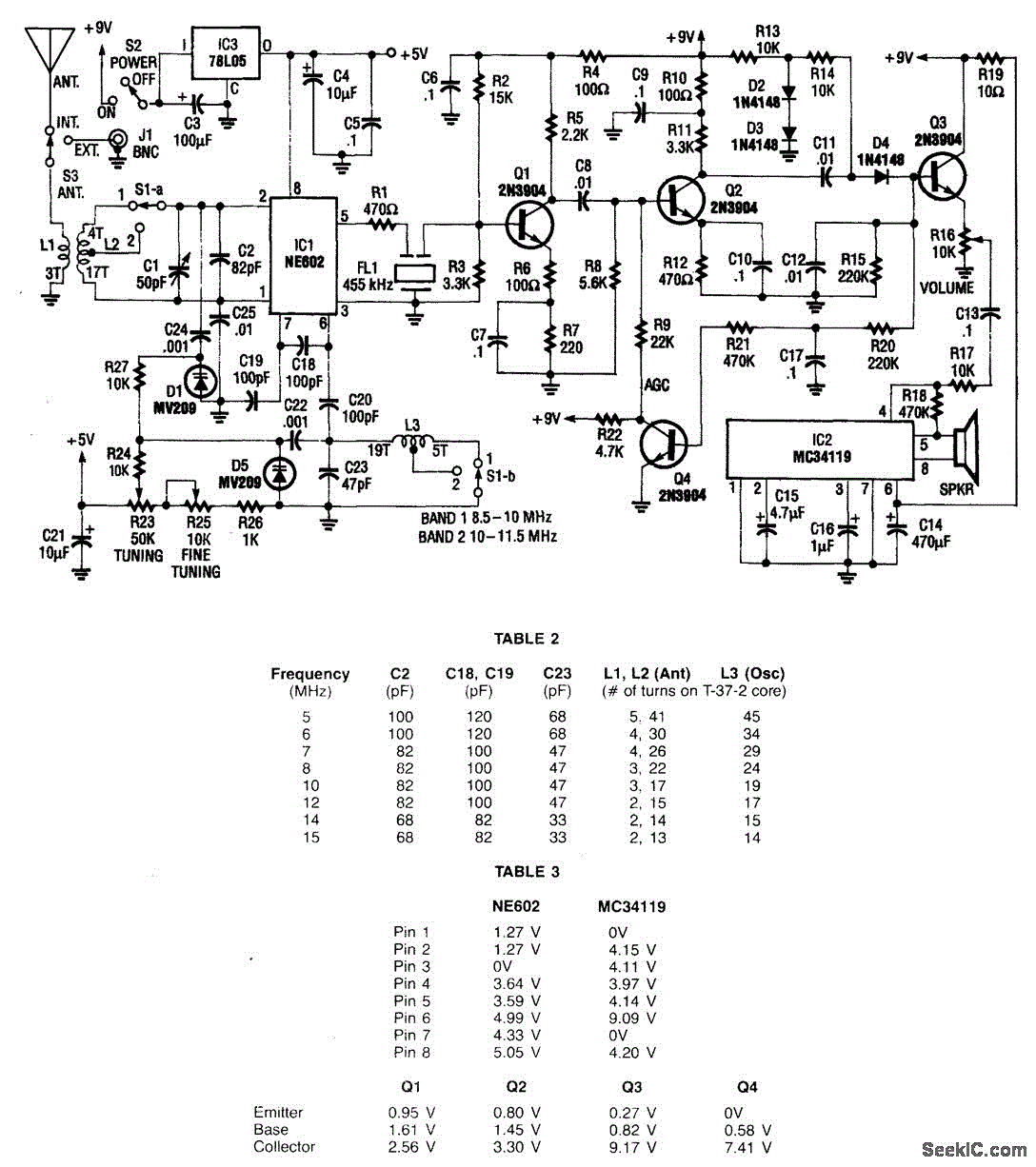
self powered sine to square wave converter
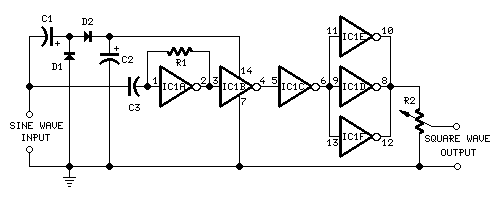
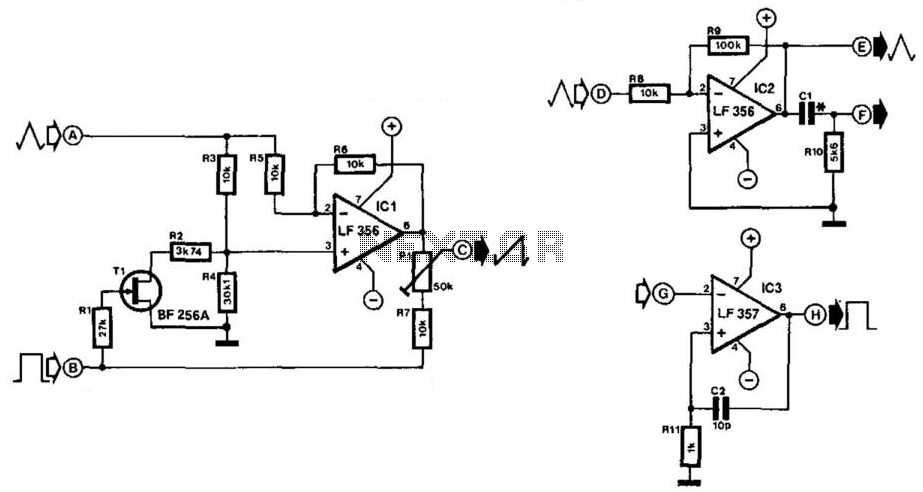
This circuit is designed to generate high-quality square waves by converting a sine wave obtained from an existing generator. A key feature of this circuit is that it does not require an external power source; it can be directly connected between a sine wave generator and the device under test.
