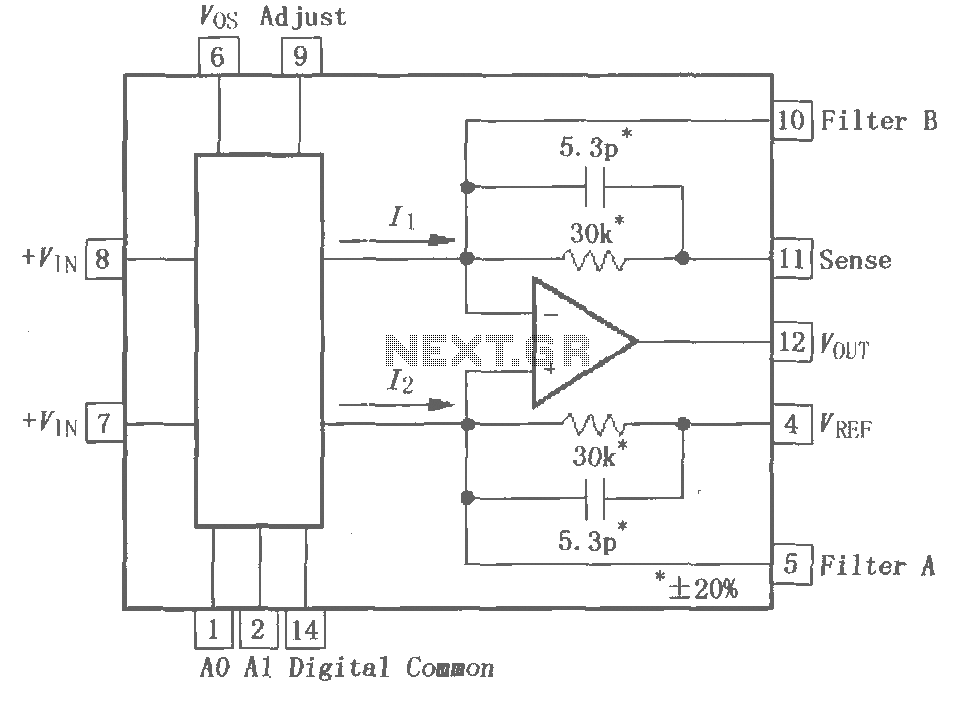
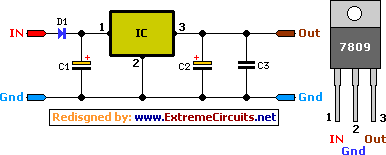
Principle Power Amplifier Design
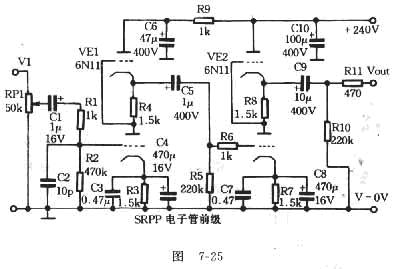
The FET amplifier is designed for enthusiasts who prefer tube sound but cannot utilize traditional tube amplifiers. It exhibits output characteristics similar to bipolar FET tube amplifiers, featuring good frequency response and sound quality comparable to tube amplifiers. Coupling it with a tube preamp is recommended. The preamplifier circuit, illustrated in Figure 7-25, is a parallel-adjusted push-pull circuit, also known as a streaming-adjusted push-pull circuit, suitable for high-frequency input stages, such as VHF/UHF. It excels in distortion, linearity, amplification, dynamic response, and low output impedance, outperforming typical triode amplifiers. Unlike many tube circuit designs, the distortion rate of the SRPP circuit decreases with increasing frequency. The circuit comprises two tubes arranged in series, with each tube sharing half of the supply voltage. The signal is processed through the lower screen of the tube, utilizing the cathode output. This configuration allows the tubes to operate in parallel. The gate operates under relatively negative cathode conditions, simplifying the bias circuit, a principle not applicable to transistors or operational amplifier circuits. The FET amplifier circuit theory, based on differential dynamic principles as shown in Figure 7-26, includes a differential input stage using a field-effect twin module NPD5565S, with parameters of VDss = 55V and iDss = 6 to 15mA, providing high input impedance. Other small N-channel power resistors can be used if the voltage rating exceeds 100V, maintaining a Gm value with less than 2 percent error. The resistor VR serves as a source of negative feedback, establishing a midpoint potential for zero resistance. VT3 and VT4 form a constant current mirror with characteristics similar to a DC circuit, facilitating DC operation while maximizing signal transmission to the next stage. VT5 and VT6 amplify voltage levels, with R4 determining their operating current size, conditioned to achieve 80 mA in Class A operation, minimizing distortion and enhancing load capacity. If the midpoint potential becomes unstable, resistance can be adjusted with R6, ensuring it does not fall below 4.7 kΩ to prevent overheating of VT3 to VT6. The amplifier's class principle, depicted in Figure 7-27, eliminates traditional capacitive coupling between amplification stages. The output power, rated at 50W per channel, is sufficient for dynamic music enjoyment, utilizing four pairs of parallel connections to reduce output damping. If matching proves challenging, two pairs may be used with an error requirement of less than 3 percent. Mica insulation is recommended for thermal conductivity, and 1/4 W metal film resistors with colored rings are used for gate resistors. The optimal resistance for sound quality is found between 330 ohms and 470 ohms. Care must be taken with the values of resistors and capacitors in the absorption circuit to avoid excessively small values. A 600W central transformer, preferably an E-type, is recommended for power amplification, with independent power channels for optimal performance.The FET amplifier, for those focused on the tube sound, which for various reasons can not be made after the courage to Jiang Sheng-class enthusiasts. bipolar FET tube amplifier and the output characteristics very similar, the frequency characteristics of a good, sound and bile after similar level, Coupled on the tube preamp is desirable.
