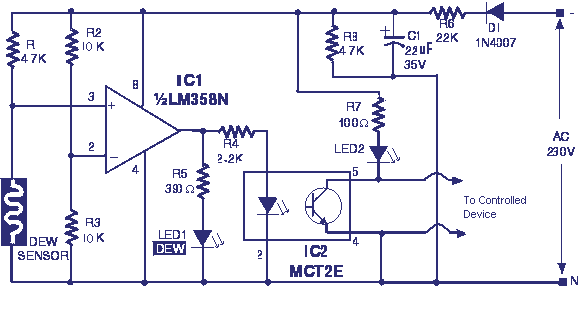
Safety / Protection Circuits

To prevent deep discharge that can damage or shorten the life of a rechargeable battery, it is essential to disconnect its load before the battery is completely discharged. The circuit protects against AC line disturbances by switching off the power supply upon detecting under-voltage or over-voltage conditions. Additionally, the circuit safeguards the battery from over-discharge, which can irreversibly reduce the battery's capacity and the number of charge/discharge cycles. This particular circuit is designed to protect a single NiMH (nickel-metal-hydride) cell by disconnecting the load when the battery is sufficiently discharged. Furthermore, a circuit is available that protects a bus from 5V swings, automatically detecting voltage to safeguard a 3.3V-limited PCI bus from 5V signal-level fluctuations. This circuit can also assess bus voltage swings within a single bus cycle, facilitating the appropriate setting of termination voltages for protection diodes or termination resistors. There is also a two-chip circuit that monitors system temperature to provide fan control and over-temperature warnings, thus preventing overheating of components such as CPUs or FPGAs. A current-limiting circuit can signal latch-up conditions and prevent destructive over-current situations in CMOS ICs. For lithium-ion batteries, a dual comparator can monitor temperature thresholds to ensure safe charging conditions. An electronic fuse circuit combines a current transducer with a solid-state relay to disconnect power at preset levels, eliminating the need for traditional fusible links. Moreover, many systems require automatic power disconnection for fault protection, applicable in high-voltage power supplies. High-side drivers, commonly used for grounded solenoid coils, require short-circuit protection to avoid damage from faults. A hot-swap controller can function as an adjustable circuit breaker, particularly in medium- and high-voltage systems. Lastly, the LCX standard logic product family features over-voltage tolerant inputs and outputs, allowing seamless interfacing between LVTTL and 5V TTL buses.
The described circuits serve critical roles in protecting electronic systems and components from various risks such as over-discharge, overheating, and voltage fluctuations. Each circuit is designed with specific functionalities tailored to address distinct challenges faced in electronic applications.
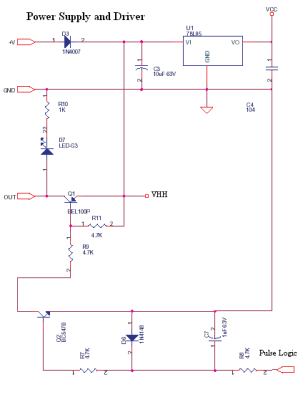
1. **Battery Protection Circuit**: This circuit employs a voltage detection mechanism to monitor the state of charge of a NiMH battery. When the voltage drops below a predetermined threshold, the circuit disconnects the load, preventing further discharge that could damage the battery. The design may include a comparator to sense the battery voltage and a relay or MOSFET switch to control the load connection.
