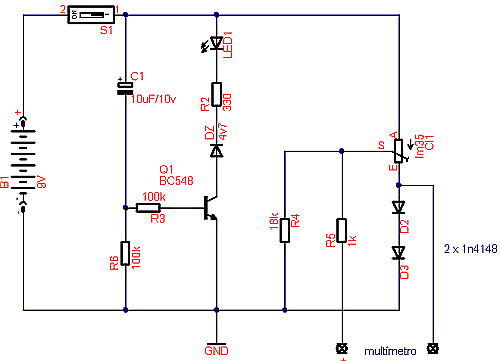
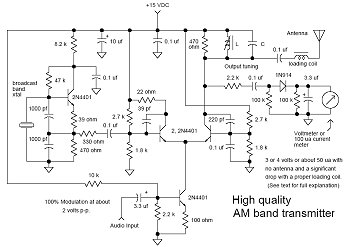
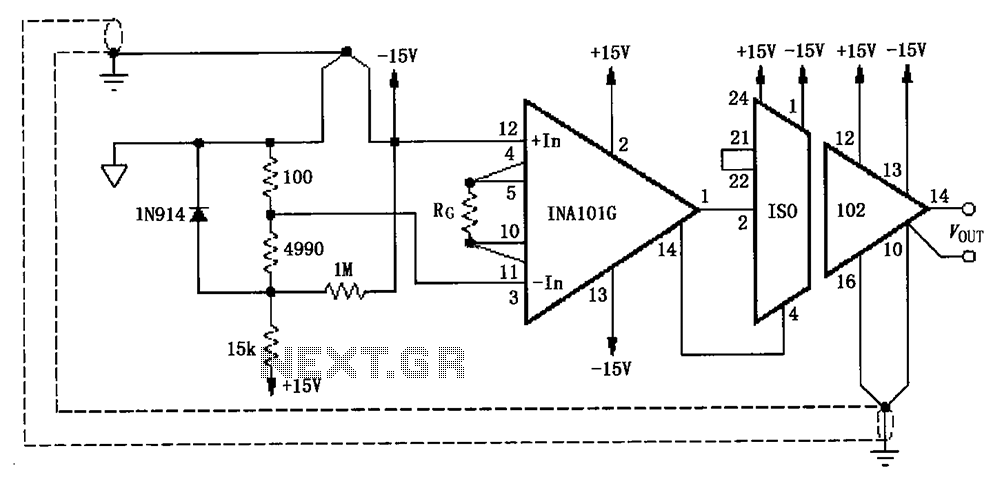
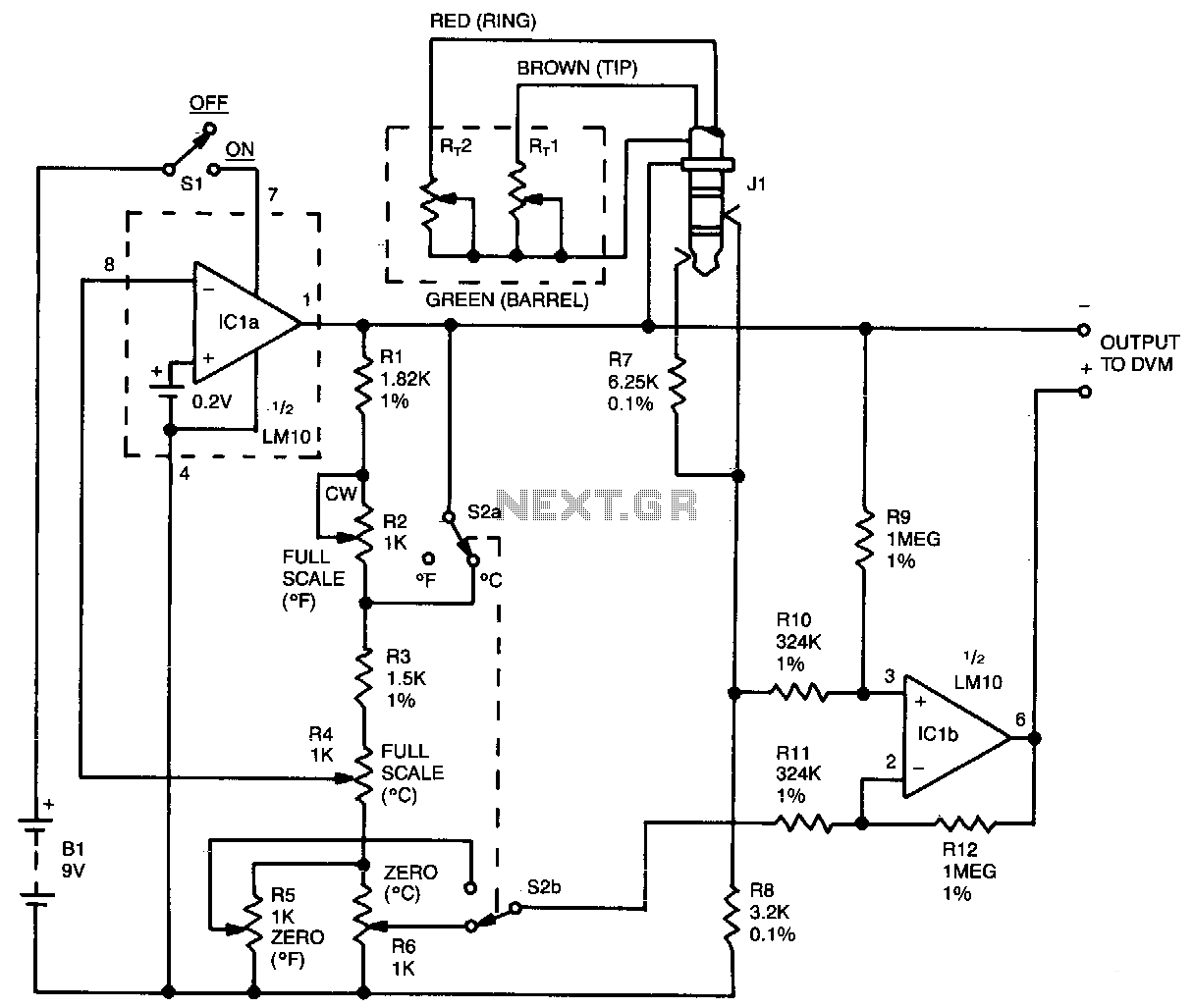
Resistance Thermometer Current Loop Transmitter
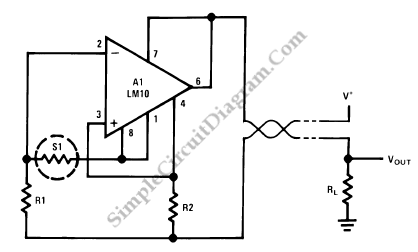
A resistance temperature sensor (RTD, resistive temperature device) is available in two types: NTC (negative temperature coefficient) and PTC (positive temperature coefficient).
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are essential components in temperature measurement systems. They operate on the principle that the electrical resistance of certain materials changes with temperature. In the case of NTC sensors, the resistance decreases as the temperature increases, making them suitable for applications requiring precise temperature monitoring in a decreasing resistance scenario. Conversely, PTC sensors exhibit an increase in resistance with rising temperature, which can be advantageous for over-temperature protection and applications where a positive response to temperature changes is necessary.
RTDs are typically constructed from pure metal, such as platinum, which provides a stable and repeatable resistance-temperature relationship. The sensor's resistance is characterized by a linear response over a specific temperature range, often from -200°C to +850°C for platinum RTDs. This linearity allows for straightforward calibration and integration into various electronic systems.
The implementation of RTDs in circuit design often requires careful consideration of the measurement circuit configuration. A common approach is to use a Wheatstone bridge circuit to enhance measurement accuracy and minimize the effects of lead resistance. This configuration allows for precise detection of the small changes in resistance that occur with temperature variations. Additionally, signal conditioning circuits, such as operational amplifiers, may be employed to amplify the output signal from the RTD for further processing.
In summary, the choice between NTC and PTC sensors depends on the specific application requirements, including the desired response to temperature changes, the range of temperature to be measured, and the necessary accuracy. Proper integration and circuit design are crucial to fully leverage the capabilities of RTDs in temperature sensing applications.Resistance temperature sensor (RTD, resistive temperature device) comes in NTC (negative temperature coefficient) and PTC (positive temperature coefficient).. 🔗 External reference
