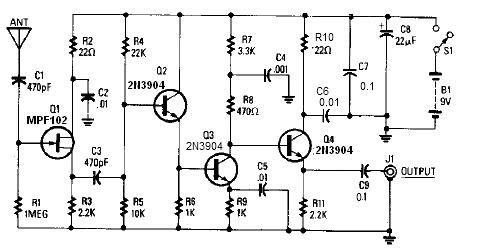
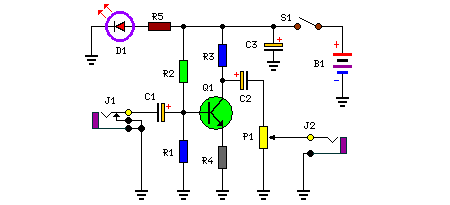
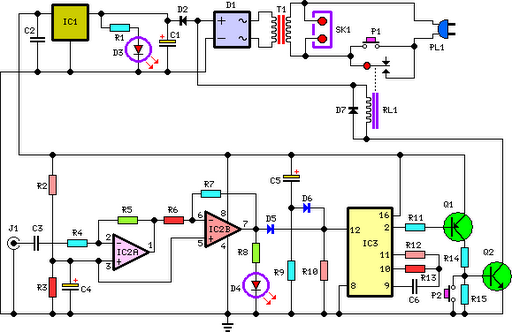
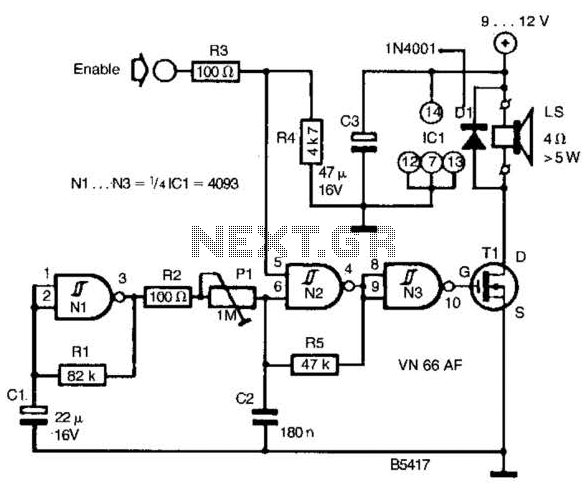
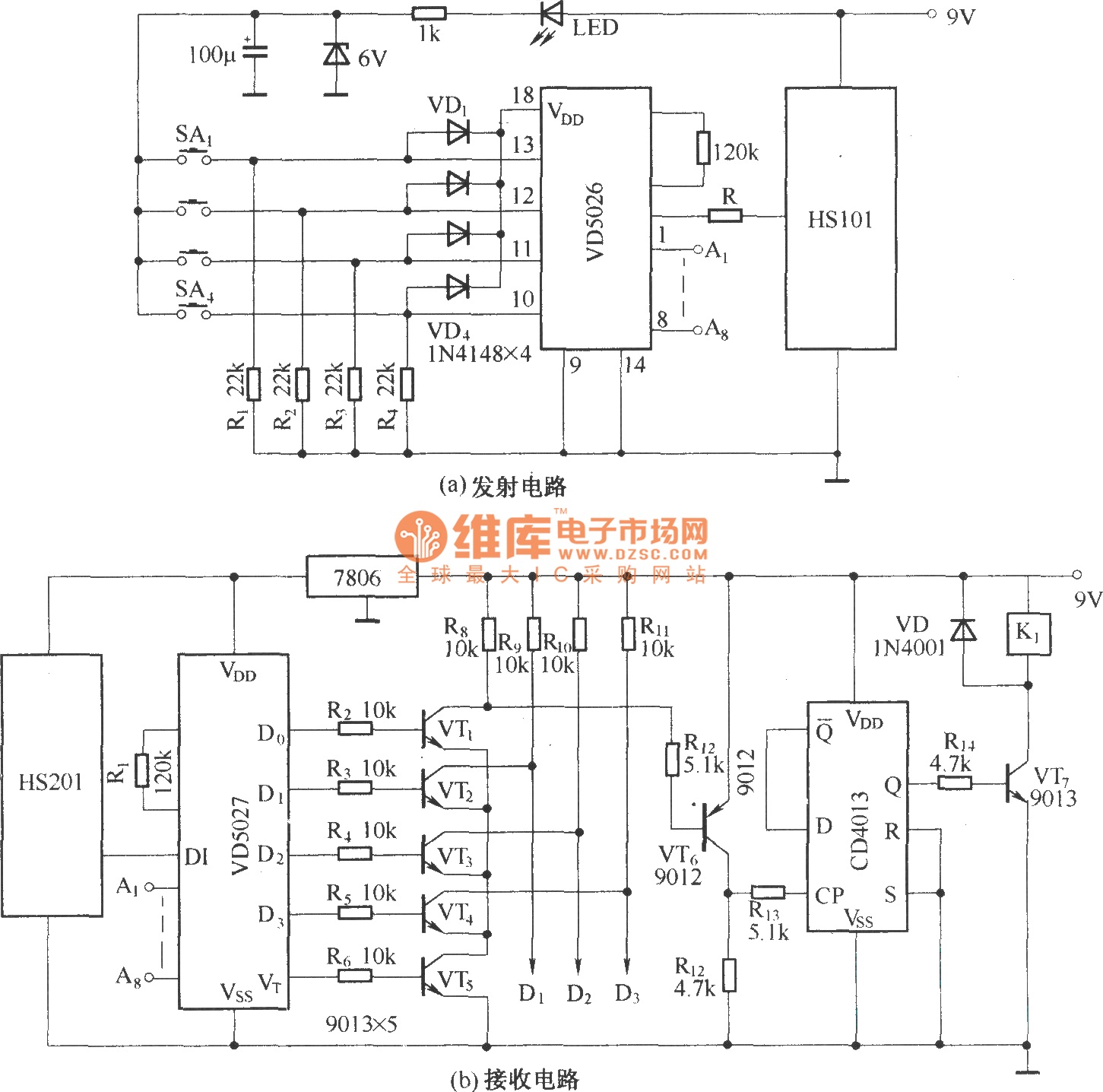
Pulse signal generating circuit
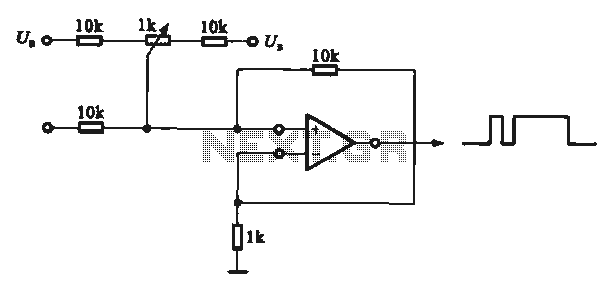
This circuit demonstrates the application of various types of pulse signal generating circuits using operational amplifiers.
The circuit utilizes operational amplifiers (op-amps) to create different forms of pulse signals, which are essential in many electronic applications, including waveform generation, timing circuits, and signal modulation. The design typically includes configurations such as astable multivibrators, monostable multivibrators, and Schmitt triggers, each serving a unique purpose in pulse generation.
In an astable multivibrator configuration, two op-amps are used to produce a continuous square wave output. This configuration relies on the feedback network of resistors and capacitors to determine the frequency and duty cycle of the output pulse. The output can be adjusted by changing the values of the resistors and capacitors in the feedback loop.
A monostable multivibrator, on the other hand, produces a single pulse output in response to an external trigger signal. This circuit typically uses one op-amp and a timing capacitor to define the width of the output pulse. The duration of the pulse can be modified by altering the capacitor value or the resistor connected to the timing circuit.
Schmitt triggers are employed to convert noisy or slowly varying signals into clean, fast transitions. This is achieved by introducing hysteresis into the input-output relationship, allowing for a more stable and reliable output pulse. The configuration of the Schmitt trigger can also be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor values to control the threshold levels.
