Programmable voltage controlled timer
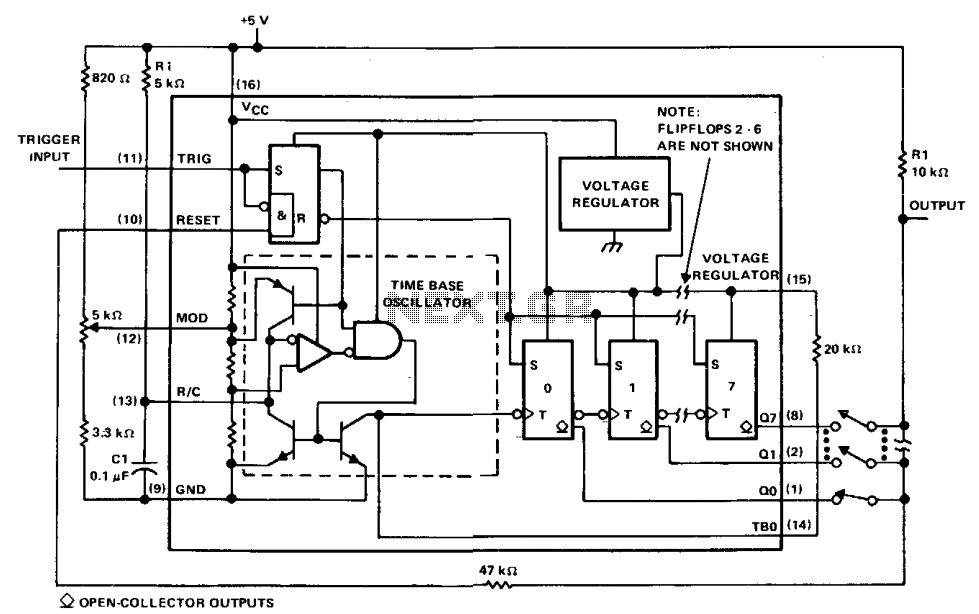
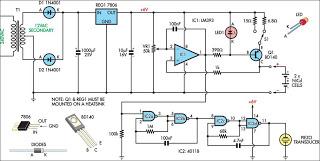
The µA2240 can be easily configured as a programmable voltage-controlled timer with a minimal number of external components. The modulation input (pin 12) allows for external adjustment of the input threshold level. A variable voltage is applied from the arm of a 10 kΩ potentiometer connected between Vcc and ground. A change in the modulation input voltage results in a change in the time base oscillator frequency and the period of the time base output (TBO). The TBO features an open-collector output connected to the regulator output via a 10 kΩ pull-up resistor. The output of the TBO drives the input to the 8-stage counter section. At start-up, a positive trigger pulse initiates the TBO and sets all counter outputs to a low state. The binary outputs are open-collector stages that can be connected together to the 10 kΩ pull-up resistor to provide a "wired-OR" output function. This circuit can generate 255 discrete time delays that are integer multiples of the time-base period. The total delay is the sum of the number of time-base periods, represented by the binary sum of the Q outputs connected. Delays ranging from 200 µs to 0.223 s are achievable with this configuration.
The µA2240 integrated circuit is designed to function as a versatile programmable timer, leveraging its internal architecture to deliver precise timing functions with minimal component requirements. The key feature of this device is its modulation input, which facilitates external control over the timing characteristics. By connecting a variable voltage from a potentiometer, users can dynamically adjust the input threshold, allowing for flexible timing applications.
The time base output (TBO) is a critical component of the µA2240's functionality. It operates in an open-collector configuration, which allows for easy interfacing with other digital circuits. The inclusion of a 10 kΩ pull-up resistor ensures that the output can be reliably pulled high when not actively driven low by the TBO. This configuration not only enhances signal integrity but also enables the TBO to drive subsequent logic stages, such as the 8-stage counter, effectively expanding the timer's capabilities.
Upon receiving a positive trigger pulse at startup, the TBO initiates its timing cycle, resetting all counter outputs to a low state. The open-collector nature of the counter outputs allows for a "wired-OR" logic configuration, where multiple outputs can be combined to generate a single output signal. This feature is particularly useful in applications requiring multiple timing conditions to be monitored simultaneously.
