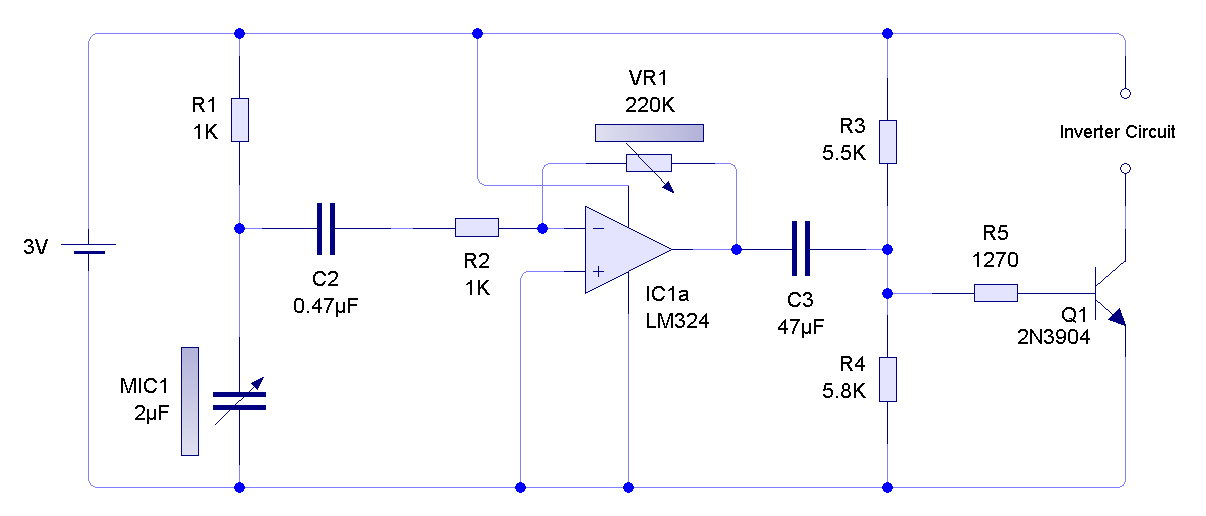
Low impedance microphone amplifiers
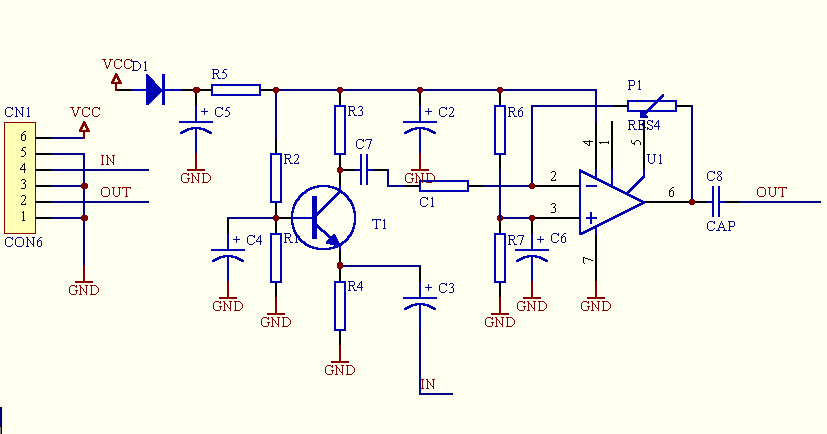
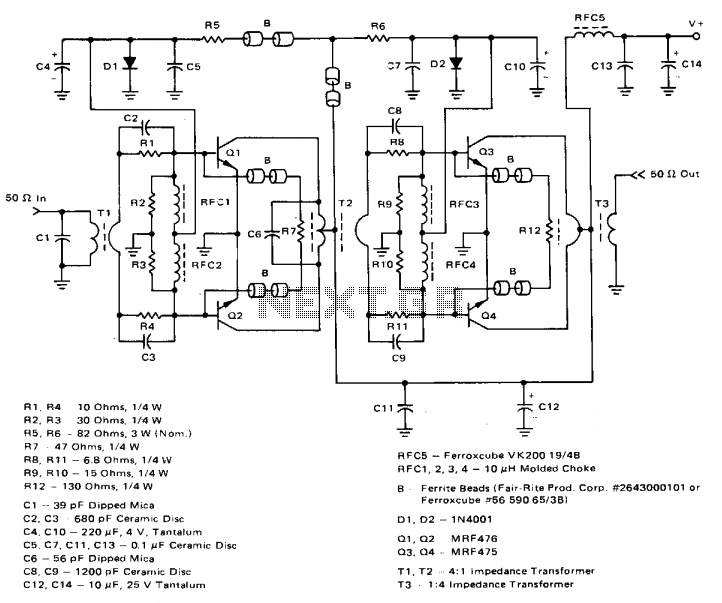
The circuit is a microphone amplifier designed for low impedance microphones, approximately 200 ohms. It operates with stabilized voltages ranging from 6 to 30 VDC. If the impedance adapter section with T1 is not constructed, the circuit can be utilized as a microphone amplifier for higher impedance microphones. In this scenario, the signal should be connected directly to capacitor C7.
