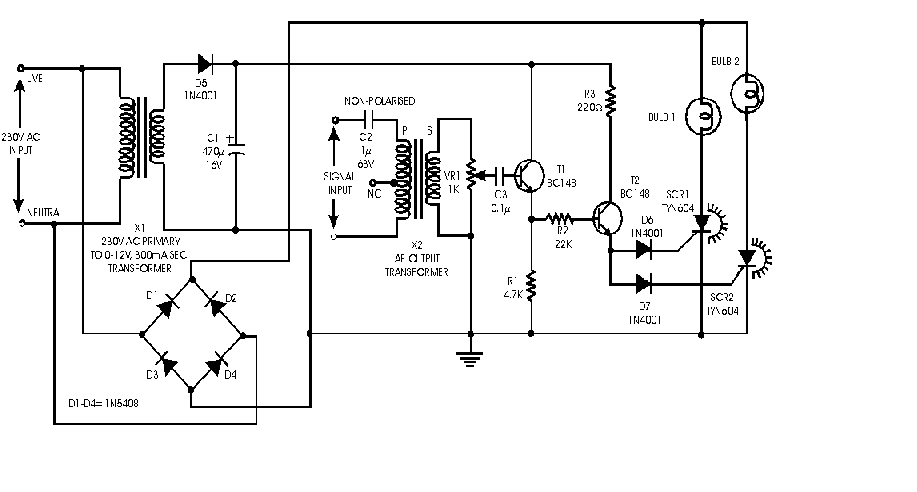
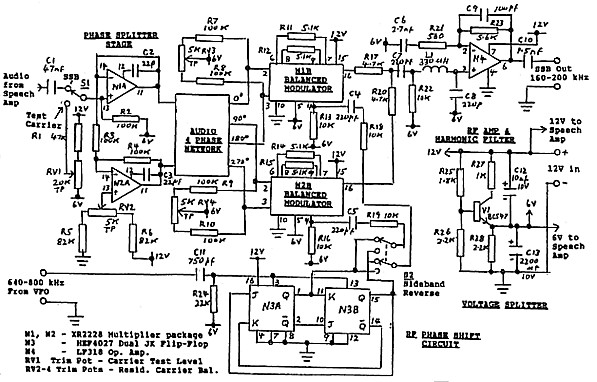
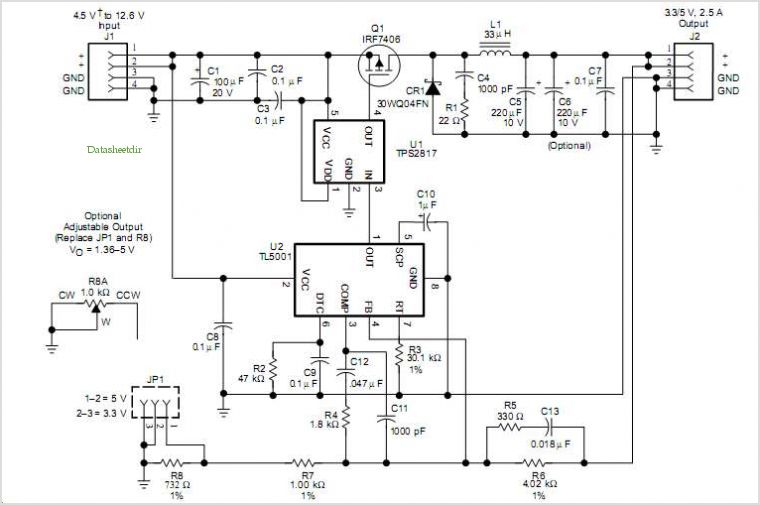
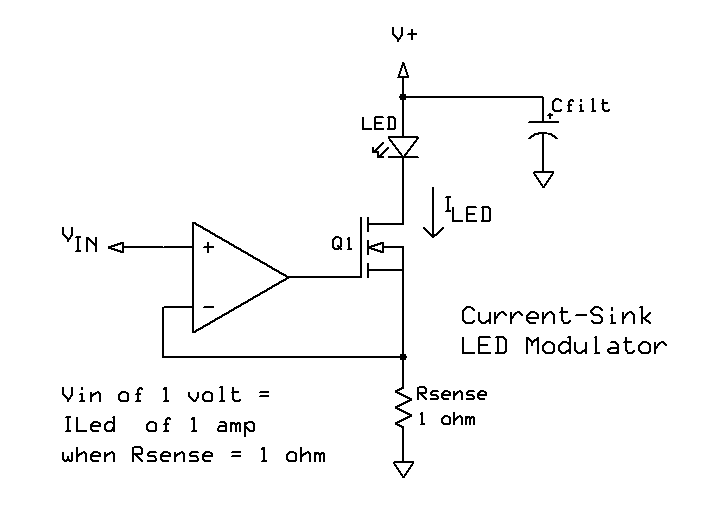
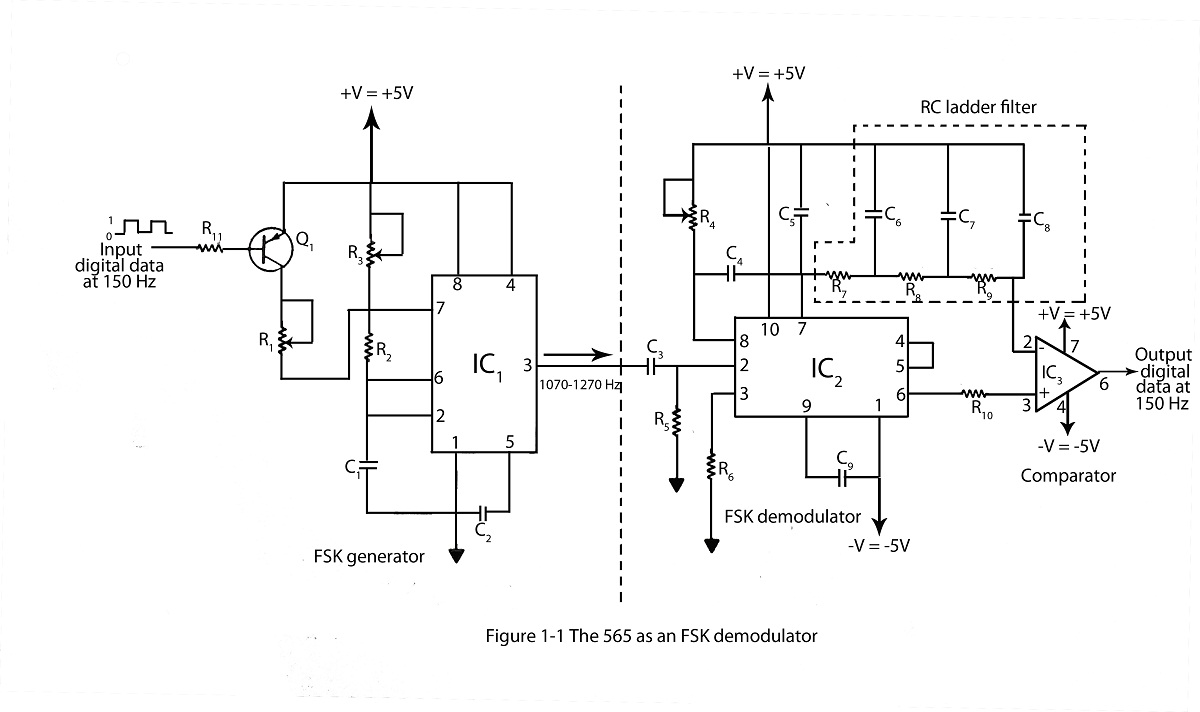
Pulse-width modulator
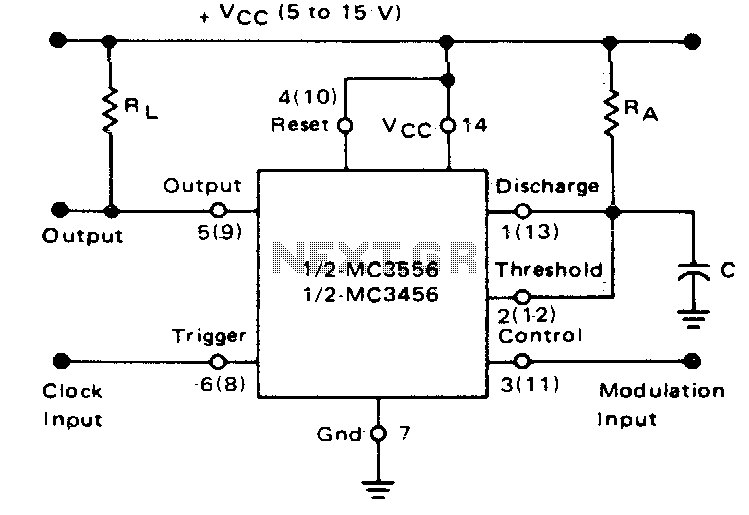
If the timer is activated by a continuous pulse train in the monostable mode, the capacitor's charge time can be adjusted by altering the control voltage at pin 3. In this way, the output pulse width can be modulated by applying a modulating signal that influences the threshold voltage.