SRPP tube preamplifier circuit, as shown in Figure 7-25. Parallel to its circuit-adjusted push-pull circuit, also known as streaming-adjusted push-pull circuit, used for high-frequency input stage, such as VHF / UHF high frequency of the first tube line, and for the importation of AF, both distortion, Linearity, magnification, dynamic and low output impedance are all winners of Group A in general triode amplifier, and many other giant tube circuit design the contrary, SRPP circuit distortion rate decreases as the frequency increased. The circuit is clearly a series of two tubes, how is the parallel-push-pull adjustment circuit This is the exchange of work, two DC power tubes in the form of series, each shoulder half of the supply voltage.
But the exchange does not signal the same pipe above the screen is the very same, enter the pipe from below the screen is, by the cathode output (of screen circuits), this becomes a two tubes in parallel work. Because the gate is on the tube for a relatively cathode negative circumstances, makes bias circuit is extremely simple, this principle can not be used in transistors or operational amplifier circuit.
FET amplifier circuit theory, differential-ranked dynamic principles such as Figure 7-26 shown. Differential input stage a field-effect twin module NPD5565S, its parameters for VDss = 55V, iDss = 6 ~ 15mA, its importation of very good (high input impedance), without the NPD5565S, can also be used other small N-channel power of resistance, Pressure demand is greater than 100 V, Gm value pairs, the error to less than 2 percent. VR is a source of negative feedback resistor is the midpoint potential for zero resistance. VT3, VT4 is a constant source mirror the characteristics of the DC Circuit similar pathway, and in terms of the exchange is open so that we can meet all of the DC work, and it also enabled the exchange as much as possible to send signals to the next level, This class is to promote the best, not because of the traditional midpoint of the ordinary DC servo amplifier circuit, making mid-point of zero potential for a very convenient and simple.
VT5, VT6 to enlarge voltage level, due to the current passion of a circuit-style, R4 decision VT5, VT6 current size of the work, the conditioning R4, so that VT5, VT6 the work of current 80 mA, work in the Group A state, on the one hand can be eliminated The reference to the terrible distortion, and it will strengthen the capacity of the load. If the midpoint of potential instability but transferred to 0. 1 (that is, the midpoint of drift), then R6 can reduce the resistance by 6. 8 kohm or 4. 7 kohm, but resistance can not be less than 4. 7 kohm, and the casual VT3 ~ VT6 Large enough area to heat. Amp-class principle as shown in Figure 7-27, and promote after-class level and the coupling between the abolition of the traditional capacitive coupling, power amplification of a bipolar FET FET, the lines per channel for the four pairs, parallel Use, reducing output damping.