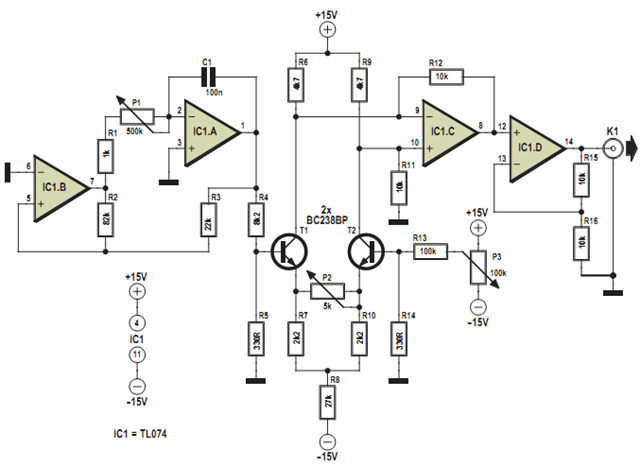
The circuit utilizes a comparator or Schmitt trigger configuration to achieve the conversion from sine to square wave. The input sine wave signal is fed into the non-inverting input of the comparator. The comparator's reference voltage can be set at half the peak value of the sine wave to ensure accurate switching. As the sine wave oscillates, the output of the comparator toggles between high and low states, effectively generating a square wave.
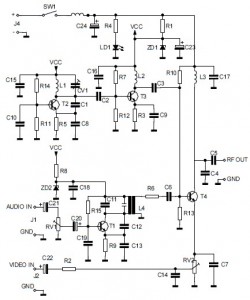
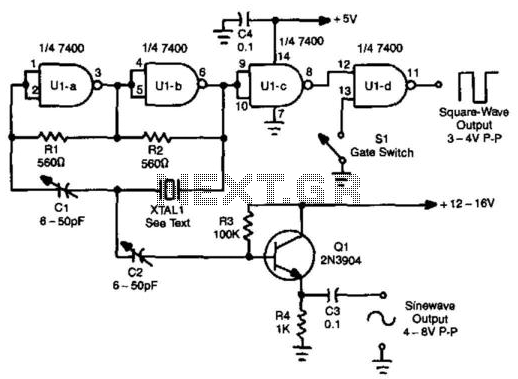
To enhance the performance of the circuit, it may include additional components such as capacitors for filtering and resistors for setting the gain or adjusting the threshold levels. The output square wave can then be used to drive various digital circuits or devices requiring a clock signal.
Furthermore, the circuit's design should ensure that it maintains signal integrity and minimizes distortion during the conversion process. Proper layout considerations, such as minimizing trace lengths and using appropriate grounding techniques, are essential to prevent noise interference. The absence of an external power source also simplifies the setup, making it ideal for portable applications or testing environments where power availability may be limited.
In summary, this circuit effectively transforms a sine wave into a square wave without the need for an external power supply, making it a practical solution for various electronic applications.This circuit is intended to provide good square waves converting a sine wave picked-up from an existing generator. Its major feature consists in the fact that no power-source is needed: thus it can be simply connected between a sine wave generator and the device under test..
🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a comparator or Schmitt trigger configuration to achieve the conversion from sine to square wave. The input sine wave signal is fed into the non-inverting input of the comparator. The comparator's reference voltage can be set at half the peak value of the sine wave to ensure accurate switching. As the sine wave oscillates, the output of the comparator toggles between high and low states, effectively generating a square wave.
To enhance the performance of the circuit, it may include additional components such as capacitors for filtering and resistors for setting the gain or adjusting the threshold levels. The output square wave can then be used to drive various digital circuits or devices requiring a clock signal.
Furthermore, the circuit's design should ensure that it maintains signal integrity and minimizes distortion during the conversion process. Proper layout considerations, such as minimizing trace lengths and using appropriate grounding techniques, are essential to prevent noise interference. The absence of an external power source also simplifies the setup, making it ideal for portable applications or testing environments where power availability may be limited.
In summary, this circuit effectively transforms a sine wave into a square wave without the need for an external power supply, making it a practical solution for various electronic applications.This circuit is intended to provide good square waves converting a sine wave picked-up from an existing generator. Its major feature consists in the fact that no power-source is needed: thus it can be simply connected between a sine wave generator and the device under test..
🔗 External reference