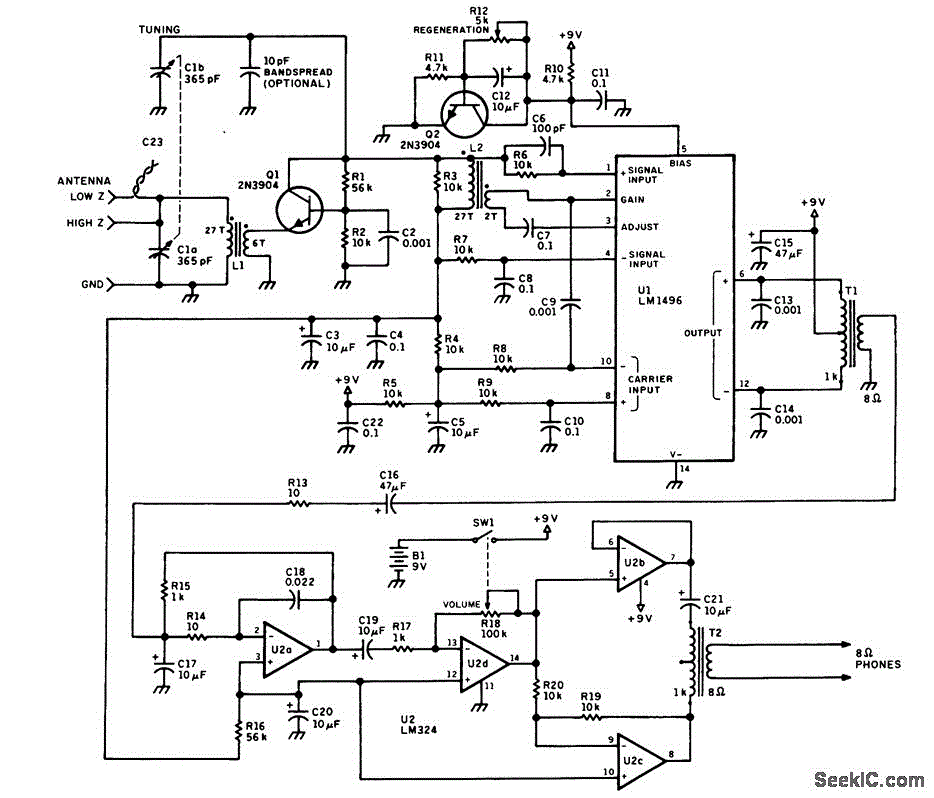
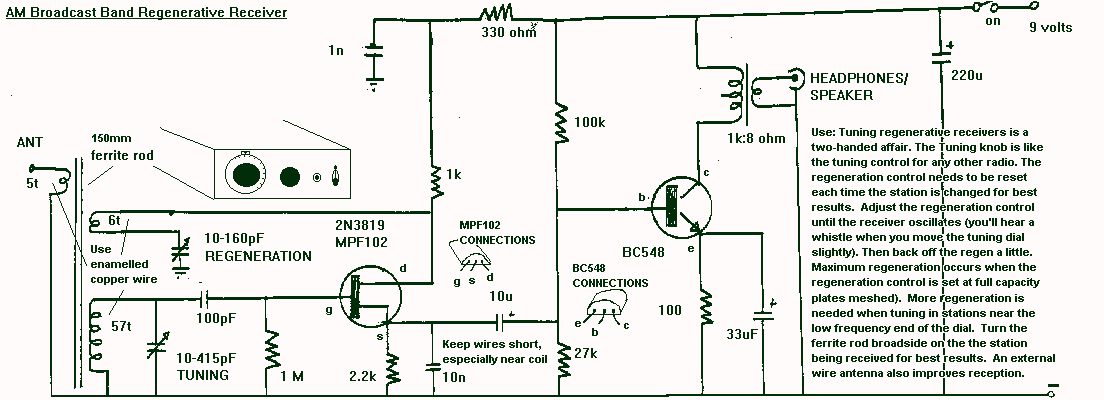
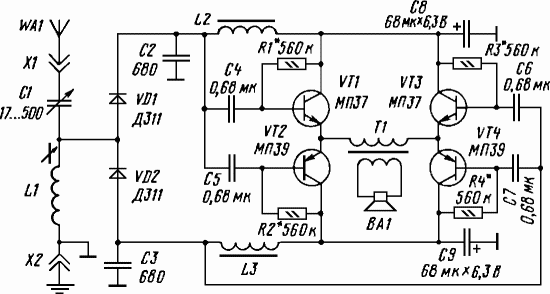
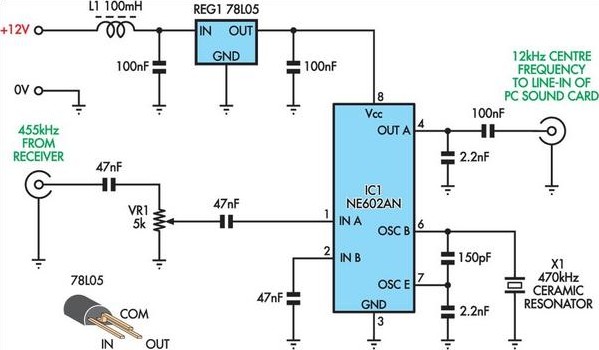
Regenerative AM Receivers

The regenerative circuit is essentially an oscillator circuit equipped with gain control, enabling the user to fine-tune the feedback to a level just below oscillation or, frequently, just above the critical threshold to produce a small oscillation. Typically, a regenerative circuit employs a tapped coil or additional windings that connect to the tuning tank, along with a tuning capacitor that provides the total tank capacitance. The component values are not critical, and the initial selections can be based on the first available components that are close to the desired values, encouraging experimentation. The circuit can utilize various small-signal NPN transistors, such as the 2N4401, 2N3904, or 2N2222. The audio output is relatively weak and requires an amplifier to drive headphones or a speaker. Suitable amplifiers can be referenced on the audio amplifier page.
