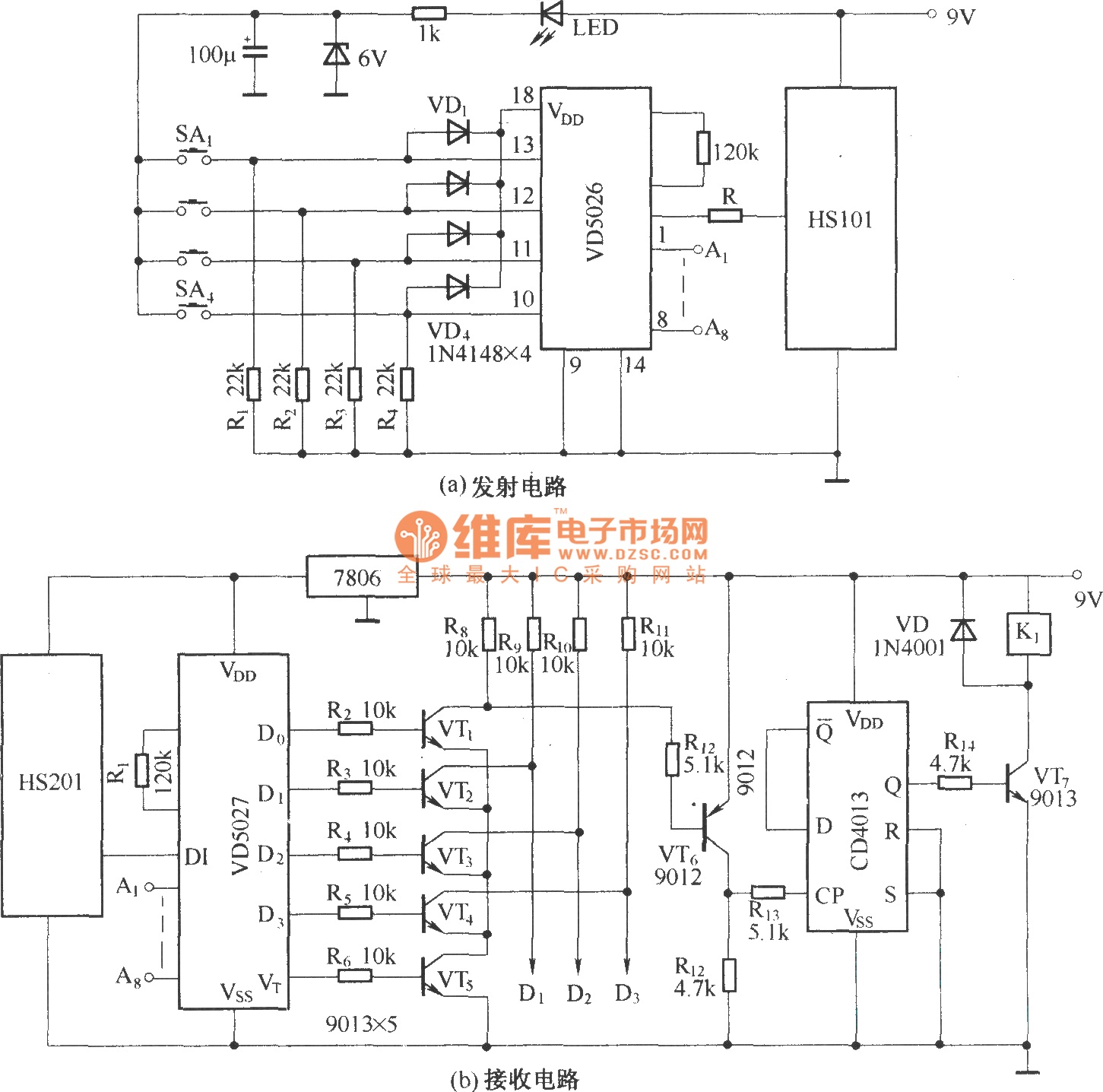
CMOS interface circuit and the switching amplifier
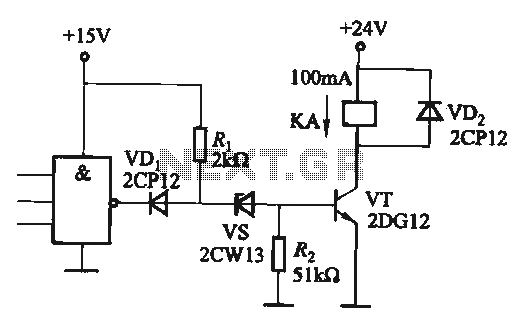
If the CMOS circuit load (actuator) is a relay device, the circuit must have a large load capacity. Non-gate drive switching amplifiers are connected to a separate element shown in the interface circuit.
In the context of a CMOS circuit where the load is a relay actuator, it is essential to ensure that the circuit is designed to handle significant load capacities. Relay devices typically require higher current and voltage levels to operate effectively, which necessitates the incorporation of appropriate driver circuits. Non-gate drive switching amplifiers are often utilized in such applications to facilitate the control of these high-power components.
The interface circuit, as referenced in the provided information, is critical for establishing the connection between the CMOS output and the relay. This interface typically includes components such as transistors or MOSFETs that act as switches, allowing the low-power CMOS signals to control the high-power relay operation without direct electrical coupling. This isolation is crucial to protect the sensitive CMOS circuitry from the high voltages and currents associated with the relay load.
The design of the interface circuit should also consider the necessary drive voltage and current requirements for the relay. Proper selection of the switching amplifier is vital to ensure that it can provide sufficient output to energize the relay coil effectively. Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF generated by the relay coil from damaging the switching amplifier or the CMOS circuit.
In summary, when designing a CMOS circuit with a relay load, it is imperative to ensure that the circuit can handle the required load capacity and that the interface circuit is appropriately designed to facilitate reliable operation of the relay while protecting the CMOS components.If the CMOS circuit load (actuator) is a relay device, the circuit must have a large load capacity. Non-gate drive switching amplifiers connected to a separate element shown in FIG interface circuit.
In the context of a CMOS circuit where the load is a relay actuator, it is essential to ensure that the circuit is designed to handle significant load capacities. Relay devices typically require higher current and voltage levels to operate effectively, which necessitates the incorporation of appropriate driver circuits. Non-gate drive switching amplifiers are often utilized in such applications to facilitate the control of these high-power components.
The interface circuit, as referenced in the provided information, is critical for establishing the connection between the CMOS output and the relay. This interface typically includes components such as transistors or MOSFETs that act as switches, allowing the low-power CMOS signals to control the high-power relay operation without direct electrical coupling. This isolation is crucial to protect the sensitive CMOS circuitry from the high voltages and currents associated with the relay load.
The design of the interface circuit should also consider the necessary drive voltage and current requirements for the relay. Proper selection of the switching amplifier is vital to ensure that it can provide sufficient output to energize the relay coil effectively. Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF generated by the relay coil from damaging the switching amplifier or the CMOS circuit.
In summary, when designing a CMOS circuit with a relay load, it is imperative to ensure that the circuit can handle the required load capacity and that the interface circuit is appropriately designed to facilitate reliable operation of the relay while protecting the CMOS components.If the CMOS circuit load (actuator) is a relay device, the circuit must have a large load capacity. Non-gate drive switching amplifiers connected to a separate element shown in FIG interface circuit.