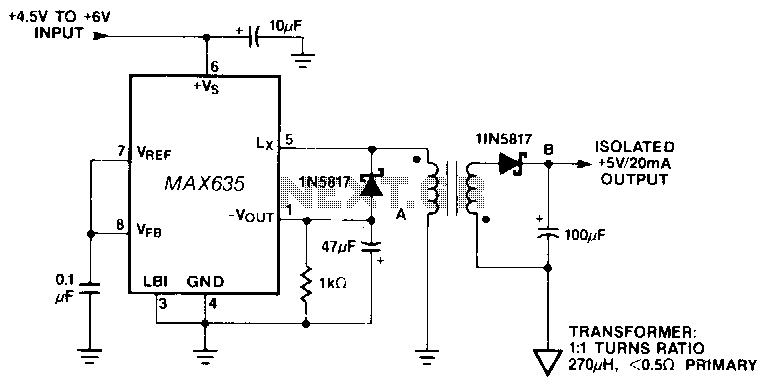
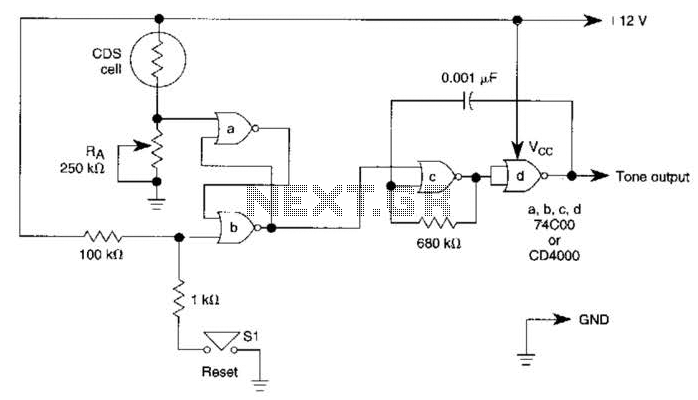
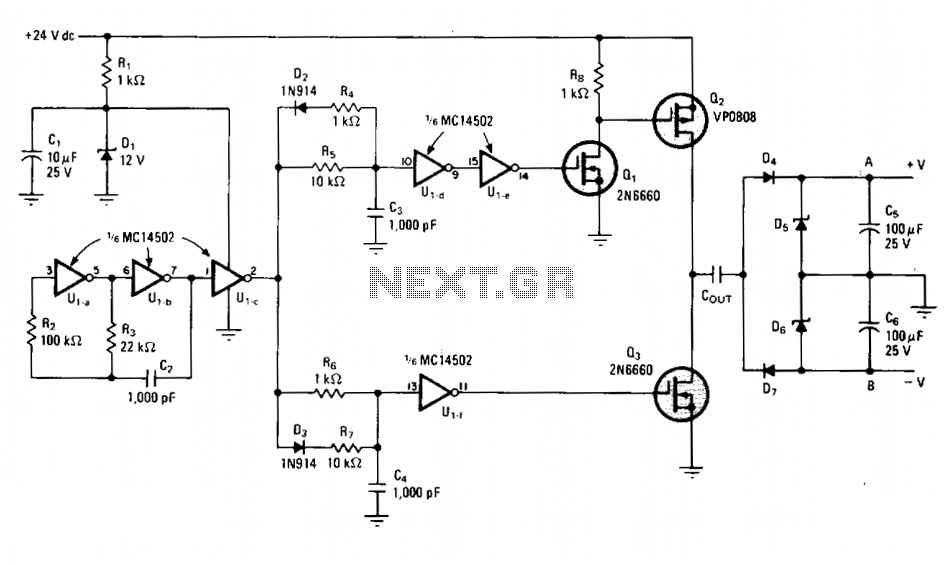
Self oscillating flyback converter
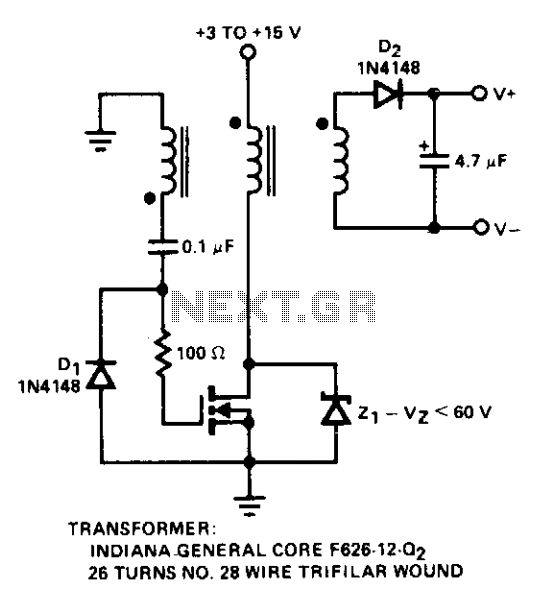
Diode D1 prevents negative spikes from occurring at the MOSFET gate. The 100-ohm resistor acts as a parasitic suppressor, while Z1 functions as a dissipative voltage regulator for the output and clips the drain voltage to a level below the rated breakdown voltage of the power FET. The low-power converter uses core characteristics to determine frequency, with the transformer shown operating at a frequency of 250 kHz.