The µA2240's architecture supports the generation of up to 255 discrete time delays, each corresponding to integer multiples of the time-base period. This is accomplished by summing the binary outputs of the counter, providing a flexible method for achieving various timing requirements. The range of delays, from 200 µs to 0.223 s, makes the µA2240 suitable for a wide range of timing applications in both consumer and industrial electronics. Overall, the µA2240 presents a robust solution for programmable timing needs, combining ease of use with extensive functionality.The µA2240 may easily be configured as a programmable voltage controlled timer with a minimum number of external components. The modulation input (pin 12), which allows external adjustment of the input threshold level. A variable voltage is applied from the arm of a 10 k ohm potentiometer connected from Vcc to ground. A change in the modulation input voltage will result in a change in the time base oscillator frequency and the period of the time base output (TBO).
The TBO has an open-collector output that is connected to the regulator output via a 10 k ohm pull-up resistor. The output of the TBO drives the input to the 8-stage counter section. At start-up, a positive trigger pulse starts the TBO and sets all counter outputs to a low state. The binary outputs are open-collector stages that may be connected together to the 10 k ohm pull-up resistor to provide a "wired-OR" output function. This circuit may be used to generate 255 discrete time delays that are integer multiples of the time-base period.
The total delay is the sum of the number of time-base periods, which is the binary sum of the Q outputs connected. Delays from 200 µß to 0.223 s are possible with this configuration.
The µA2240 integrated circuit is designed to function as a versatile programmable timer, leveraging its internal architecture to deliver precise timing functions with minimal component requirements. The key feature of this device is its modulation input, which facilitates external control over the timing characteristics. By connecting a variable voltage from a potentiometer, users can dynamically adjust the input threshold, allowing for flexible timing applications.
The time base output (TBO) is a critical component of the µA2240's functionality. It operates in an open-collector configuration, which allows for easy interfacing with other digital circuits. The inclusion of a 10 kΩ pull-up resistor ensures that the output can be reliably pulled high when not actively driven low by the TBO. This configuration not only enhances signal integrity but also enables the TBO to drive subsequent logic stages, such as the 8-stage counter, effectively expanding the timer's capabilities.
Upon receiving a positive trigger pulse at startup, the TBO initiates its timing cycle, resetting all counter outputs to a low state. The open-collector nature of the counter outputs allows for a "wired-OR" logic configuration, where multiple outputs can be combined to generate a single output signal. This feature is particularly useful in applications requiring multiple timing conditions to be monitored simultaneously.
The µA2240's architecture supports the generation of up to 255 discrete time delays, each corresponding to integer multiples of the time-base period. This is accomplished by summing the binary outputs of the counter, providing a flexible method for achieving various timing requirements. The range of delays, from 200 µs to 0.223 s, makes the µA2240 suitable for a wide range of timing applications in both consumer and industrial electronics. Overall, the µA2240 presents a robust solution for programmable timing needs, combining ease of use with extensive functionality.The µA2240 may easily be configured as a programmable voltage controlled timer with a minimum number of external components. The modulation input (pin 12), which allows external adjustment of the input threshold level. A variable voltage is applied from the arm of a 10 k ohm potentiometer connected from Vcc to ground. A change in the modulation input voltage will result in a change in the time base oscillator frequency and the period of the time base output (TBO).
The TBO has an open-collector output that is connected to the regulator output via a 10 k ohm pull-up resistor. The output of the TBO drives the input to the 8-stage counter section. At start-up, a positive trigger pulse starts the TBO and sets all counter outputs to a low state. The binary outputs are open-collector stages that may be connected together to the 10 k ohm pull-up resistor to provide a "wired-OR" output function. This circuit may be used to generate 255 discrete time delays that are integer multiples of the time-base period.
The total delay is the sum of the number of time-base periods, which is the binary sum of the Q outputs connected. Delays from 200 µß to 0.223 s are possible with this configuration.