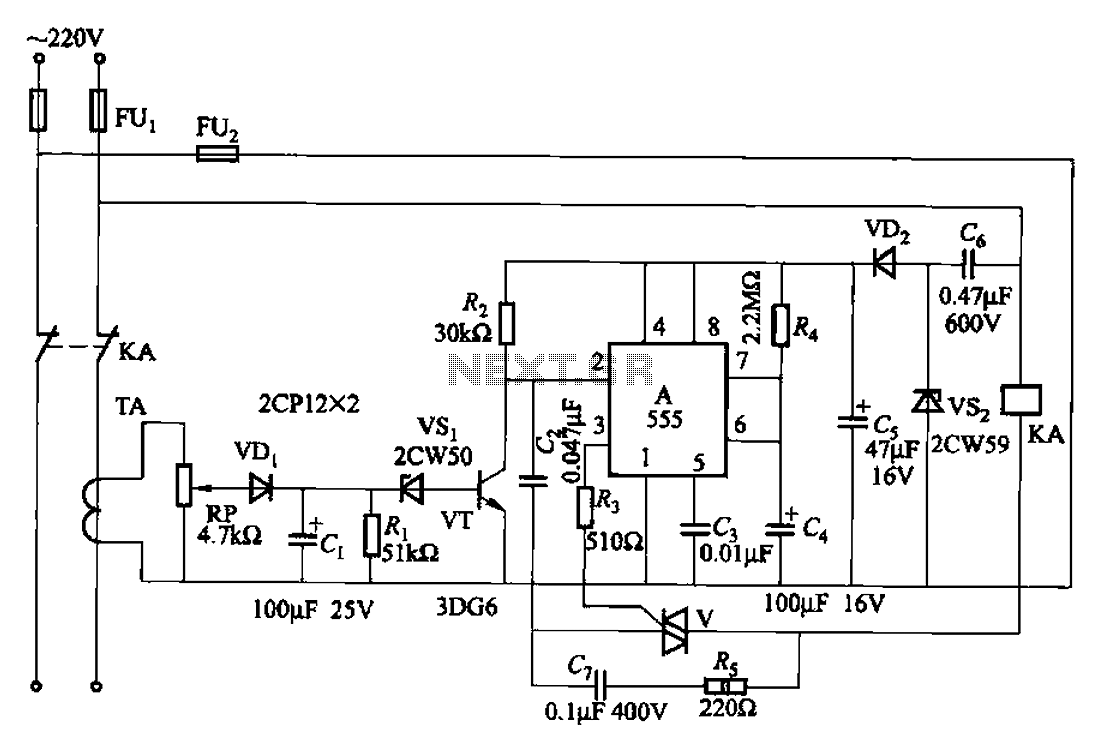
2. **AC Line Disturbance Protection**: This circuit features a voltage monitoring system that can detect both under-voltage and over-voltage conditions. It typically includes a voltage reference and a relay that disconnects the power supply when voltage levels fall outside acceptable limits, thereby protecting sensitive components from damage.
3. **Bus Voltage Protection**: Designed to protect low-voltage buses from higher voltage swings, this circuit can include a series of diodes or voltage clamping devices that shunt excess voltage away from the bus, ensuring that the components connected to the bus operate within safe voltage levels.
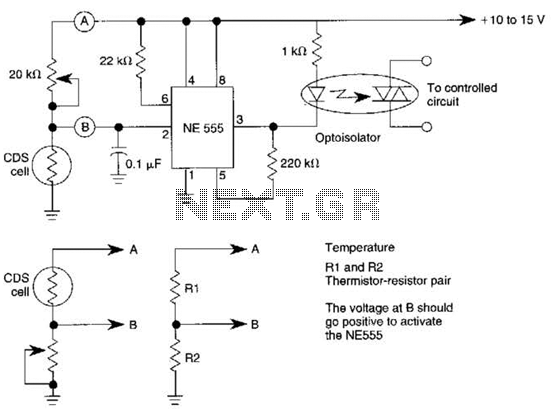
4. **Thermal Protection Circuit**: Utilizing temperature sensors, this circuit monitors the operating temperature of critical components. It activates a fan or triggers a shutdown signal when temperatures exceed safe limits, thereby preventing damage due to overheating.
