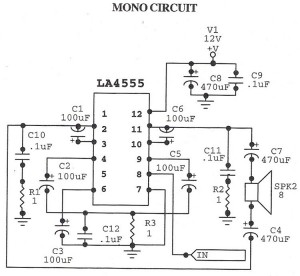
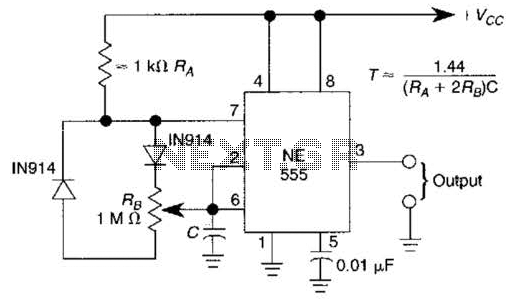
Radio harmonic detection circuit
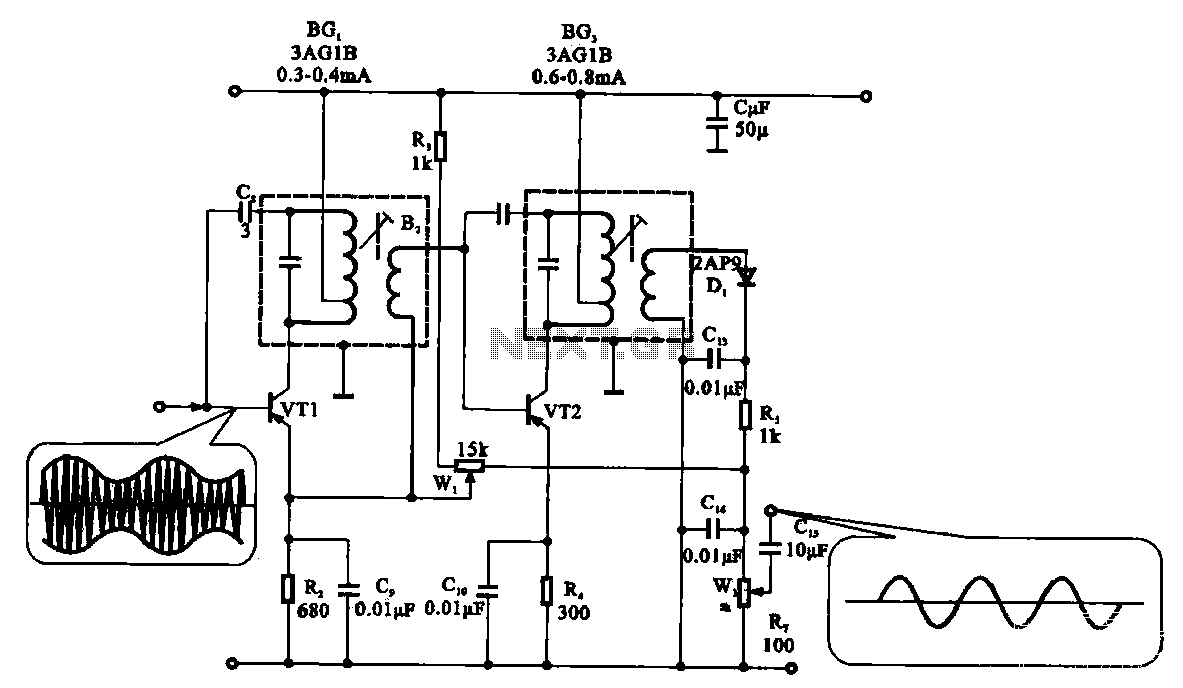
The demodulation and detection circuit is a radio AM intermediate frequency (IF) signal amplifier that performs two-stage detection using diode Dr. It extracts the audio signal from the IF carrier detection and subsequently sends it to the power amplifier stage. The demodulation and detection waveforms can be displayed using a multimeter and oscilloscope for debugging and testing purposes.
The described circuit primarily focuses on the demodulation of amplitude-modulated signals. The initial stage involves amplifying the intermediate frequency (IF) signal, which is crucial for enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio before demodulation. The two-stage detection process utilizes a diode (referred to as Dr) to rectify the IF signal, allowing the extraction of the audio information.
In the first stage of detection, the diode conducts during the positive half-cycle of the IF signal, allowing the audio envelope to pass while blocking the negative half-cycle. This results in a pulsating DC signal that corresponds to the audio waveform. The second stage further refines this signal, typically involving additional filtering to smooth out the rectified waveform and eliminate high-frequency components that are not part of the audio signal.
After the demodulation and detection process, the resulting audio signal is forwarded to a power amplifier stage. This stage is responsible for boosting the audio signal's power level to drive speakers or other audio output devices effectively. The overall design ensures that the audio output maintains fidelity to the original modulated signal while providing sufficient power for practical applications.
For testing and debugging purposes, the circuit's performance can be monitored using a multimeter to measure voltage levels and an oscilloscope to visualize the waveforms at various points in the circuit. This allows engineers to verify the integrity of the demodulation process and make necessary adjustments for optimal performance.FIG demodulation and detection circuit is a radio, AM intermediate frequency signal IF amplifier after a two-stage detection performed by the diode Dr, the audio signal from th e IF carrier detection, and then sending the subsequent stage of the power amplifier. Demodulation and detection of the waveform can be shown with a multimeter and wave vase debugging and testing
The described circuit primarily focuses on the demodulation of amplitude-modulated signals. The initial stage involves amplifying the intermediate frequency (IF) signal, which is crucial for enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio before demodulation. The two-stage detection process utilizes a diode (referred to as Dr) to rectify the IF signal, allowing the extraction of the audio information.
In the first stage of detection, the diode conducts during the positive half-cycle of the IF signal, allowing the audio envelope to pass while blocking the negative half-cycle. This results in a pulsating DC signal that corresponds to the audio waveform. The second stage further refines this signal, typically involving additional filtering to smooth out the rectified waveform and eliminate high-frequency components that are not part of the audio signal.
After the demodulation and detection process, the resulting audio signal is forwarded to a power amplifier stage. This stage is responsible for boosting the audio signal's power level to drive speakers or other audio output devices effectively. The overall design ensures that the audio output maintains fidelity to the original modulated signal while providing sufficient power for practical applications.
For testing and debugging purposes, the circuit's performance can be monitored using a multimeter to measure voltage levels and an oscilloscope to visualize the waveforms at various points in the circuit. This allows engineers to verify the integrity of the demodulation process and make necessary adjustments for optimal performance.FIG demodulation and detection circuit is a radio, AM intermediate frequency signal IF amplifier after a two-stage detection performed by the diode Dr, the audio signal from th e IF carrier detection, and then sending the subsequent stage of the power amplifier. Demodulation and detection of the waveform can be shown with a multimeter and wave vase debugging and testing