QuickChip Design Example 2Low Power Silicon BJT LNA for 1.9GHz
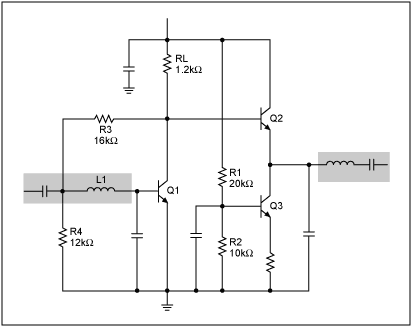
This document presents a very low-power monolithic 1.9GHz silicon Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) that operates with a total current consumption of 1.75mA, which includes the bias circuit.
The described Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) operates at a frequency of 1.9GHz, making it suitable for various wireless communication applications, such as mobile phones and satellite communications. The monolithic design indicates that the entire circuit is integrated onto a single silicon chip, which enhances performance by reducing parasitic capacitance and inductance associated with discrete components.
The total current draw of 1.75mA is particularly noteworthy as it signifies a low-power operation, which is essential for battery-powered devices. The inclusion of the bias circuit within this current specification ensures that the LNA maintains optimal performance across varying temperature and voltage conditions, thereby providing consistent gain and noise figure.
In terms of performance metrics, the LNA is expected to exhibit a low noise figure, which is crucial for amplifying weak signals without introducing significant additional noise. The device's gain, input and output impedance, and linearity should be characterized to ensure compatibility with subsequent stages in a receiver chain.
The circuit design may employ various techniques to achieve low power consumption while maintaining high performance, such as using cascode configurations, current steering, and optimized transistor sizing. Additionally, the integration of on-chip passive components can further minimize the overall footprint of the device, making it ideal for compact designs.
Overall, the 1.9GHz silicon LNA represents a significant advancement in low-power RF amplification technology, suitable for modern communication systems that demand both efficiency and high performance.Presented in this letter is a very low-power monolithic 1.9GHz silicon LNA which draws a total current of 1.75mA including bias circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The described Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) operates at a frequency of 1.9GHz, making it suitable for various wireless communication applications, such as mobile phones and satellite communications. The monolithic design indicates that the entire circuit is integrated onto a single silicon chip, which enhances performance by reducing parasitic capacitance and inductance associated with discrete components.
The total current draw of 1.75mA is particularly noteworthy as it signifies a low-power operation, which is essential for battery-powered devices. The inclusion of the bias circuit within this current specification ensures that the LNA maintains optimal performance across varying temperature and voltage conditions, thereby providing consistent gain and noise figure.
In terms of performance metrics, the LNA is expected to exhibit a low noise figure, which is crucial for amplifying weak signals without introducing significant additional noise. The device's gain, input and output impedance, and linearity should be characterized to ensure compatibility with subsequent stages in a receiver chain.
The circuit design may employ various techniques to achieve low power consumption while maintaining high performance, such as using cascode configurations, current steering, and optimized transistor sizing. Additionally, the integration of on-chip passive components can further minimize the overall footprint of the device, making it ideal for compact designs.
Overall, the 1.9GHz silicon LNA represents a significant advancement in low-power RF amplification technology, suitable for modern communication systems that demand both efficiency and high performance.Presented in this letter is a very low-power monolithic 1.9GHz silicon LNA which draws a total current of 1.75mA including bias circuit.. 🔗 External reference