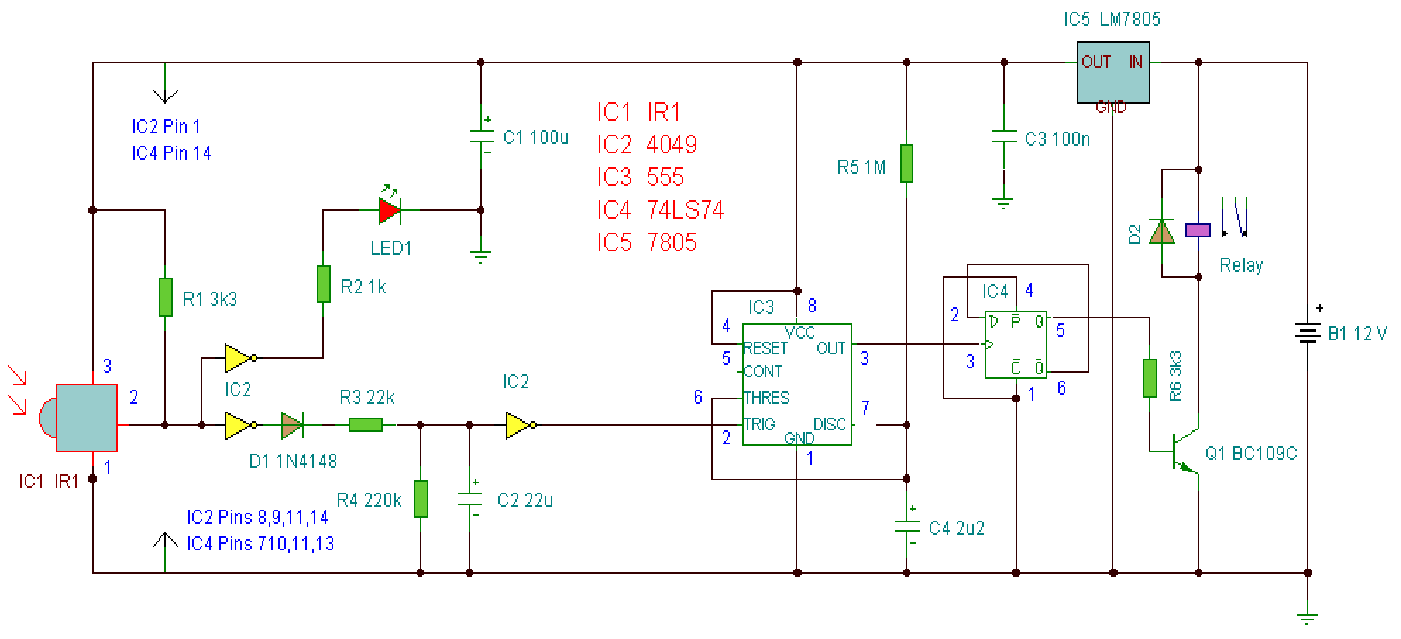
5. **Current Limiting Circuit**: This circuit employs a current sensing resistor and a comparator to detect excessive current levels. Upon detection, it can signal an external latch-up condition to prevent over-current damage to CMOS ICs, ensuring operational integrity.
6. **Lithium-Ion Battery Charger Protection**: By integrating a thermistor and a dual comparator, this circuit monitors the temperature of the lithium-ion battery during charging. It ensures that charging does not occur below 0 °C or above 50 °C, thus maintaining battery health and safety.
7. **Electronic Fuse**: This innovative circuit design combines a current transducer and a solid-state relay to act as a fuse that can be reset. It disconnects the load when current exceeds a preset limit, providing a reliable and reusable alternative to traditional fuses.
8. **High-Side Driver Protection**: This circuit incorporates short-circuit protection mechanisms to safeguard high-side drivers used for solenoid activation. It may utilize current sensing and feedback control to ensure safe operation under fault conditions.
9. **Hot-Swap Controller**: This circuit allows for the safe insertion and removal of components in live circuits. It includes features such as inrush current limiting and fault detection to prevent damage during hot-swapping operations.
10. **Voltage Level Shifter**: The LCX family of logic products provides a means to interface between different voltage levels, ensuring compatibility between LVTTL and 5V TTL systems. The design ensures over-voltage tolerance, protecting the logic devices from damage.
These circuits collectively enhance the reliability and safety of electronic devices across various applications, ensuring longevity and performance even in demanding environments.To avoid the deep discharge that can destroy or shorten the life of a rechargeable battery, you must disconnect its load before the discharge is complete Circuit Protects Against AC Line Disturbances : 07/29/98 EDN-Design Ideas / operates by switching off the power supply u pon detection of under voltage or over voltage conditions Circuit Protects Battery From Over discharge : 04/12/01 EDN-Design Ideas / PDF contains multiple circuits - scroll to find the one of interest / In some applications, it is undesirable to Over discharge the battery, because it could irreversibly reduce the battery`s capacity and the number of discharge/charge cycles. This circuit protects a single NiMH (nickel-metal-hydride) cell by disconnecting the load from the battery when it gets discharged enough.
Circuit protects bus from 5V swings : 11/14/2002 EDN - Design Ideas / The circuit in Figure 1 automatically detects voltage and protects a bus, such as a 3. 3V-limited PCI bus, from 5V signal-level swings. You can also use the circuit to determine bus-voltage swings within one bus-cycle for setting appropriate termination voltages of protection diodes or termination resistors.
