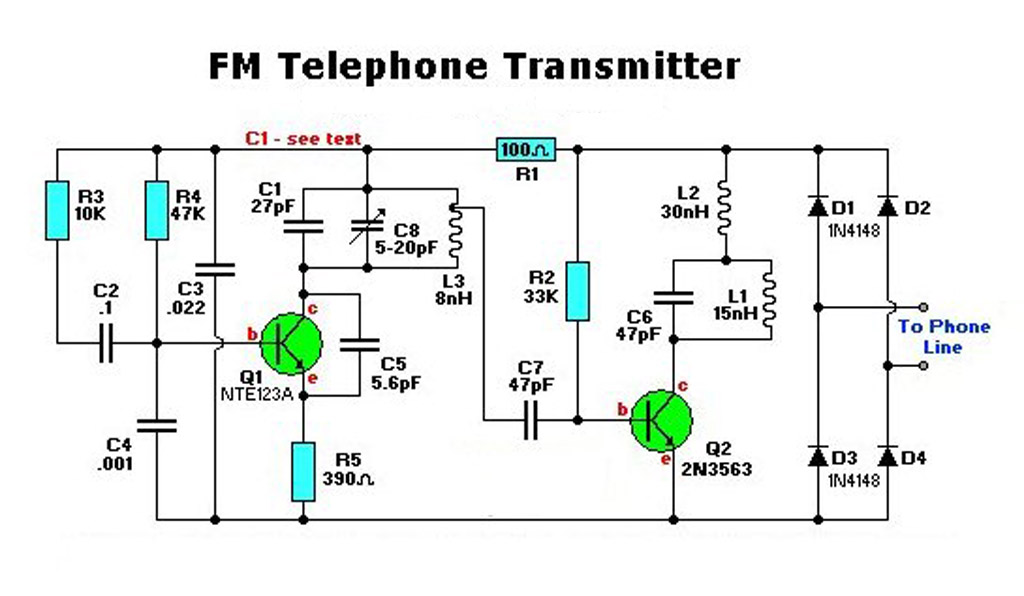
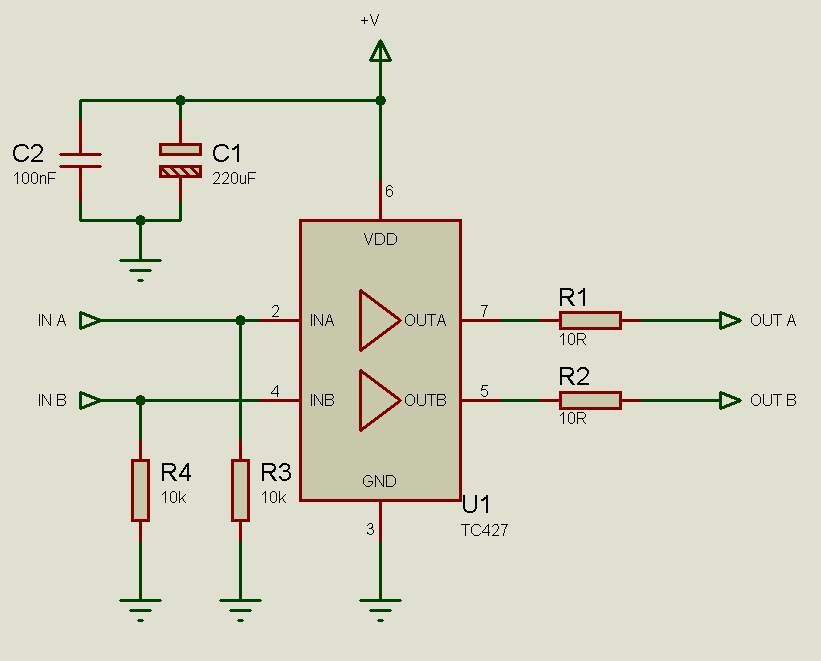
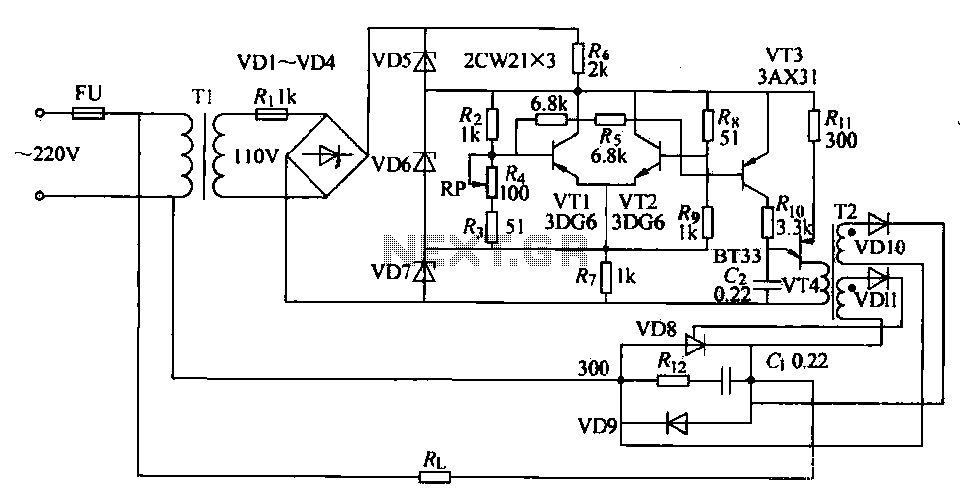
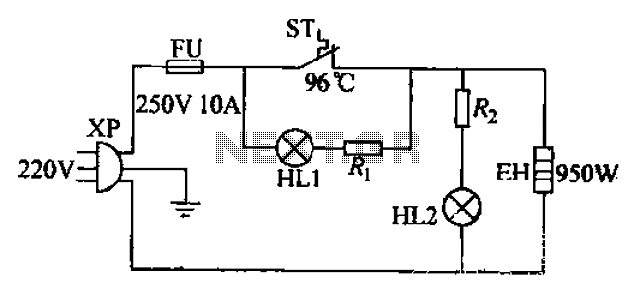
Radar Calibrator Circuit
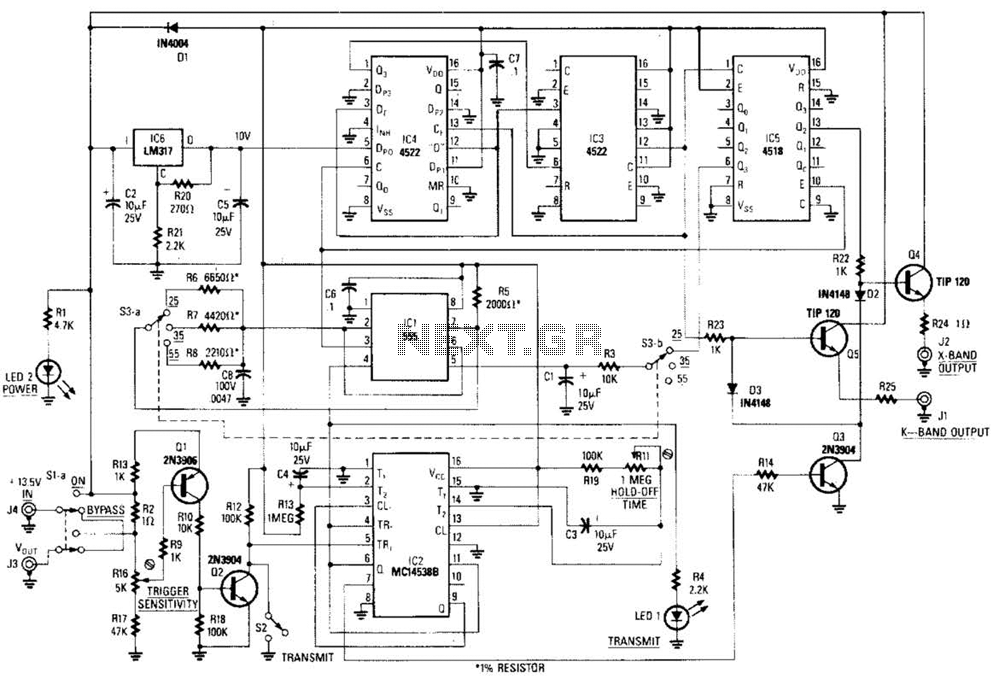
This circuit is a system designed to generate a pulsed modulation signal for a Gunn diode microwave oscillator. It features several preset speed settings (S3 a and b). A 555 timer is employed in conjunction with a frequency divider chain to create Doppler shift equivalents of 25, 35, and 55 rnph, applicable for both X- and D-band radars.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave signal. This signal is then fed into a frequency divider chain, which is composed of flip-flops that divide the frequency of the input signal by a predetermined factor. The output of this chain produces various frequency outputs corresponding to the desired Doppler shift values.
The Gunn diode, which operates at microwave frequencies, is modulated by the pulsed signal generated from the 555 timer. The modulation of the Gunn diode allows for the generation of microwave signals that can be utilized in radar systems. The Doppler effect is crucial for measuring the speed of objects, and the circuit is designed to provide specific modulation frequencies that correspond to the desired speed settings.
The preset speed settings (S3 a and b) are implemented using a switch mechanism, allowing users to select between different operational modes easily. This flexibility is essential for applications requiring accurate speed measurements in radar technology.
Overall, this circuit design is integral for enhancing the performance of radar systems by providing modulated microwave signals that can adapt to various operational requirements in both X-band and D-band radar applications. The combination of the 555 timer and the frequency divider chain ensures precise control over the output frequencies, facilitating reliable Doppler shift measurements. This circuit is basically a system that generates a pulsed modulation signal for a Gunn diode microwave oscillator. Several speed settings are preset (S3 a and b). A 555 timer is used with a frequency divider chain to produce Doppler shift equivalents of 25, 35, and 55 rnph,
