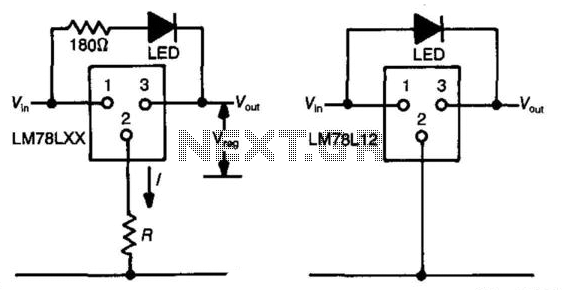
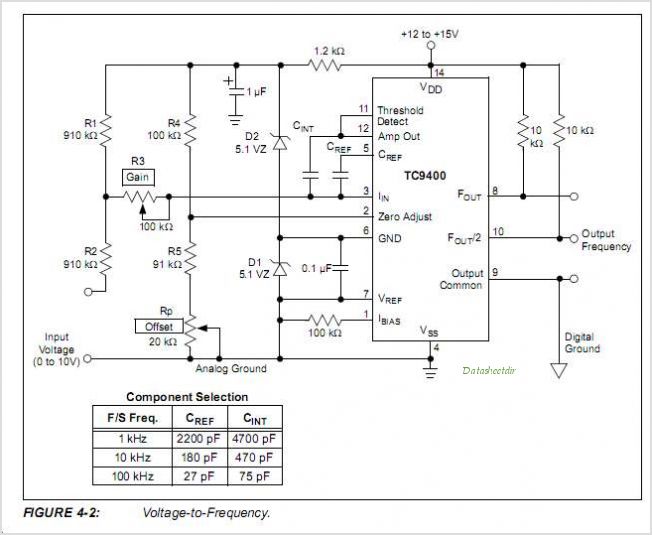
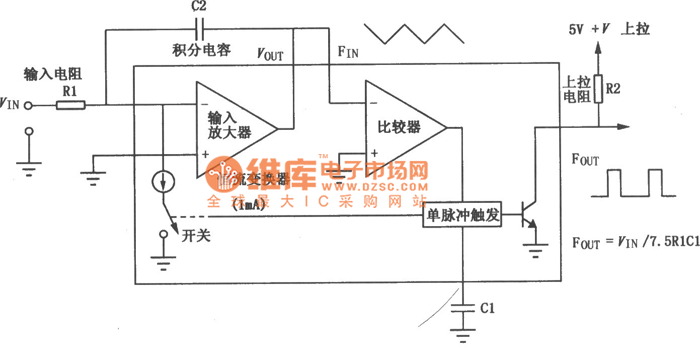
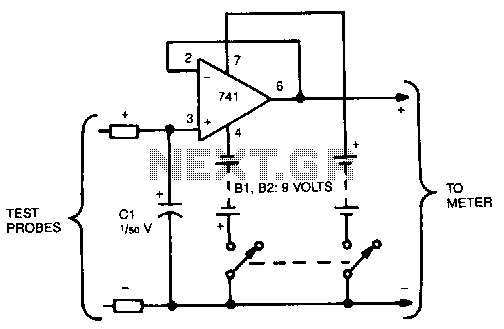
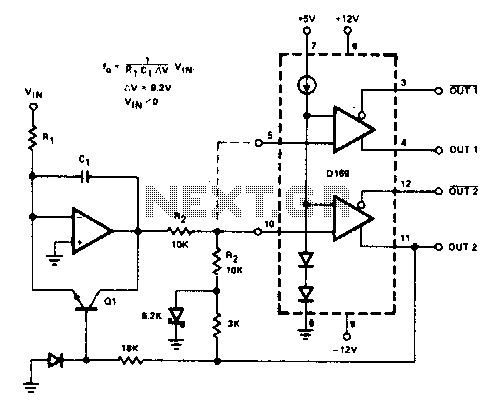
Regulated voltage divider

Integrated circuits (ICs) that require 3 or 6 volts can be powered from a battery or a fixed regulated supply with a higher voltage using the circuit illustrated. It is essential to mount the transistor on a heatsink, as significant power will be dissipated by its collector. Additional filtering can be achieved by incorporating a capacitor (C1) as shown. The capacitance is effectively multiplied by the gain of the transistor, allowing a ripple of 200 mV (peak to peak) at the input to be reduced to 2 mV in this manner. The maximum output current is contingent upon the supply rating and the type of transistor used, provided that it is equipped with a heatsink.