This line output power of 50 W, enough to enjoy the dynamic music. Per channel for the four pairs, if matching more difficult, may be two pairs, matching the requirements of error of less than 3 percent. The use of mica insulation, thermal conductivity and painted Guizhi. The gate of the power of resistance used colored ring 1 / 4 W metal film resistors. Resistance is, the more sounds "warm", the test in the 330 ohm to 470 ohm between for the best. Absorption circuit in the value of R and C can not be too small, can not. Power transformers used 600 W Central transformer, such as E-type transformers are better, and to promote class-amp and power per channel to separate independent.
🔗 External reference
SRPP tube preamplifier circuit, as shown in Figure 7-25. Parallel to its circuit-adjusted push-pull circuit, also known as streaming-adjusted push-pull circuit, used for high-frequency input stage, such as VHF / UHF high frequency of the first tube line, and for the importation of AF, both distortion, Linearity, magnification, dynamic and low output impedance are all winners of Group A in general triode amplifier, and many other giant tube circuit design the contrary, SRPP circuit distortion rate decreases as the frequency increased. The circuit is clearly a series of two tubes, how is the parallel-push-pull adjustment circuit This is the exchange of work, two DC power tubes in the form of series, each shoulder half of the supply voltage.
But the exchange does not signal the same pipe above the screen is the very same, enter the pipe from below the screen is, by the cathode output (of screen circuits), this becomes a two tubes in parallel work. Because the gate is on the tube for a relatively cathode negative circumstances, makes bias circuit is extremely simple, this principle can not be used in transistors or operational amplifier circuit.
FET amplifier circuit theory, differential-ranked dynamic principles such as Figure 7-26 shown. Differential input stage a field-effect twin module NPD5565S, its parameters for VDss = 55V, iDss = 6 ~ 15mA, its importation of very good (high input impedance), without the NPD5565S, can also be used other small N-channel power of resistance, Pressure demand is greater than 100 V, Gm value pairs, the error to less than 2 percent. VR is a source of negative feedback resistor is the midpoint potential for zero resistance. VT3, VT4 is a constant source mirror the characteristics of the DC Circuit similar pathway, and in terms of the exchange is open so that we can meet all of the DC work, and it also enabled the exchange as much as possible to send signals to the next level, This class is to promote the best, not because of the traditional midpoint of the ordinary DC servo amplifier circuit, making mid-point of zero potential for a very convenient and simple.
VT5, VT6 to enlarge voltage level, due to the current passion of a circuit-style, R4 decision VT5, VT6 current size of the work, the conditioning R4, so that VT5, VT6 the work of current 80 mA, work in the Group A state, on the one hand can be eliminated The reference to the terrible distortion, and it will strengthen the capacity of the load. If the midpoint of potential instability but transferred to 0. 1 (that is, the midpoint of drift), then R6 can reduce the resistance by 6. 8 kohm or 4. 7 kohm, but resistance can not be less than 4. 7 kohm, and the casual VT3 ~ VT6 Large enough area to heat. Amp-class principle as shown in Figure 7-27, and promote after-class level and the coupling between the abolition of the traditional capacitive coupling, power amplification of a bipolar FET FET, the lines per channel for the four pairs, parallel Use, reducing output damping.
This line output power of 50 W, enough to enjoy the dynamic music. Per channel for the four pairs, if matching more difficult, may be two pairs, matching the requirements of error of less than 3 percent. The use of mica insulation, thermal conductivity and painted Guizhi. The gate of the power of resistance used colored ring 1 / 4 W metal film resistors. Resistance is, the more sounds "warm", the test in the 330 ohm to 470 ohm between for the best. Absorption circuit in the value of R and C can not be too small, can not. Power transformers used 600 W Central transformer, such as E-type transformers are better, and to promote class-amp and power per channel to separate independent.
🔗 External reference