for both X- and D-band radars.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer in astable mode to generate a continuous square wave signal. This signal is then fed into a frequency divider chain, which is composed of flip-flops that divide the frequency of the input signal by a predetermined factor. The output of this chain produces various frequency outputs corresponding to the desired Doppler shift values.
The Gunn diode, which operates at microwave frequencies, is modulated by the pulsed signal generated from the 555 timer. The modulation of the Gunn diode allows for the generation of microwave signals that can be utilized in radar systems. The Doppler effect is crucial for measuring the speed of objects, and the circuit is designed to provide specific modulation frequencies that correspond to the desired speed settings.
The preset speed settings (S3 a and b) are implemented using a switch mechanism, allowing users to select between different operational modes easily. This flexibility is essential for applications requiring accurate speed measurements in radar technology.
Overall, this circuit design is integral for enhancing the performance of radar systems by providing modulated microwave signals that can adapt to various operational requirements in both X-band and D-band radar applications. The combination of the 555 timer and the frequency divider chain ensures precise control over the output frequencies, facilitating reliable Doppler shift measurements. This circuit is basically a system that generates a pulsed modulation signal for a Gunn diode microwave oscillator. Several speed settings are preset (S3 a and b). A 555 timer is used with a frequency divider chain to produce Doppler shift equivalents of 25, 35, and 55 rnph,
for both X- and D-band radars.