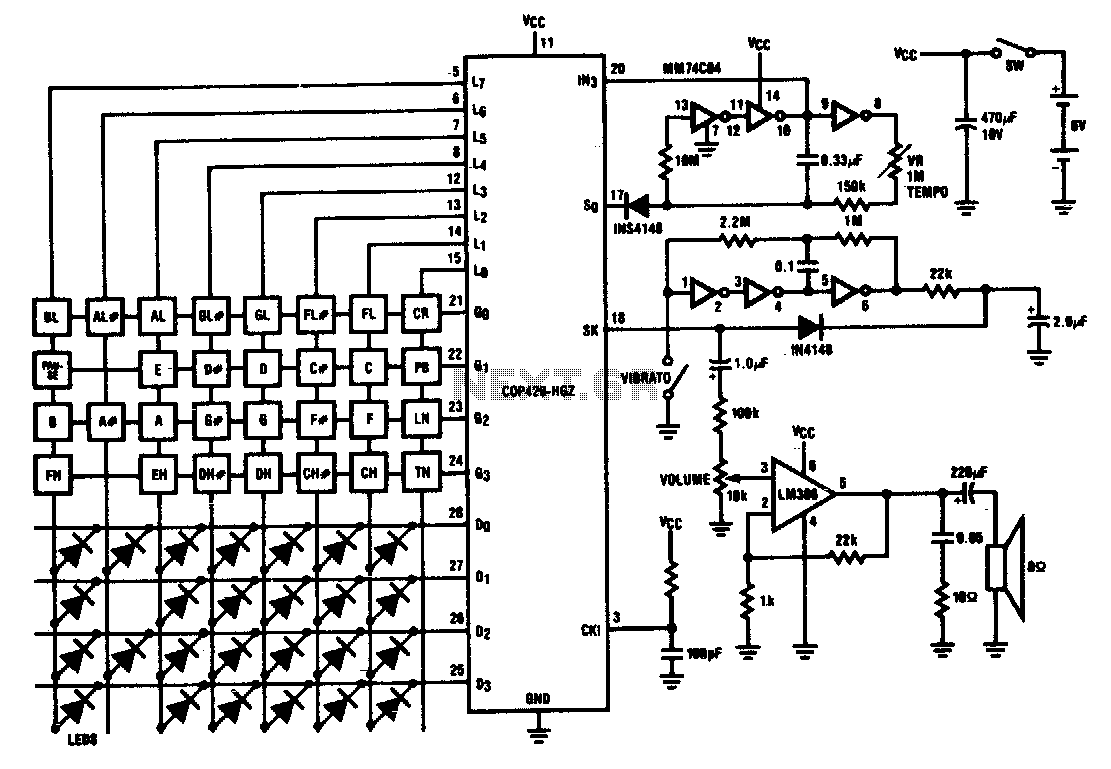
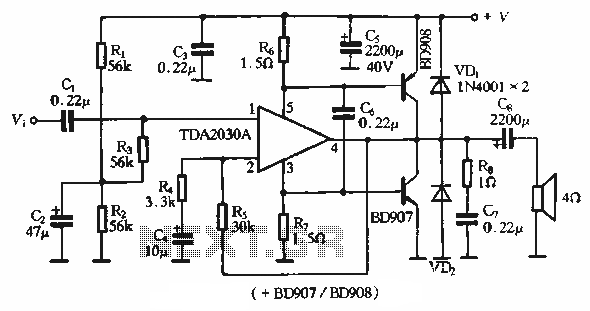
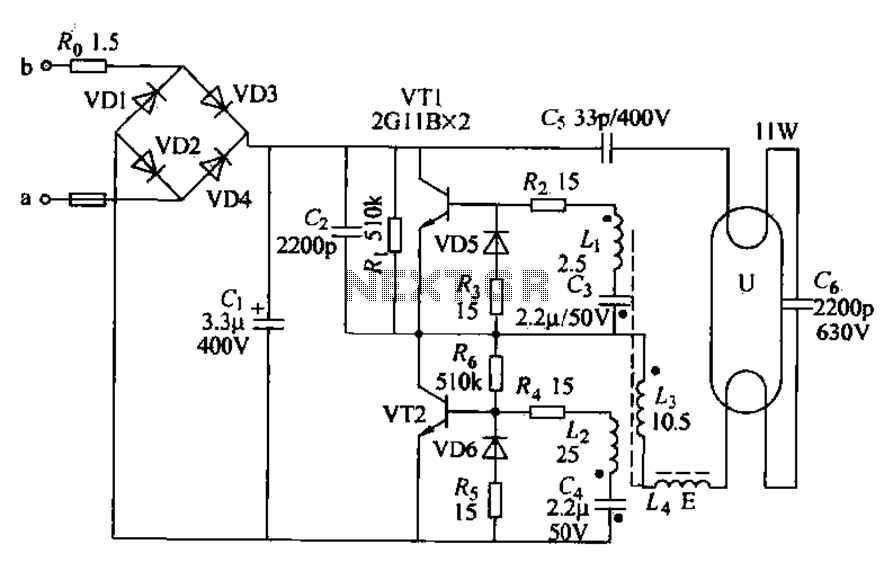
Radio control car receiver principle circuit diagram
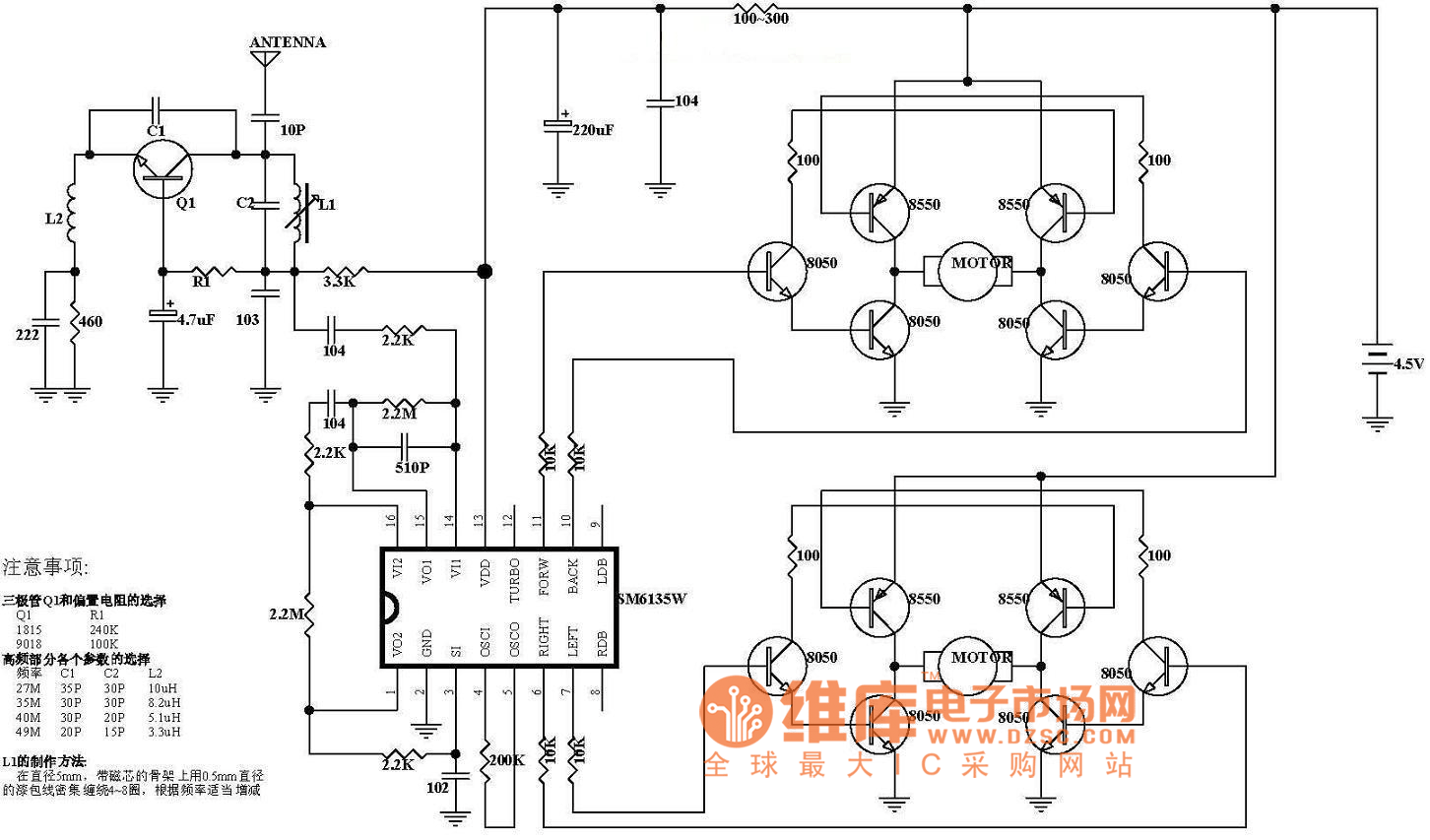
The diagram illustrates the principle circuit of a radio control car receiver. Important notes include the selection of transistor Q1, which is specified as either 1815 or 9018, along with the bias resistor R1, which has values of 240K and 100K. Additionally, the high-frequency parameters are detailed for various frequency ranges: C1, C2, L2 are specified as 27M, 35pF, 30pF, 10µH; 35M, 30pF, 30pF, 8.2µH; 40M, 30pF, 20pF, 5.1µH; and 49M, 20pF, 15pF, 3.3µH. The production method for inductor L1 involves using enameled wire with a diameter of 5mm.