In a monostable timer circuit, such as those utilizing the 555 timer IC, the operation relies on a single stable state and a temporary unstable state. When triggered by a pulse, the timer generates a single output pulse of a defined duration. The width of this output pulse is primarily determined by the time constant formed by the resistor-capacitor (RC) network connected to the timing capacitor.
In this configuration, pin 3 serves as the control voltage input, allowing for dynamic adjustment of the threshold voltage that dictates when the timer resets. By varying the voltage at pin 3, the effective threshold voltage can be modified, thus altering the charge time of the capacitor. This adjustment leads to a change in the output pulse width, enabling applications such as pulse width modulation (PWM) where precise control over the pulse duration is required.
The ability to apply a modulating signal to pin 3 introduces an additional layer of flexibility. This signal can be derived from various sources, such as a potentiometer, another waveform generator, or a digital control signal, allowing for real-time modulation of the output pulse width. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the timing characteristics need to adapt to varying conditions, such as in motor speed control, light dimming, or audio signal processing.
The overall functionality of the monostable timer in this context emphasizes the importance of the RC network and control voltage manipulation, showcasing its versatility in electronic design for a range of applications requiring precise timing control.if the timer is triggered with a continuous pulse train in the monostable mode of operation, the charge time of the capacitor can be varied by changing the control voltage at pin 3 In this manner, the output pulse width can be modulated by applying a modulating signal that controls the threshold voltage.
In a monostable timer circuit, such as those utilizing the 555 timer IC, the operation relies on a single stable state and a temporary unstable state. When triggered by a pulse, the timer generates a single output pulse of a defined duration. The width of this output pulse is primarily determined by the time constant formed by the resistor-capacitor (RC) network connected to the timing capacitor.
In this configuration, pin 3 serves as the control voltage input, allowing for dynamic adjustment of the threshold voltage that dictates when the timer resets. By varying the voltage at pin 3, the effective threshold voltage can be modified, thus altering the charge time of the capacitor. This adjustment leads to a change in the output pulse width, enabling applications such as pulse width modulation (PWM) where precise control over the pulse duration is required.
The ability to apply a modulating signal to pin 3 introduces an additional layer of flexibility. This signal can be derived from various sources, such as a potentiometer, another waveform generator, or a digital control signal, allowing for real-time modulation of the output pulse width. This feature is particularly useful in applications where the timing characteristics need to adapt to varying conditions, such as in motor speed control, light dimming, or audio signal processing.
The overall functionality of the monostable timer in this context emphasizes the importance of the RC network and control voltage manipulation, showcasing its versatility in electronic design for a range of applications requiring precise timing control.if the timer is triggered with a continuous pulse train in the monostable mode of operation, the charge time of the capacitor can be varied by changing the control voltage at pin 3 In this manner, the output pulse width can be modulated by applying a modulating signal that controls the threshold voltage.