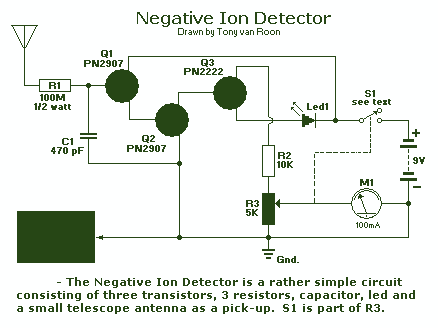
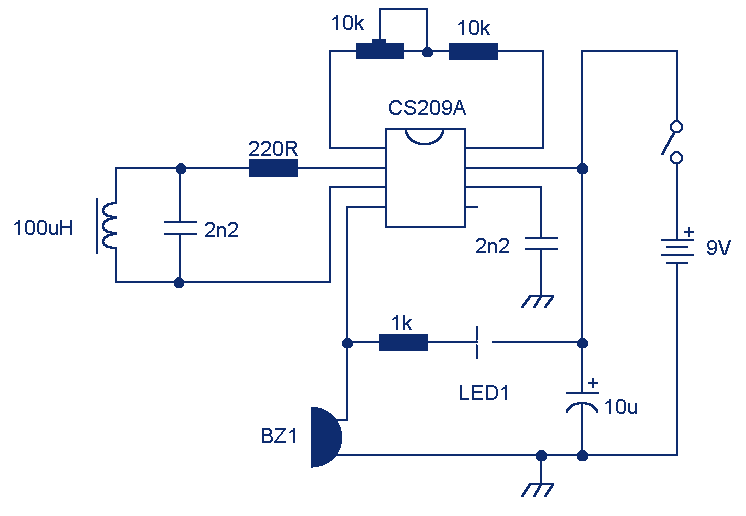
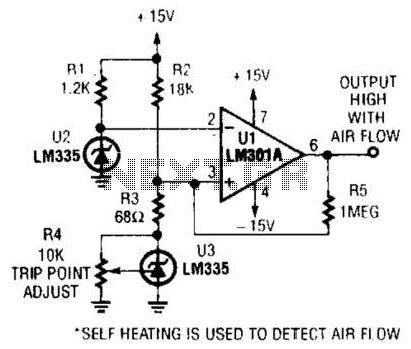
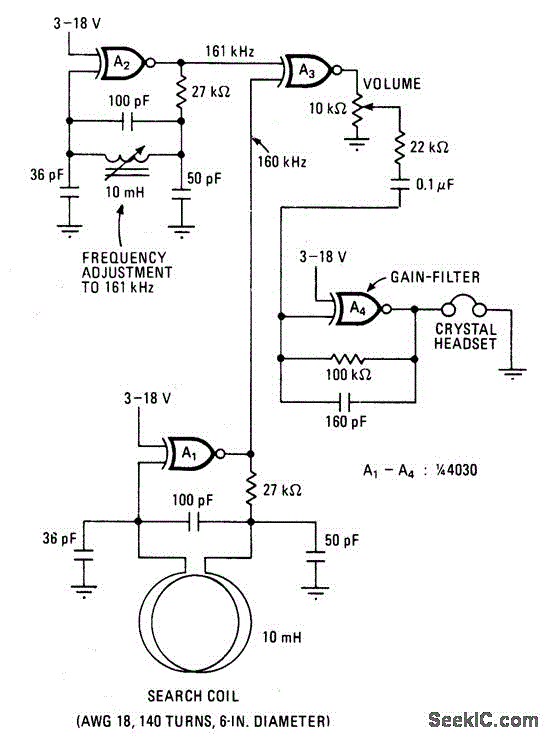
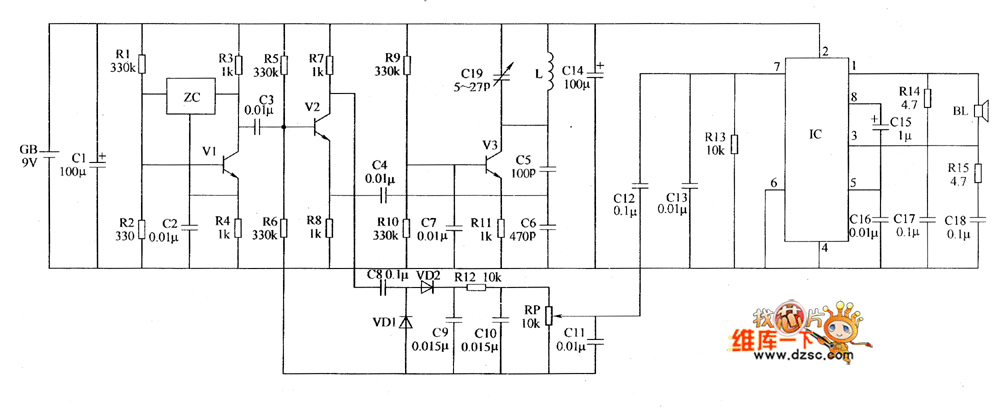
rain detector

This rain detector provides immediate notification when it begins to rain, allowing time to close windows and secure belongings. Alternatively, a molded power supply with a simple voltage regulator can be employed to reduce the voltage to 3 volts. The battery-operated circuit consumes negligible current when the sensor is dry, and the current draw remains low when the buzzer is activated, ensuring that a pair of AA batteries will last for an extended period. When triggered, the buzzer emits a pulse approximately once per second for a brief duration, producing a sound reminiscent of dripping water. A slower, longer beep can be achieved by increasing the capacitance of the 1 µF capacitor. The circuit functions as a basic flasher circuit that operates effectively at just 3 volts using standard silicon transistors. The value of the 10 kΩ resistor can be increased to extend the beep duration without affecting the beep rate; however, beyond a certain point, the circuit may no longer operate correctly, depending on the transistors' gain.