Circuit protects system from overheating : 11/08/2001 EDN - Design Ideas / The two-chip circuit in Figure 1 provides fan control and over temperature warning and shutdown signals to protect systems from excessive heat. The circuit monitors the temperature of the pc board and the die temperature of a CPU, an FPGA, or another IC with an on-chip temperature-sensing transistor.
Current Limiter Provides Latch up Signal : 01/01/98 EDN-Design Ideas / Current-limiting circuit both signals a latch-up condition and prevents latch-up-induced over current destruction of a CMOS IC or group of ICs. Dual comparator thermally protects lithium ion battery : 09/18/03 EDN-Design Ideas / Most manufacturers recommend that you don`t change lithium-ion batteries at temperatures lower than 0 °C or higher than 50 °C.
You can monitor both thresholds by adding a thermistor and dual (window) comparator to a lithium-ion battery charger (Figure 1). Electronic Fuse Emulates Fast or Slow Blow Fuses : 11/09/00 EDN-Design Ideas / PDF contains multiple circuits - scroll to find the one of interest / The electronic-fuse circuit in this article combines the properties of a current transducer and a solid-state relay to disconnect low power at preset levels.
Using this circuit lets you avoid the bother of stocking and replacing fusible links. Handy Circuit Gives Systems Flexible Fault Protection : 08/04/03 Electronic Design - Design Briefs / Many applications must include a capability to automatically disconnect power from an operating circuit. Such applications include thermal shutdown of high-voltage power supplies in radar and X-ray systems, shutdown to limit inrush current during.
High side driver has fault protection : 09/05/2002 EDN - Design Ideas / High-side drivers find common use in driving grounded solenoid coils and other loads. Short-circuit protection for such drivers is essential for avoiding damage from wiring faults and other causes.
Polymer fuses are generally too slow, and discrete current-limiting circuits are large and cumbersome. Hot-Swap Controller Makes Adjustable Circuit Breaker : 11/10/03 Electronic Design - Design Briefs / Medium- and high-voltage systems that range from 9 to 72 V often require one or more of the following circuit capabilities: hot-swap control, circuit-breaker fault protection, and inrush current limiting.
Over voltage-tolerant quad buffer used as voltage level shifter : 02/23/98 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / The LCX standard logic product family was designed with over voltage-tolerant inputs and outputs, enabling users to easily interface LVTTL and 5-V TTL buses. Because the LCX outputs are over voltage-tolerant when disabled, s 🔗 External reference
The described circuits serve critical roles in protecting electronic systems and components from various risks such as over-discharge, overheating, and voltage fluctuations. Each circuit is designed with specific functionalities tailored to address distinct challenges faced in electronic applications.
1. **Battery Protection Circuit**: This circuit employs a voltage detection mechanism to monitor the state of charge of a NiMH battery. When the voltage drops below a predetermined threshold, the circuit disconnects the load, preventing further discharge that could damage the battery. The design may include a comparator to sense the battery voltage and a relay or MOSFET switch to control the load connection.
2. **AC Line Disturbance Protection**: This circuit features a voltage monitoring system that can detect both under-voltage and over-voltage conditions. It typically includes a voltage reference and a relay that disconnects the power supply when voltage levels fall outside acceptable limits, thereby protecting sensitive components from damage.
3. **Bus Voltage Protection**: Designed to protect low-voltage buses from higher voltage swings, this circuit can include a series of diodes or voltage clamping devices that shunt excess voltage away from the bus, ensuring that the components connected to the bus operate within safe voltage levels.
4. **Thermal Protection Circuit**: Utilizing temperature sensors, this circuit monitors the operating temperature of critical components. It activates a fan or triggers a shutdown signal when temperatures exceed safe limits, thereby preventing damage due to overheating.
5. **Current Limiting Circuit**: This circuit employs a current sensing resistor and a comparator to detect excessive current levels. Upon detection, it can signal an external latch-up condition to prevent over-current damage to CMOS ICs, ensuring operational integrity.
6. **Lithium-Ion Battery Charger Protection**: By integrating a thermistor and a dual comparator, this circuit monitors the temperature of the lithium-ion battery during charging. It ensures that charging does not occur below 0 °C or above 50 °C, thus maintaining battery health and safety.
7. **Electronic Fuse**: This innovative circuit design combines a current transducer and a solid-state relay to act as a fuse that can be reset. It disconnects the load when current exceeds a preset limit, providing a reliable and reusable alternative to traditional fuses.