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are essential components in temperature measurement systems. They operate on the principle that the electrical resistance of certain materials changes with temperature. In the case of NTC sensors, the resistance decreases as the temperature increases, making them suitable for applications requiring precise temperature monitoring in a decreasing resistance scenario. Conversely, PTC sensors exhibit an increase in resistance with rising temperature, which can be advantageous for over-temperature protection and applications where a positive response to temperature changes is necessary.
RTDs are typically constructed from pure metal, such as platinum, which provides a stable and repeatable resistance-temperature relationship. The sensor's resistance is characterized by a linear response over a specific temperature range, often from -200°C to +850°C for platinum RTDs. This linearity allows for straightforward calibration and integration into various electronic systems.
The implementation of RTDs in circuit design often requires careful consideration of the measurement circuit configuration. A common approach is to use a Wheatstone bridge circuit to enhance measurement accuracy and minimize the effects of lead resistance. This configuration allows for precise detection of the small changes in resistance that occur with temperature variations. Additionally, signal conditioning circuits, such as operational amplifiers, may be employed to amplify the output signal from the RTD for further processing.
In summary, the choice between NTC and PTC sensors depends on the specific application requirements, including the desired response to temperature changes, the range of temperature to be measured, and the necessary accuracy. Proper integration and circuit design are crucial to fully leverage the capabilities of RTDs in temperature sensing applications.Resistance temperature sensor (RTD, resistive temperature device) comes in NTC (negative temperature coefficient) and PTC (positive temperature coefficient).. 🔗 External reference