Rms-to-dc converter
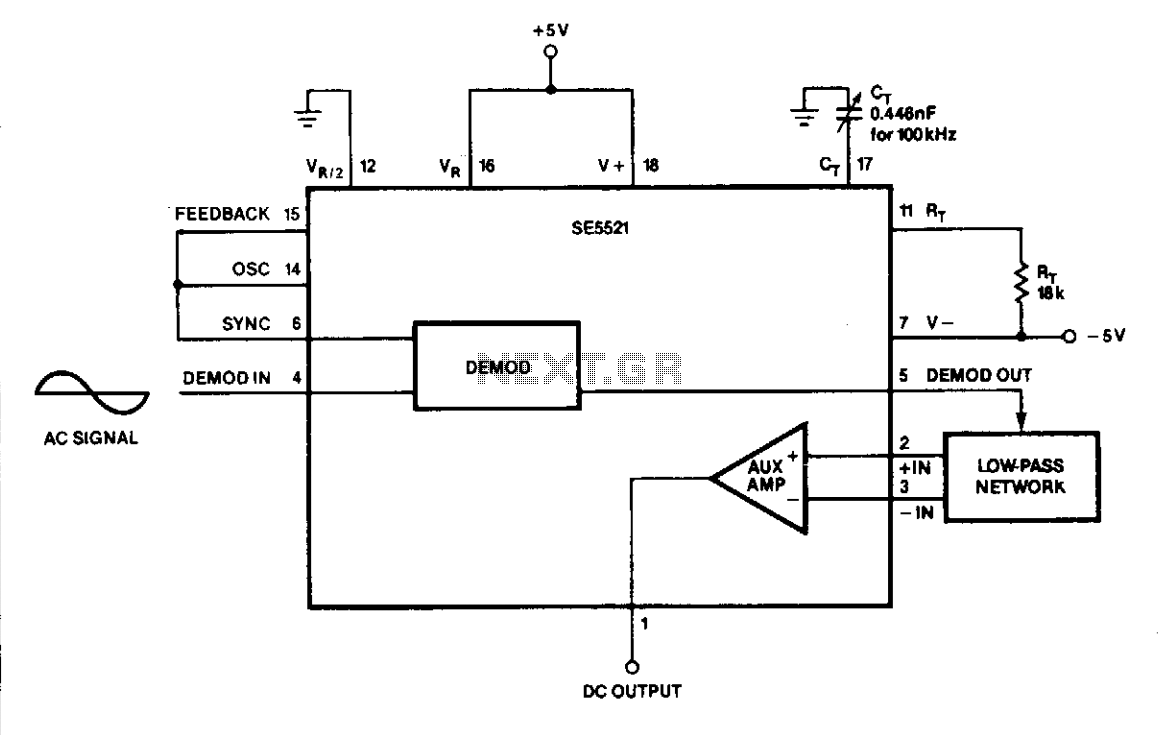
The DC output at Pin 1 varies linearly with the RMS input at Pin 4. The variable capacitor (CT) is adjusted until the sync signal is in phase with the AC signal. An AC voltmeter can be easily constructed due to the circuit's simplicity and low component count, making it particularly attractive. The demodulator output provides a full-wave rectified signal from the AC input at Pin 4. The DC component on the rectified signal at Pin 5 varies linearly with the RMS input at Pin 4, thus offering an accurate RMS-to-DC conversion at the output of the filter at Pin 1. The variable capacitor (CT) is fine-tuned until the oscillator signal to the sync input of the demodulator is synchronized with the AC signal at Pin 4.
The described circuit functions as a straightforward RMS-to-DC converter, utilizing a demodulator to process the AC input signal. At Pin 4, the AC input is fed into the demodulator, which is designed to rectify this signal. The rectification process is full-wave, meaning that both halves of the AC waveform are utilized, resulting in a more efficient conversion to DC.
Pin 5 serves as the output of the demodulator, where the rectified signal can be observed. This signal contains a DC component that is directly proportional to the RMS value of the AC input at Pin 4. The linear relationship between the DC output at Pin 1 and the RMS input at Pin 4 ensures that the circuit can provide accurate voltage readings, making it suitable for applications requiring precise measurements.
The circuit's simplicity is underscored by its low component count, which not only reduces costs but also enhances reliability. The variable capacitor (CT) plays a crucial role in ensuring that the demodulator operates correctly. By adjusting CT, the sync signal is aligned with the AC input, optimizing the performance of the demodulator. This adjustment is critical for achieving accurate phase alignment, which ensures that the rectification process occurs effectively.
The output at Pin 1 can be connected to an AC voltmeter or other measuring devices to display the converted DC value. The design's straightforward nature allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it an attractive option for engineers and hobbyists alike. Overall, the circuit provides a reliable method for converting AC signals to a DC representation, suitable for various electronic measurement applications.The DC output at Pin 1 vanes linearly with the RMS input at Pin 4. 2 CT is tweaked until the svnc signal is in phase with the AC signal. An ac voltmeter may be easily constructed. Simplicity of the circuit and low component count make it particularly attractive. The demodulator output is a full-wave rectified signal from the ac input at Pin 4. The dc component on the rectified signal at Pin 5 varies linearity with the rms input at Pin 4 and thus provides an accurate rms-to-dc conversion at the output of the filter (Pin 1). CT is a variable capacitor that is tweaked until the oscillator signal to the sync input of the demodulator is in phase with the ac signal at Pin 4.
The described circuit functions as a straightforward RMS-to-DC converter, utilizing a demodulator to process the AC input signal. At Pin 4, the AC input is fed into the demodulator, which is designed to rectify this signal. The rectification process is full-wave, meaning that both halves of the AC waveform are utilized, resulting in a more efficient conversion to DC.
Pin 5 serves as the output of the demodulator, where the rectified signal can be observed. This signal contains a DC component that is directly proportional to the RMS value of the AC input at Pin 4. The linear relationship between the DC output at Pin 1 and the RMS input at Pin 4 ensures that the circuit can provide accurate voltage readings, making it suitable for applications requiring precise measurements.
The circuit's simplicity is underscored by its low component count, which not only reduces costs but also enhances reliability. The variable capacitor (CT) plays a crucial role in ensuring that the demodulator operates correctly. By adjusting CT, the sync signal is aligned with the AC input, optimizing the performance of the demodulator. This adjustment is critical for achieving accurate phase alignment, which ensures that the rectification process occurs effectively.
The output at Pin 1 can be connected to an AC voltmeter or other measuring devices to display the converted DC value. The design's straightforward nature allows for easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it an attractive option for engineers and hobbyists alike. Overall, the circuit provides a reliable method for converting AC signals to a DC representation, suitable for various electronic measurement applications.The DC output at Pin 1 vanes linearly with the RMS input at Pin 4. 2 CT is tweaked until the svnc signal is in phase with the AC signal. An ac voltmeter may be easily constructed. Simplicity of the circuit and low component count make it particularly attractive. The demodulator output is a full-wave rectified signal from the ac input at Pin 4. The dc component on the rectified signal at Pin 5 varies linearity with the rms input at Pin 4 and thus provides an accurate rms-to-dc conversion at the output of the filter (Pin 1). CT is a variable capacitor that is tweaked until the oscillator signal to the sync input of the demodulator is in phase with the ac signal at Pin 4.