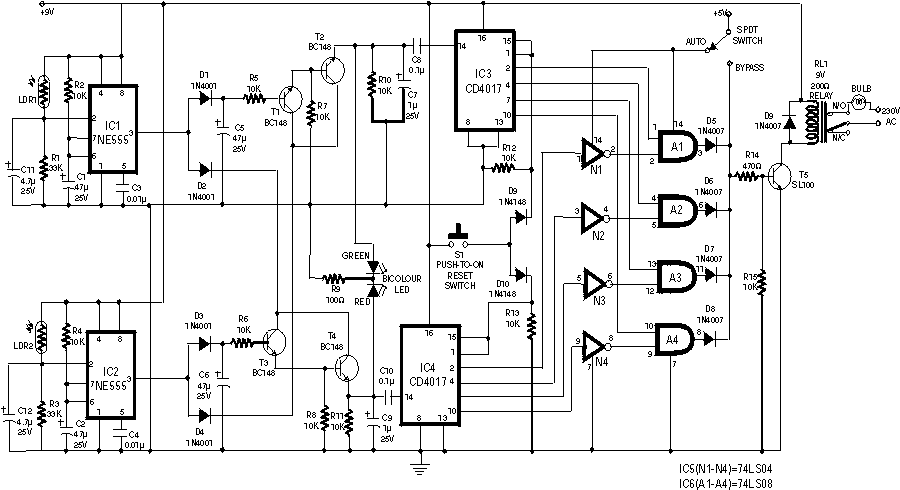
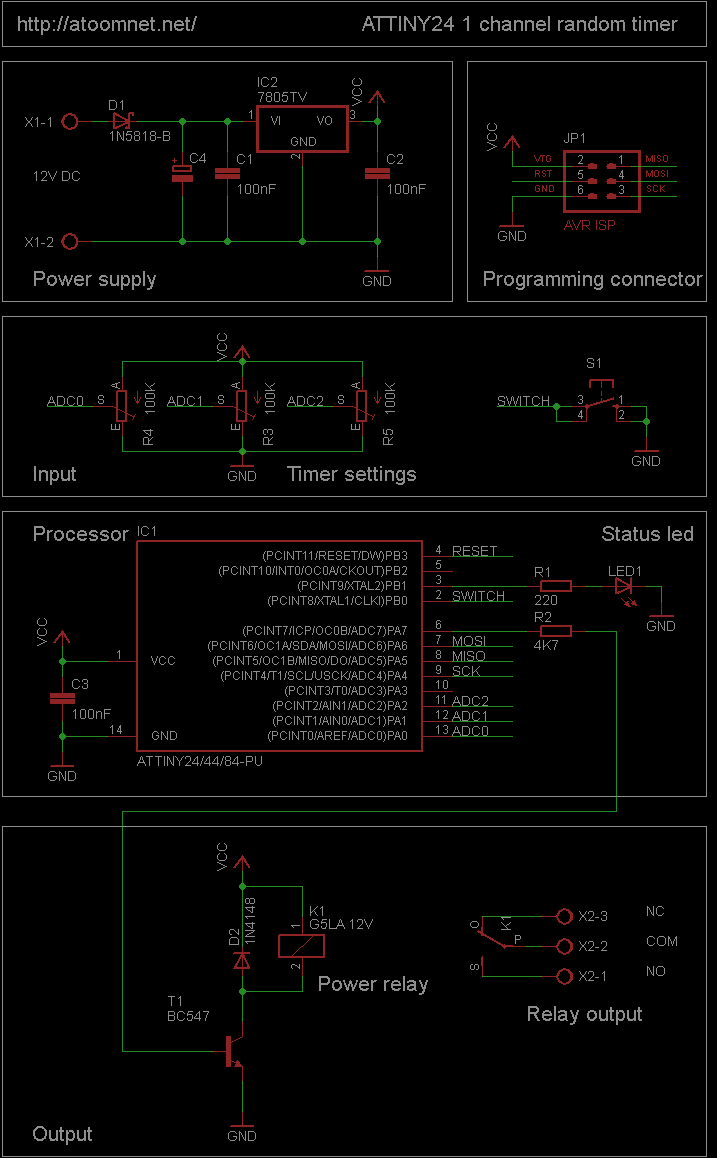
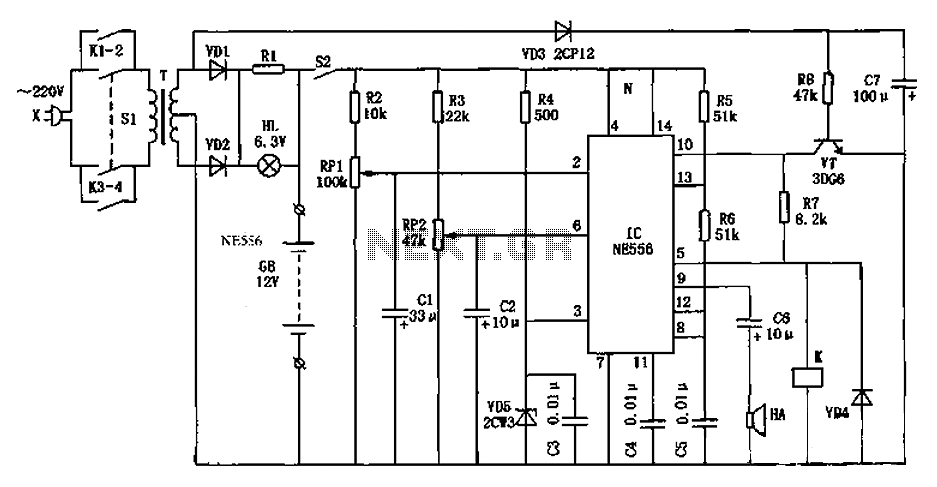
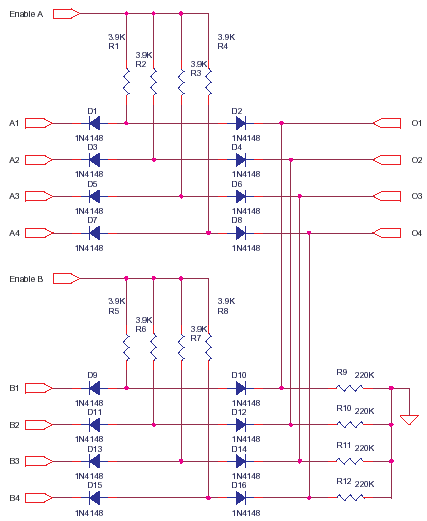
Air-Flow Detector Circuit
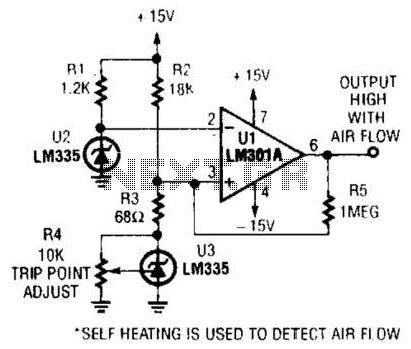
Two precision temperature sensors are utilized to measure a slight temperature difference. When airflow is present, the self-heating of the LM335 is minimized, resulting in an unequal output from the two temperature sensors. This disparity is further amplified by Ul.
The circuit employs two precision temperature sensors, such as the LM335, which are capable of detecting minute variations in temperature. The LM335 is a temperature-to-voltage converter that provides a linear output voltage proportional to the temperature in Kelvin. In this configuration, both sensors are placed in a manner that allows them to experience different thermal conditions based on the airflow in the environment.
When airflow occurs, it mitigates the self-heating effect typically observed in the LM335 sensors. Self-heating can lead to inaccuracies in temperature readings, as the sensor's own heat can skew the measured temperature. By reducing self-heating through airflow, the sensors can provide a more accurate differential reading.
The output from the two sensors is then processed by an operational amplifier (Ul) configured as a differential amplifier. This amplifier amplifies the voltage difference between the outputs of the two temperature sensors. The gain of the amplifier can be set to a specific value to ensure that even small temperature differences are effectively amplified for further processing or display.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors for setting the gain of the amplifier, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly a microcontroller for digital processing of the amplified signal. The overall design aims to create a highly sensitive temperature measurement system that can detect small changes in temperature due to environmental variations, making it suitable for applications in HVAC systems, environmental monitoring, and industrial processes. Two precision temperature sensors are used to detect a small temperature difference. When air flow occurs, self-heating of the LM335 is reduced, and the output of the two temperature sensors is unequal. This is amplified by Ul.