8. **High-Side Driver Protection**: This circuit incorporates short-circuit protection mechanisms to safeguard high-side drivers used for solenoid activation. It may utilize current sensing and feedback control to ensure safe operation under fault conditions.
9. **Hot-Swap Controller**: This circuit allows for the safe insertion and removal of components in live circuits. It includes features such as inrush current limiting and fault detection to prevent damage during hot-swapping operations.
10. **Voltage Level Shifter**: The LCX family of logic products provides a means to interface between different voltage levels, ensuring compatibility between LVTTL and 5V TTL systems. The design ensures over-voltage tolerance, protecting the logic devices from damage.
These circuits collectively enhance the reliability and safety of electronic devices across various applications, ensuring longevity and performance even in demanding environments.To avoid the deep discharge that can destroy or shorten the life of a rechargeable battery, you must disconnect its load before the discharge is complete Circuit Protects Against AC Line Disturbances : 07/29/98 EDN-Design Ideas / operates by switching off the power supply u pon detection of under voltage or over voltage conditions Circuit Protects Battery From Over discharge : 04/12/01 EDN-Design Ideas / PDF contains multiple circuits - scroll to find the one of interest / In some applications, it is undesirable to Over discharge the battery, because it could irreversibly reduce the battery`s capacity and the number of discharge/charge cycles. This circuit protects a single NiMH (nickel-metal-hydride) cell by disconnecting the load from the battery when it gets discharged enough.
Circuit protects bus from 5V swings : 11/14/2002 EDN - Design Ideas / The circuit in Figure 1 automatically detects voltage and protects a bus, such as a 3. 3V-limited PCI bus, from 5V signal-level swings. You can also use the circuit to determine bus-voltage swings within one bus-cycle for setting appropriate termination voltages of protection diodes or termination resistors.
Circuit protects system from overheating : 11/08/2001 EDN - Design Ideas / The two-chip circuit in Figure 1 provides fan control and over temperature warning and shutdown signals to protect systems from excessive heat. The circuit monitors the temperature of the pc board and the die temperature of a CPU, an FPGA, or another IC with an on-chip temperature-sensing transistor.
Current Limiter Provides Latch up Signal : 01/01/98 EDN-Design Ideas / Current-limiting circuit both signals a latch-up condition and prevents latch-up-induced over current destruction of a CMOS IC or group of ICs. Dual comparator thermally protects lithium ion battery : 09/18/03 EDN-Design Ideas / Most manufacturers recommend that you don`t change lithium-ion batteries at temperatures lower than 0 °C or higher than 50 °C.
You can monitor both thresholds by adding a thermistor and dual (window) comparator to a lithium-ion battery charger (Figure 1). Electronic Fuse Emulates Fast or Slow Blow Fuses : 11/09/00 EDN-Design Ideas / PDF contains multiple circuits - scroll to find the one of interest / The electronic-fuse circuit in this article combines the properties of a current transducer and a solid-state relay to disconnect low power at preset levels.
Using this circuit lets you avoid the bother of stocking and replacing fusible links. Handy Circuit Gives Systems Flexible Fault Protection : 08/04/03 Electronic Design - Design Briefs / Many applications must include a capability to automatically disconnect power from an operating circuit. Such applications include thermal shutdown of high-voltage power supplies in radar and X-ray systems, shutdown to limit inrush current during.
High side driver has fault protection : 09/05/2002 EDN - Design Ideas / High-side drivers find common use in driving grounded solenoid coils and other loads. Short-circuit protection for such drivers is essential for avoiding damage from wiring faults and other causes.
Polymer fuses are generally too slow, and discrete current-limiting circuits are large and cumbersome. Hot-Swap Controller Makes Adjustable Circuit Breaker : 11/10/03 Electronic Design - Design Briefs / Medium- and high-voltage systems that range from 9 to 72 V often require one or more of the following circuit capabilities: hot-swap control, circuit-breaker fault protection, and inrush current limiting.
Over voltage-tolerant quad buffer used as voltage level shifter : 02/23/98 Electronic Design - Ideas for Design / The LCX standard logic product family was designed with over voltage-tolerant inputs and outputs, enabling users to easily interface LVTTL and 5-V TTL buses. Because the LCX outputs are over voltage-tolerant when disabled, s 🔗 External reference