The microphone amplifier circuit is structured to enhance the audio signal from low impedance microphones, which are commonly used in various audio applications. The operational voltage range of 6 to 30 VDC ensures compatibility with a wide array of power supply configurations, allowing for flexibility in different setups.
The inclusion of an impedance adapter utilizing transformer T1 is crucial when working with low impedance microphones. This transformer effectively matches the microphone's output impedance with the input impedance of the amplifier, optimizing signal transfer and minimizing potential signal loss. If the impedance adapter is omitted, the circuit can still function as an amplifier for higher impedance microphones, which typically have an output that can be directly coupled to the amplifier’s input through C7. This capacitor serves as a coupling component, blocking any DC component while allowing the AC audio signal to pass through to the amplifier stage.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to set gain levels, filter noise, and stabilize the amplifier's performance. Proper design considerations should be taken into account to ensure that the amplifier maintains a low noise floor and provides sufficient gain to amplify the microphone's output to usable levels for further processing or amplification.
Overall, this microphone amplifier circuit is a versatile solution for audio applications requiring the amplification of low impedance signals, with the added benefit of adaptability for higher impedance microphones when necessary.The circuit is a microphone amplifier for use with low impedance (~200 ohm) microphones. It will work with stabilized voltages between 6-30VDC. If you don`t build the impedance adapter part with T1, you get a micamp for higher impedance microphones. In this case, you should directly connect the signal to C7. 🔗 External reference
The microphone amplifier circuit is structured to enhance the audio signal from low impedance microphones, which are commonly used in various audio applications. The operational voltage range of 6 to 30 VDC ensures compatibility with a wide array of power supply configurations, allowing for flexibility in different setups.
The inclusion of an impedance adapter utilizing transformer T1 is crucial when working with low impedance microphones. This transformer effectively matches the microphone's output impedance with the input impedance of the amplifier, optimizing signal transfer and minimizing potential signal loss. If the impedance adapter is omitted, the circuit can still function as an amplifier for higher impedance microphones, which typically have an output that can be directly coupled to the amplifier’s input through C7. This capacitor serves as a coupling component, blocking any DC component while allowing the AC audio signal to pass through to the amplifier stage.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to set gain levels, filter noise, and stabilize the amplifier's performance. Proper design considerations should be taken into account to ensure that the amplifier maintains a low noise floor and provides sufficient gain to amplify the microphone's output to usable levels for further processing or amplification.
Overall, this microphone amplifier circuit is a versatile solution for audio applications requiring the amplification of low impedance signals, with the added benefit of adaptability for higher impedance microphones when necessary.The circuit is a microphone amplifier for use with low impedance (~200 ohm) microphones. It will work with stabilized voltages between 6-30VDC. If you don`t build the impedance adapter part with T1, you get a micamp for higher impedance microphones. In this case, you should directly connect the signal to C7. 🔗 External reference