The regenerative circuit operates by utilizing feedback to enhance signal strength, allowing for the amplification of weak radio signals. The oscillator's performance is contingent upon the precise configuration of the tapped coil and the tuning capacitor, which together form a resonant tank circuit. This tank circuit is critical for determining the oscillation frequency, which is typically set to match the frequency of the desired radio signal.
The gain control mechanism is achieved through the manipulation of feedback, which can be adjusted to achieve the desired level of oscillation. This adjustment is crucial, as it allows the user to stabilize the circuit and prevent it from entering a state of runaway oscillation. The feedback loop is formed by connecting a portion of the output signal back to the input through the tapped coil, which enhances the regenerative effect.
In terms of components, the choice of the small-signal NPN transistor is flexible, as many types can fulfill the requirements of the circuit. The transistor functions as the active element that amplifies the RF signal. The audio output stage, while capable of producing sound, typically requires additional amplification to drive higher loads such as headphones or speakers. This necessitates the integration of an audio amplifier stage, which can be selected based on power requirements and compatibility with the regenerative circuit's output.
Overall, the regenerative circuit is a versatile and experimental platform for audio and radio frequency applications, allowing users to explore the principles of oscillation and amplification with a range of readily available components.The regen is basically an oscillator circuit with a gain control that allows the user to adjust the feedback to a point just below oscillation or, quite often, just above the critical level such that a small oscillation is present. The typical regen uses a tapped coil or additional windings to connect into the tuning tank and the tuning capacitor
provides the total tank capacitance. The components are not critical and the values were pretty much the first ones found on the bench that were near the `right` value so don`t hesitate to experiment. The transistor could be just about any small-signal NPN including the 2N4401, 2N3904, 2N2222, or others.
The audio output is fairly weak and will need an amplifier to drive headphones or a speaker. See the audio amplifier page for suitable amps.
The regenerative circuit operates by utilizing feedback to enhance signal strength, allowing for the amplification of weak radio signals. The oscillator's performance is contingent upon the precise configuration of the tapped coil and the tuning capacitor, which together form a resonant tank circuit. This tank circuit is critical for determining the oscillation frequency, which is typically set to match the frequency of the desired radio signal.
The gain control mechanism is achieved through the manipulation of feedback, which can be adjusted to achieve the desired level of oscillation. This adjustment is crucial, as it allows the user to stabilize the circuit and prevent it from entering a state of runaway oscillation. The feedback loop is formed by connecting a portion of the output signal back to the input through the tapped coil, which enhances the regenerative effect.
In terms of components, the choice of the small-signal NPN transistor is flexible, as many types can fulfill the requirements of the circuit. The transistor functions as the active element that amplifies the RF signal. The audio output stage, while capable of producing sound, typically requires additional amplification to drive higher loads such as headphones or speakers. This necessitates the integration of an audio amplifier stage, which can be selected based on power requirements and compatibility with the regenerative circuit's output.
Overall, the regenerative circuit is a versatile and experimental platform for audio and radio frequency applications, allowing users to explore the principles of oscillation and amplification with a range of readily available components.The regen is basically an oscillator circuit with a gain control that allows the user to adjust the feedback to a point just below oscillation or, quite often, just above the critical level such that a small oscillation is present. The typical regen uses a tapped coil or additional windings to connect into the tuning tank and the tuning capacitor
provides the total tank capacitance. The components are not critical and the values were pretty much the first ones found on the bench that were near the `right` value so don`t hesitate to experiment. The transistor could be just about any small-signal NPN including the 2N4401, 2N3904, 2N2222, or others.
The audio output is fairly weak and will need an amplifier to drive headphones or a speaker. See the audio amplifier page for suitable amps.