In this circuit, Diode D1 is strategically placed at the MOSFET gate to protect against negative voltage spikes that could potentially damage the gate structure. This diode ensures that any negative transients are clamped, maintaining the gate voltage within safe limits and thus enhancing the reliability of the MOSFET operation.
The 100-ohm resistor serves a critical role as a parasitic suppressor. Its primary function is to dampen high-frequency oscillations that may arise due to parasitic inductance and capacitance in the circuit. By providing a controlled resistance, it helps to stabilize the gate drive signal and minimizes the risk of unintended switching, which can lead to inefficiencies or failure in the circuit.
Z1, the voltage regulator, is essential for managing the output voltage levels. It acts as a clipping device that ensures the drain voltage remains below the maximum breakdown voltage specified for the power FET. This regulation is crucial in preventing overvoltage conditions that could compromise the integrity of the FET and lead to catastrophic failure.
The low-power converter described utilizes the core characteristics of its components to determine the operational frequency, which is set at 250 kHz in this case. The transformer design is optimized for this frequency, allowing for efficient energy transfer and minimal losses. The choice of frequency is critical, as it affects the overall performance, efficiency, and thermal management of the converter. Operating at 250 kHz strikes a balance between minimizing component size and maintaining effective power conversion, making it suitable for applications where space and efficiency are paramount.Diode Dl prevents negative spikes from occurring at the MOSFET gate, the 100 ohm resistor is a parasitic suppressor, and Z1 serves as a dissipative voltage regulator for the output and also clips the drain voltage to a level below the rated power FET breakdown voltage. Low-power converter uses the core characteristics to determine frequency. With the transformer shown, operating frequency is 250 kHz.
In this circuit, Diode D1 is strategically placed at the MOSFET gate to protect against negative voltage spikes that could potentially damage the gate structure. This diode ensures that any negative transients are clamped, maintaining the gate voltage within safe limits and thus enhancing the reliability of the MOSFET operation.
The 100-ohm resistor serves a critical role as a parasitic suppressor. Its primary function is to dampen high-frequency oscillations that may arise due to parasitic inductance and capacitance in the circuit. By providing a controlled resistance, it helps to stabilize the gate drive signal and minimizes the risk of unintended switching, which can lead to inefficiencies or failure in the circuit.
Z1, the voltage regulator, is essential for managing the output voltage levels. It acts as a clipping device that ensures the drain voltage remains below the maximum breakdown voltage specified for the power FET. This regulation is crucial in preventing overvoltage conditions that could compromise the integrity of the FET and lead to catastrophic failure.
The low-power converter described utilizes the core characteristics of its components to determine the operational frequency, which is set at 250 kHz in this case. The transformer design is optimized for this frequency, allowing for efficient energy transfer and minimal losses. The choice of frequency is critical, as it affects the overall performance, efficiency, and thermal management of the converter. Operating at 250 kHz strikes a balance between minimizing component size and maintaining effective power conversion, making it suitable for applications where space and efficiency are paramount.Diode Dl prevents negative spikes from occurring at the MOSFET gate, the 100 ohm resistor is a parasitic suppressor, and Z1 serves as a dissipative voltage regulator for the output and also clips the drain voltage to a level below the rated power FET breakdown voltage. Low-power converter uses the core characteristics to determine frequency. With the transformer shown, operating frequency is 250 kHz.