Overall, the pulse signal generating circuit using operational amplifiers is a versatile tool in electronics, allowing for precise control over timing and waveform characteristics in various applications.It shows the use of various forms of pulse signal generating circuit operational amplifier.
The circuit utilizes operational amplifiers (op-amps) to create different forms of pulse signals, which are essential in many electronic applications, including waveform generation, timing circuits, and signal modulation. The design typically includes configurations such as astable multivibrators, monostable multivibrators, and Schmitt triggers, each serving a unique purpose in pulse generation.
In an astable multivibrator configuration, two op-amps are used to produce a continuous square wave output. This configuration relies on the feedback network of resistors and capacitors to determine the frequency and duty cycle of the output pulse. The output can be adjusted by changing the values of the resistors and capacitors in the feedback loop.
A monostable multivibrator, on the other hand, produces a single pulse output in response to an external trigger signal. This circuit typically uses one op-amp and a timing capacitor to define the width of the output pulse. The duration of the pulse can be modified by altering the capacitor value or the resistor connected to the timing circuit.
Schmitt triggers are employed to convert noisy or slowly varying signals into clean, fast transitions. This is achieved by introducing hysteresis into the input-output relationship, allowing for a more stable and reliable output pulse. The configuration of the Schmitt trigger can also be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor values to control the threshold levels.
Overall, the pulse signal generating circuit using operational amplifiers is a versatile tool in electronics, allowing for precise control over timing and waveform characteristics in various applications.It shows the use of various forms of pulse signal generating circuit operational amplifier.