The circuit employs two precision temperature sensors, such as the LM335, which are capable of detecting minute variations in temperature. The LM335 is a temperature-to-voltage converter that provides a linear output voltage proportional to the temperature in Kelvin. In this configuration, both sensors are placed in a manner that allows them to experience different thermal conditions based on the airflow in the environment.
When airflow occurs, it mitigates the self-heating effect typically observed in the LM335 sensors. Self-heating can lead to inaccuracies in temperature readings, as the sensor's own heat can skew the measured temperature. By reducing self-heating through airflow, the sensors can provide a more accurate differential reading.
The output from the two sensors is then processed by an operational amplifier (Ul) configured as a differential amplifier. This amplifier amplifies the voltage difference between the outputs of the two temperature sensors. The gain of the amplifier can be set to a specific value to ensure that even small temperature differences are effectively amplified for further processing or display.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors for setting the gain of the amplifier, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly a microcontroller for digital processing of the amplified signal. The overall design aims to create a highly sensitive temperature measurement system that can detect small changes in temperature due to environmental variations, making it suitable for applications in HVAC systems, environmental monitoring, and industrial processes. Two precision temperature sensors are used to detect a small temperature difference. When air flow occurs, self-heating of the LM335 is reduced, and the output of the two temperature sensors is unequal. This is amplified by Ul.