The rain detector circuit is designed to utilize a minimalistic approach while providing essential functionality. The core of the circuit consists of a moisture sensor that detects the presence of water. When water is detected, the sensor triggers a transistor switch that activates a buzzer. The circuit operates on a low voltage of 3 volts, making it suitable for battery operation, which is ideal for portable or outdoor applications.
The buzzer is designed to produce a short, pulsing sound that mimics the sound of dripping water. This is achieved through a simple timing circuit that includes a capacitor and a resistor. The 1 µF capacitor, in conjunction with the resistor, determines the frequency and duration of the buzzer's sound. Adjusting the capacitor value allows for customization of the sound characteristics, making it possible to create a longer or slower beep if desired.
The choice of using silicon transistors in the design ensures that the circuit can operate efficiently at low voltages. The transistors act as switches that control the current flowing to the buzzer, enabling it to produce sound only when rain is detected. The 10 kΩ resistor plays a crucial role in setting the timing for the buzzer. By increasing its value, the duration of the beep can be extended without altering the frequency, although care must be taken to avoid exceeding the operational limits of the transistors.
Overall, this rain detector circuit is a practical solution for alerting users to rain conditions, ensuring that they can take timely action to protect their belongings. Its low power consumption and simple design make it an excellent choice for various applications, from home use to outdoor events.This rain detector will give you a heads-up the instant it starts to rain, hopefully giving you time to close windows and bring in possessions Alternately, a molded power supply with a simple voltage regulator to drop the voltage to 3 volts could be used The battery-powered circuit draws virtually no current when the sensor is dry and the current consumption is low when the buzzer is activated so a couple of AA cells will last a long time When the circuit is triggered, the buzzer is pulsed about once per second for a very short time, giving it a dripping water sound which seems appropriate. A slower, longer beep may be had by increasing the 1 uF capacitor. The circuit is basically a handy flasher circuit that operates well on only 3 volts using ordinary silicon transistors The 10 k resistor may be increased for a longer beep time without decreasing the beep rate but at some point the circuit will cease to function properly, depending on the gain of the transistors.
🔗 External reference
The rain detector circuit is designed to utilize a minimalistic approach while providing essential functionality. The core of the circuit consists of a moisture sensor that detects the presence of water. When water is detected, the sensor triggers a transistor switch that activates a buzzer. The circuit operates on a low voltage of 3 volts, making it suitable for battery operation, which is ideal for portable or outdoor applications.
The buzzer is designed to produce a short, pulsing sound that mimics the sound of dripping water. This is achieved through a simple timing circuit that includes a capacitor and a resistor. The 1 µF capacitor, in conjunction with the resistor, determines the frequency and duration of the buzzer's sound. Adjusting the capacitor value allows for customization of the sound characteristics, making it possible to create a longer or slower beep if desired.
The choice of using silicon transistors in the design ensures that the circuit can operate efficiently at low voltages. The transistors act as switches that control the current flowing to the buzzer, enabling it to produce sound only when rain is detected. The 10 kΩ resistor plays a crucial role in setting the timing for the buzzer. By increasing its value, the duration of the beep can be extended without altering the frequency, although care must be taken to avoid exceeding the operational limits of the transistors.
Overall, this rain detector circuit is a practical solution for alerting users to rain conditions, ensuring that they can take timely action to protect their belongings. Its low power consumption and simple design make it an excellent choice for various applications, from home use to outdoor events.This rain detector will give you a heads-up the instant it starts to rain, hopefully giving you time to close windows and bring in possessions Alternately, a molded power supply with a simple voltage regulator to drop the voltage to 3 volts could be used The battery-powered circuit draws virtually no current when the sensor is dry and the current consumption is low when the buzzer is activated so a couple of AA cells will last a long time When the circuit is triggered, the buzzer is pulsed about once per second for a very short time, giving it a dripping water sound which seems appropriate. A slower, longer beep may be had by increasing the 1 uF capacitor. The circuit is basically a handy flasher circuit that operates well on only 3 volts using ordinary silicon transistors The 10 k resistor may be increased for a longer beep time without decreasing the beep rate but at some point the circuit will cease to function properly, depending on the gain of the transistors.
🔗 External reference