The radio control car receiver circuit operates by receiving modulated signals transmitted from a remote control unit. The transistor Q1 serves as a key component in amplifying the received signals, with the choice of either the 1815 or 9018 model depending on the desired frequency response and gain characteristics. The bias resistor R1 is critical for setting the operating point of the transistor, ensuring optimal performance in the circuit.
The circuit includes capacitors C1 and C2, which are essential for filtering and tuning the receiver to the desired frequency. The specified values for these capacitors vary across different frequency bands, allowing the circuit to effectively handle the specific frequencies utilized in radio control applications. The inductors L2 are also tailored for the respective frequency ranges, with different inductance values being used to optimize the circuit's selectivity and bandwidth.
Inductor L1, produced using enameled wire with a diameter of 5mm, plays a vital role in the circuit's performance. The choice of wire gauge and winding technique affects the inductor's resistance and inductance, which are critical parameters for achieving the desired frequency response. Proper construction techniques must be employed to minimize losses and ensure reliable operation.
Overall, the design and component selection outlined in the circuit diagram are integral to the effective functioning of the radio control car receiver, enabling it to accurately receive and process control signals for the operation of the vehicle.Here is the diagram of radio controlcarreceiverprinciple circuit. Notes:The choice of transistor Q1 and the bias resistorQ1 1815 9018R1 240K 100K The choice of the high-frequency parameters partFrequency C1 C2 L227M 35P 30P 10uH35M 30P 30P 8.2uH40M 30P 20P 5.1uH49M 20P 15P 3.3uH The production method of L1In the diameter of 5mm, use Enameled wire diamet.. 🔗 External reference
The radio control car receiver circuit operates by receiving modulated signals transmitted from a remote control unit. The transistor Q1 serves as a key component in amplifying the received signals, with the choice of either the 1815 or 9018 model depending on the desired frequency response and gain characteristics. The bias resistor R1 is critical for setting the operating point of the transistor, ensuring optimal performance in the circuit.
The circuit includes capacitors C1 and C2, which are essential for filtering and tuning the receiver to the desired frequency. The specified values for these capacitors vary across different frequency bands, allowing the circuit to effectively handle the specific frequencies utilized in radio control applications. The inductors L2 are also tailored for the respective frequency ranges, with different inductance values being used to optimize the circuit's selectivity and bandwidth.
Inductor L1, produced using enameled wire with a diameter of 5mm, plays a vital role in the circuit's performance. The choice of wire gauge and winding technique affects the inductor's resistance and inductance, which are critical parameters for achieving the desired frequency response. Proper construction techniques must be employed to minimize losses and ensure reliable operation.
Overall, the design and component selection outlined in the circuit diagram are integral to the effective functioning of the radio control car receiver, enabling it to accurately receive and process control signals for the operation of the vehicle.Here is the diagram of radio controlcarreceiverprinciple circuit. Notes:The choice of transistor Q1 and the bias resistorQ1 1815 9018R1 240K 100K The choice of the high-frequency parameters partFrequency C1 C2 L227M 35P 30P 10uH35M 30P 30P 8.2uH40M 30P 20P 5.1uH49M 20P 15P 3.3uH The production method of L1In the diameter of 5mm, use Enameled wire diamet.. 🔗 External reference