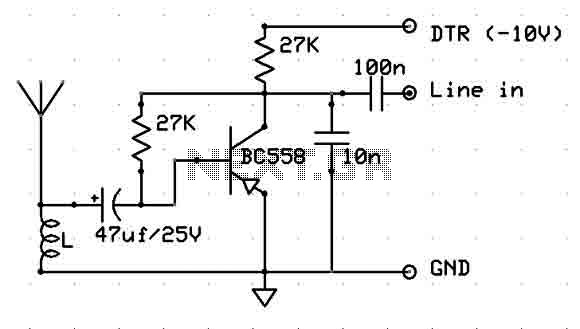
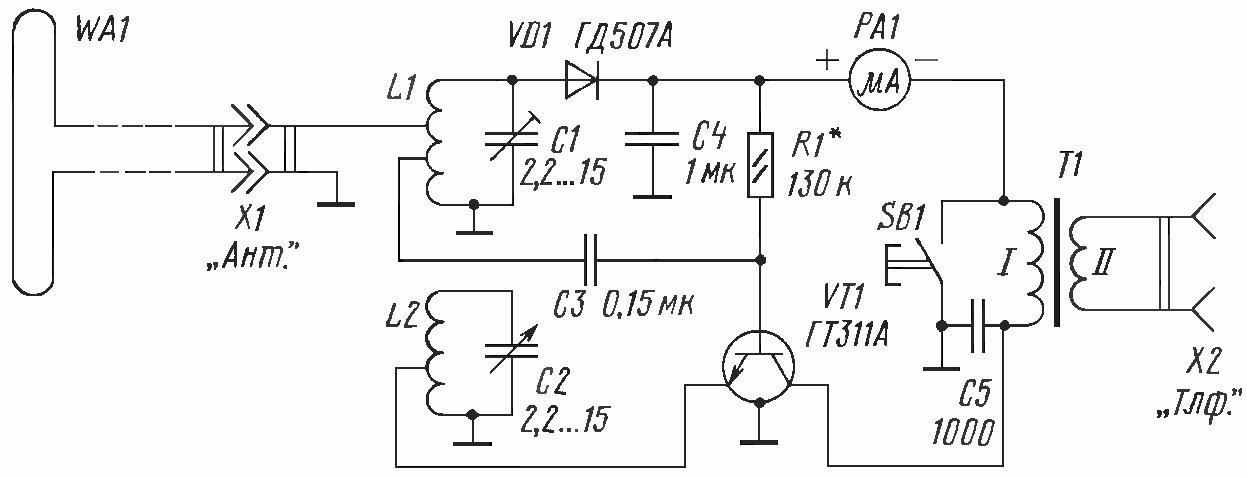
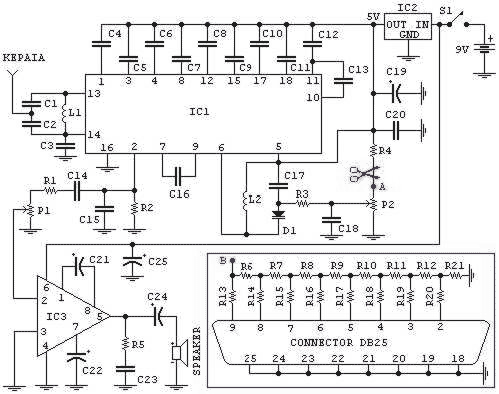
Radio Clock for PC`s
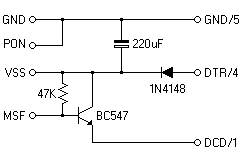
The three best known of these signals are the DCF77 signal broadcast from Mainflingen near Frankfurt in Germany on 77.5kHz which can be received throughout most of central and northern Europe. The MSF signal broadcast from outside Rugby in England by the National Physical Laboratory at 60kHz which can be received anywhere in the British Isles and large parts of northern Europe.
The DCF77 and MSF signals are time synchronization signals that are crucial for various applications, including radio-controlled clocks and timing systems. The DCF77 signal, transmitted at 77.5 kHz, is characterized by its long-range capabilities, allowing it to be received across a wide area, including central and northern Europe. This signal encodes time information using amplitude modulation, where binary data is represented by the presence or absence of a carrier wave.
On the other hand, the MSF signal operates at a frequency of 60 kHz and serves a similar purpose. It is transmitted with high precision from Rugby, England, and is designed to provide accurate timekeeping across the British Isles and parts of northern Europe. The transmission includes a time code that conveys information such as the current time, date, and daylight saving time adjustments.
Both signals utilize low-frequency radio waves, which have excellent propagation characteristics, allowing them to penetrate buildings and travel long distances. These signals are typically received by specialized receivers that can decode the time information and synchronize clocks accordingly. The design of such receivers often includes a tuned circuit to select the desired frequency, followed by demodulation circuitry to extract the time code from the received signal.
In applications where precision timing is essential, such as in telecommunications, GPS systems, and scientific research, the integration of these time signals into electronic systems ensures that devices maintain accurate timekeeping, thus enhancing their functionality and reliability.The three best known of these signals are the DCF77 signal broadcast from Mainflingen near Frankfurt in Germany on 77.5kHz which can be received through out most of central and northern europe. The MSF signal broadcast from outside Rugby in England by the National Physical Laboratory at 60kHz which can be received in the anywehere in the British Isles and large parts of northern europe.
🔗 External reference
The DCF77 and MSF signals are time synchronization signals that are crucial for various applications, including radio-controlled clocks and timing systems. The DCF77 signal, transmitted at 77.5 kHz, is characterized by its long-range capabilities, allowing it to be received across a wide area, including central and northern Europe. This signal encodes time information using amplitude modulation, where binary data is represented by the presence or absence of a carrier wave.
On the other hand, the MSF signal operates at a frequency of 60 kHz and serves a similar purpose. It is transmitted with high precision from Rugby, England, and is designed to provide accurate timekeeping across the British Isles and parts of northern Europe. The transmission includes a time code that conveys information such as the current time, date, and daylight saving time adjustments.
Both signals utilize low-frequency radio waves, which have excellent propagation characteristics, allowing them to penetrate buildings and travel long distances. These signals are typically received by specialized receivers that can decode the time information and synchronize clocks accordingly. The design of such receivers often includes a tuned circuit to select the desired frequency, followed by demodulation circuitry to extract the time code from the received signal.
In applications where precision timing is essential, such as in telecommunications, GPS systems, and scientific research, the integration of these time signals into electronic systems ensures that devices maintain accurate timekeeping, thus enhancing their functionality and reliability.The three best known of these signals are the DCF77 signal broadcast from Mainflingen near Frankfurt in Germany on 77.5kHz which can be received through out most of central and northern europe. The MSF signal broadcast from outside Rugby in England by the National Physical Laboratory at 60kHz which can be received in the anywehere in the British Isles and large parts of northern europe.
🔗 External reference