The circuit described utilizes a transistor as a linear voltage regulator to step down a higher voltage supply to the required 3 or 6 volts for powering integrated circuits. The configuration typically includes a voltage divider network or feedback mechanism to stabilize the output voltage. The transistor operates in the active region, where it regulates the output voltage while allowing for variations in load current.
The heatsink is a critical component in this design, as it dissipates the heat generated by the transistor during operation. The amount of power dissipated is a function of the voltage drop across the transistor and the current flowing through it. Therefore, selecting an appropriate heatsink based on the maximum expected power dissipation is essential to ensure reliable operation and prevent thermal failure.
The inclusion of capacitor C1 serves to smooth out voltage fluctuations at the output. The effectiveness of this filtering is enhanced by the transistor's gain, which effectively increases the capacitance seen at the output. This results in a significant reduction of ripple voltage, making the output more stable and suitable for sensitive IC applications.
The maximum output current capability of the circuit will depend on the specifications of both the power supply and the transistor selected. It is advisable to consult the datasheets for the chosen components to ensure they can handle the required load current while maintaining safe operating temperatures with the heatsink in place. Overall, this circuit design is a practical solution for powering low-voltage ICs from higher voltage sources while maintaining output stability and efficiency.ICs requiring 3 or 6 volts can be run from a battery or fixed regulated supply of a higher voltage by using the circuit shown. The transistor should be mounted on a heatsink as considerable power will be dissipated by its collector.
Additional filtering can be obtained by fitting a capacitor (Cl) as shown. The capacitance is effectively multiplied by the gain of the transistor, A ripple of 200 mV (peak to peak) at the input can be reduced to 2 mV in this fashion Maximum output current depends on the supply rating and transistor type (with heatsink) - used.
The circuit described utilizes a transistor as a linear voltage regulator to step down a higher voltage supply to the required 3 or 6 volts for powering integrated circuits. The configuration typically includes a voltage divider network or feedback mechanism to stabilize the output voltage. The transistor operates in the active region, where it regulates the output voltage while allowing for variations in load current.
The heatsink is a critical component in this design, as it dissipates the heat generated by the transistor during operation. The amount of power dissipated is a function of the voltage drop across the transistor and the current flowing through it. Therefore, selecting an appropriate heatsink based on the maximum expected power dissipation is essential to ensure reliable operation and prevent thermal failure.
The inclusion of capacitor C1 serves to smooth out voltage fluctuations at the output. The effectiveness of this filtering is enhanced by the transistor's gain, which effectively increases the capacitance seen at the output. This results in a significant reduction of ripple voltage, making the output more stable and suitable for sensitive IC applications.
The maximum output current capability of the circuit will depend on the specifications of both the power supply and the transistor selected. It is advisable to consult the datasheets for the chosen components to ensure they can handle the required load current while maintaining safe operating temperatures with the heatsink in place. Overall, this circuit design is a practical solution for powering low-voltage ICs from higher voltage sources while maintaining output stability and efficiency.ICs requiring 3 or 6 volts can be run from a battery or fixed regulated supply of a higher voltage by using the circuit shown. The transistor should be mounted on a heatsink as considerable power will be dissipated by its collector.
Additional filtering can be obtained by fitting a capacitor (Cl) as shown. The capacitance is effectively multiplied by the gain of the transistor, A ripple of 200 mV (peak to peak) at the input can be reduced to 2 mV in this fashion Maximum output current depends on the supply rating and transistor type (with heatsink) - used.