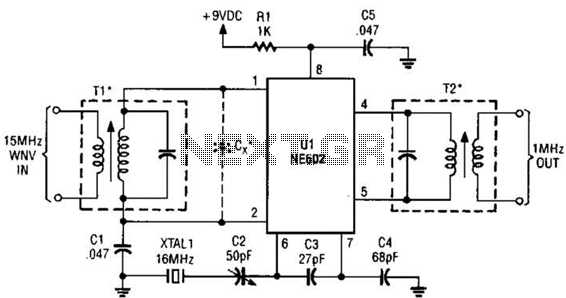
RF detector electronic project circuit design using 2N2222 transistors
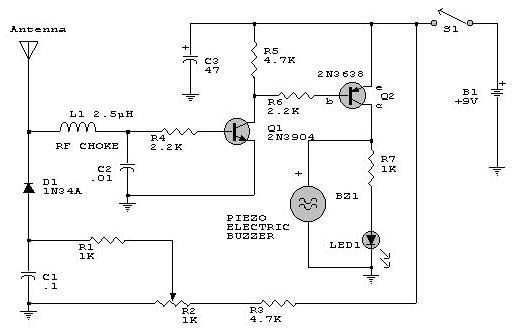
This electronic RF detector project is constructed using common transistors and a few standard electronic components. The RF detector is capable of responding to RF signals below the standard broadcast band and extending to over 500 MHz, providing both visual and audible indications upon signal reception. By adjusting the bias of diode D2 with the R2 potentiometer, the circuit can detect both low power and strong signals. The circuit can be powered by a simple 9-volt battery or any other 9-volt DC power supply. If the RF detector is insufficiently sensitive, a wideband RF amplifier can be connected between the antenna and the detector diode. To minimize stray inductance, it is important to keep the leads of the diode and capacitor (C1) short. The transistors utilized can include 2N3906, 2N2907, or other PNP high-gain transistors for Q2, and PN2222A, 2N3904, or other NPN high-gain transistors for Q1.
This RF detector circuit is a versatile tool for various applications, including amateur radio, signal analysis, and educational projects. The design incorporates a straightforward configuration that allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting. The use of common transistors such as the 2N3906 and PN2222A ensures that the circuit can be built with readily available components.
The circuit operates by first capturing RF signals through an antenna, which feeds into the detector diode. The diode rectifies the RF signal, converting it into a DC voltage that can be processed by the following stages. The biasing of diode D2, adjusted using potentiometer R2, is critical for optimizing the sensitivity of the detector. This adjustment allows the circuit to effectively respond to a wide range of signal strengths, ensuring reliable operation under varying conditions.
For enhanced performance, particularly in low-signal environments, the addition of a wideband RF amplifier between the antenna and the detector diode is recommended. This amplifier boosts the incoming RF signals, improving the overall sensitivity of the detector. Careful layout considerations, such as keeping the leads of the diode and capacitor (C1) short, help reduce stray inductance, which can adversely affect performance.
The visual indication of signal reception can be implemented using an LED, while an audible indication can be achieved with a small speaker or piezo buzzer. This dual-indication system allows the user to easily identify the presence of RF signals, making the circuit practical for field use.
In summary, this RF detector circuit is a compact and effective solution for detecting a wide range of RF signals, with straightforward adjustments for sensitivity and easy integration of additional components for enhanced performance.This electronic rf detector electronic project is designed using common transistors and other few common electronic parts. This rf detector responds to RF signals bellow the standard broadcast band to well over 500 MHz and provides an visual, and audible indication when the signal is received.
By adjusting the bias of D2 with the R2 potentiomete r the circuit can detect low power or strong signals. The circuit can be powered using a simple 9 volts battery or any other 9 volts DC power supply circuit. If the rf detector is not enough sensitive you can connect a good wideband RF amp between the antenna and the detector diode.
Keep diode and capacitor (C1) leads short to minimize stray inductance. The used transistors can be : 2N3906, 2N2907 or other PNP high gain transistor for Q2 and PN2222A, 2N3904 or other NPN high gain transistor for Q1. 🔗 External reference
This RF detector circuit is a versatile tool for various applications, including amateur radio, signal analysis, and educational projects. The design incorporates a straightforward configuration that allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting. The use of common transistors such as the 2N3906 and PN2222A ensures that the circuit can be built with readily available components.
The circuit operates by first capturing RF signals through an antenna, which feeds into the detector diode. The diode rectifies the RF signal, converting it into a DC voltage that can be processed by the following stages. The biasing of diode D2, adjusted using potentiometer R2, is critical for optimizing the sensitivity of the detector. This adjustment allows the circuit to effectively respond to a wide range of signal strengths, ensuring reliable operation under varying conditions.
For enhanced performance, particularly in low-signal environments, the addition of a wideband RF amplifier between the antenna and the detector diode is recommended. This amplifier boosts the incoming RF signals, improving the overall sensitivity of the detector. Careful layout considerations, such as keeping the leads of the diode and capacitor (C1) short, help reduce stray inductance, which can adversely affect performance.
The visual indication of signal reception can be implemented using an LED, while an audible indication can be achieved with a small speaker or piezo buzzer. This dual-indication system allows the user to easily identify the presence of RF signals, making the circuit practical for field use.
In summary, this RF detector circuit is a compact and effective solution for detecting a wide range of RF signals, with straightforward adjustments for sensitivity and easy integration of additional components for enhanced performance.This electronic rf detector electronic project is designed using common transistors and other few common electronic parts. This rf detector responds to RF signals bellow the standard broadcast band to well over 500 MHz and provides an visual, and audible indication when the signal is received.
By adjusting the bias of D2 with the R2 potentiomete r the circuit can detect low power or strong signals. The circuit can be powered using a simple 9 volts battery or any other 9 volts DC power supply circuit. If the rf detector is not enough sensitive you can connect a good wideband RF amp between the antenna and the detector diode.
Keep diode and capacitor (C1) leads short to minimize stray inductance. The used transistors can be : 2N3906, 2N2907 or other PNP high gain transistor for Q2 and PN2222A, 2N3904 or other NPN high gain transistor for Q1. 🔗 External reference