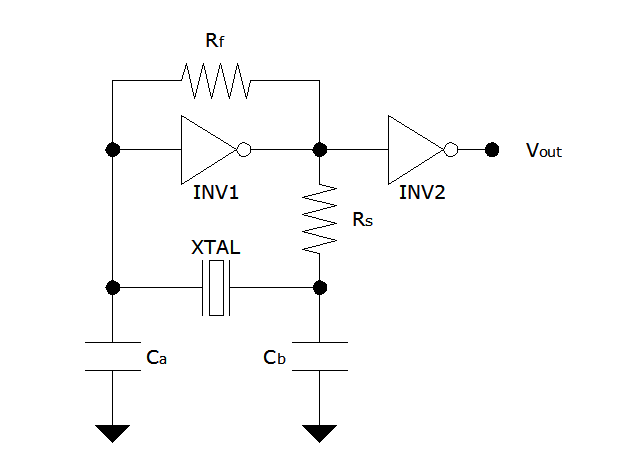
RC oscillator
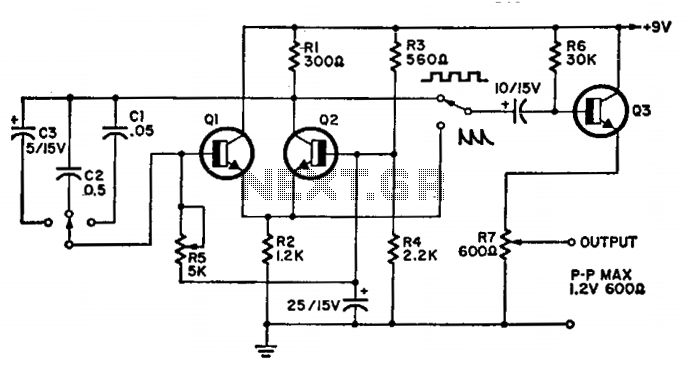
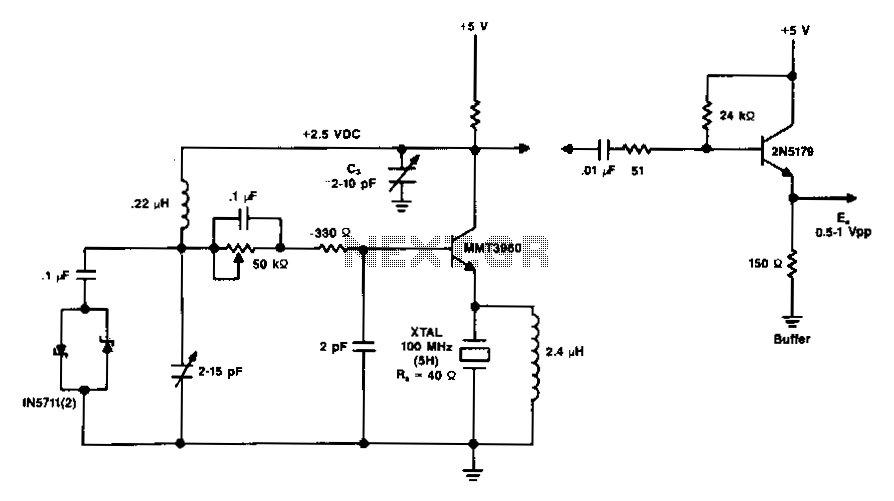
The circuit operates within a frequency range of 15 Hz to 30 kHz and serves as a function generator. The 2N2926 transistor or its equivalent can be utilized in this design.
This function generator circuit is designed to produce a variety of waveforms, including sine, square, and triangle waves, across the specified frequency range of 15 Hz to 30 kHz. The versatility of the circuit allows it to be used in various applications, such as testing audio equipment, simulating signals for control systems, and providing reference signals for other electronic circuits.
The core of the circuit typically utilizes a combination of operational amplifiers (op-amps) and transistors to achieve the desired waveform generation. For the transistor section, the 2N2926 or an equivalent transistor is recommended due to its suitable frequency response and amplification characteristics. The transistor can be configured in various ways, such as in a common-emitter configuration, to amplify the output signal effectively.
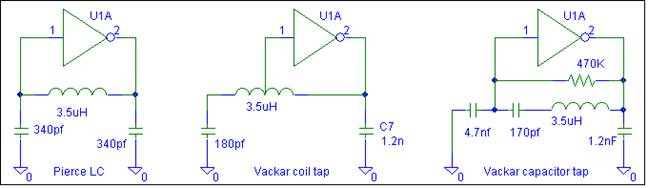
To generate different types of waveforms, the circuit may employ a combination of feedback networks and timing components, such as resistors and capacitors, which determine the frequency and shape of the output signal. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by changing the values of these passive components. For instance, in a square wave generator configuration, the duty cycle can be controlled by varying the resistor-capacitor (RC) time constants.
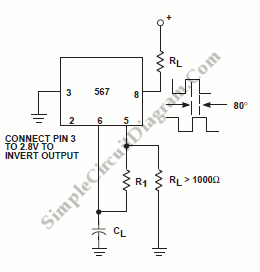
In addition to the basic components, the circuit may also include features such as amplitude control, output buffering, and protection diodes to safeguard the transistors from voltage spikes. Proper layout and grounding techniques are essential to minimize noise and ensure stable operation, particularly at higher frequencies.
Overall, this function generator circuit provides a reliable and flexible solution for generating periodic waveforms across a broad frequency range, making it an invaluable tool for electronics testing and experimentation.The circuit covers 15 Hz-30 kHz and is useful as a function generator. The 2N2926 or equivalent transistors can be used.
This function generator circuit is designed to produce a variety of waveforms, including sine, square, and triangle waves, across the specified frequency range of 15 Hz to 30 kHz. The versatility of the circuit allows it to be used in various applications, such as testing audio equipment, simulating signals for control systems, and providing reference signals for other electronic circuits.
The core of the circuit typically utilizes a combination of operational amplifiers (op-amps) and transistors to achieve the desired waveform generation. For the transistor section, the 2N2926 or an equivalent transistor is recommended due to its suitable frequency response and amplification characteristics. The transistor can be configured in various ways, such as in a common-emitter configuration, to amplify the output signal effectively.
To generate different types of waveforms, the circuit may employ a combination of feedback networks and timing components, such as resistors and capacitors, which determine the frequency and shape of the output signal. The frequency of oscillation can be adjusted by changing the values of these passive components. For instance, in a square wave generator configuration, the duty cycle can be controlled by varying the resistor-capacitor (RC) time constants.
In addition to the basic components, the circuit may also include features such as amplitude control, output buffering, and protection diodes to safeguard the transistors from voltage spikes. Proper layout and grounding techniques are essential to minimize noise and ensure stable operation, particularly at higher frequencies.
Overall, this function generator circuit provides a reliable and flexible solution for generating periodic waveforms across a broad frequency range, making it an invaluable tool for electronics testing and experimentation.The circuit covers 15 Hz-30 kHz and is useful as a function generator. The 2N2926 or equivalent transistors can be used.