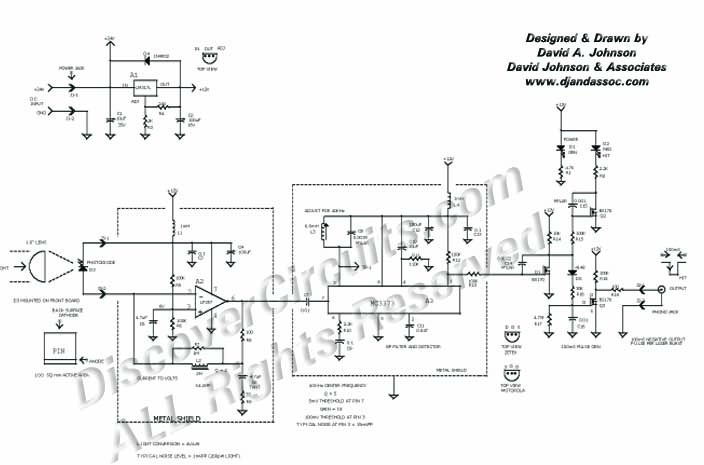
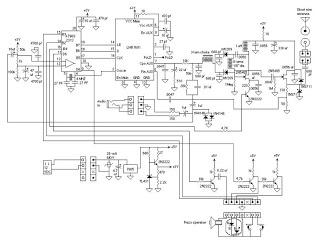
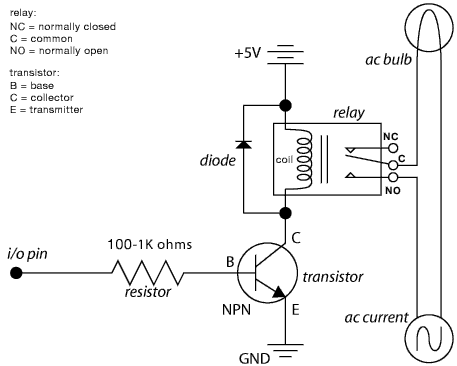
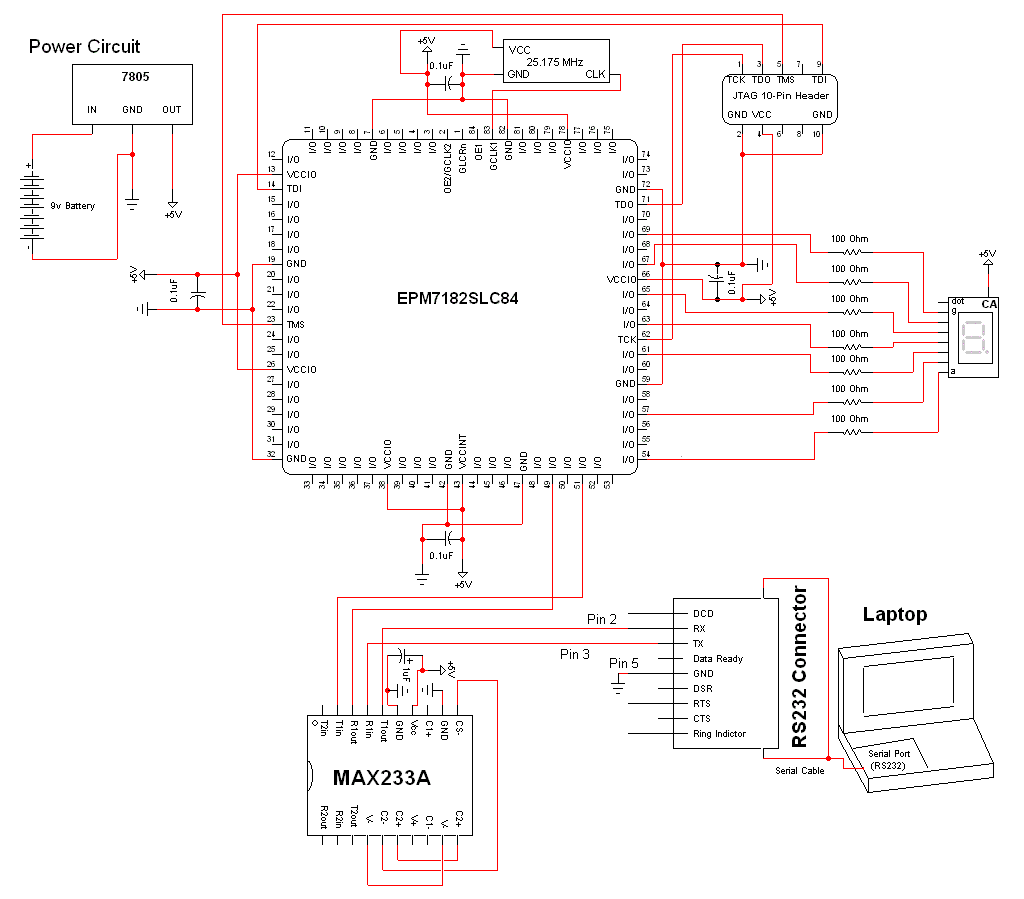
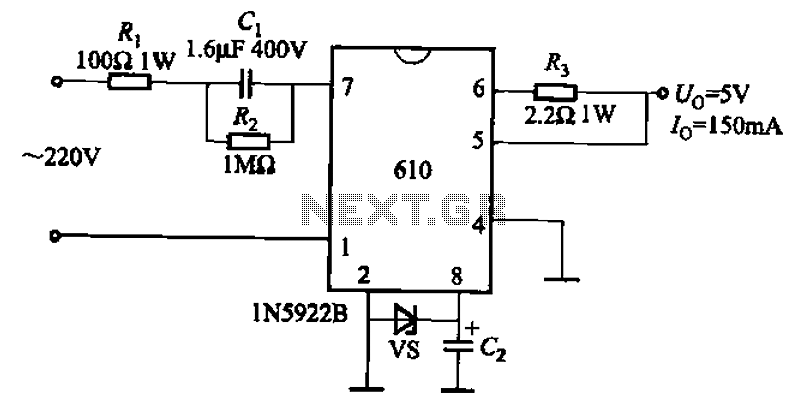
Sensitive envelope detector circuit diagram
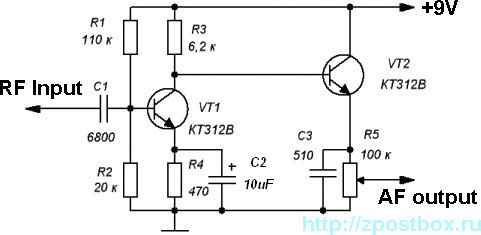
This is a highly sensitive envelope detector designed for AM radio applications. The circuit, illustrated in Figure 1, enables linear detection of weak signals with a modulation depth of 80-85%. The first stage (VT1) functions as a common-emitter amplifier for input signals, while the second stage operates as an emitter-follower circuit (VT2). The transistor VT2 is designed to operate at low current due to the high resistance of resistor R5. The AM demodulation process occurs at the lower end of the volt-ampere curve, ensuring high linearity of demodulation through the implementation of deep negative feedback in the emitter-follower circuit.
The envelope detector circuit described employs two transistors to achieve effective AM signal demodulation. The first stage, VT1, is configured as a common-emitter amplifier, which amplifies the incoming AM signal. This stage is critical for enhancing weak signals, allowing for better detection of the envelope of the modulated waveform. The common-emitter configuration is known for providing significant voltage gain, which is essential when dealing with low-level AM signals.
Following the amplification stage, the second transistor, VT2, is configured as an emitter-follower. This configuration is characterized by its high input impedance and low output impedance, which effectively isolates the first stage from the load. The low current operation of VT2, facilitated by the high resistance of resistor R5, is crucial in minimizing power consumption while maintaining performance. This low current operation also helps to reduce thermal noise, further enhancing the sensitivity of the envelope detector.
The demodulation process occurs at the lower bend of the volt-ampere curve, a region that allows for optimal linearity in signal processing. The deep negative feedback employed in the emitter-follower stage significantly contributes to the high linearity of the demodulated output. This feedback mechanism helps to stabilize the gain and improve the overall fidelity of the detected audio signal.
In summary, this envelope detector circuit leverages the strengths of both common-emitter and emitter-follower configurations to achieve precise AM signal demodulation, making it suitable for applications requiring high sensitivity and linear detection of modulated signals.This is a very sensitive envelope detector for AM radio. The circuit (see Fig. 1) provides linear detection of weak signals with modulation depth of 80. 85% The first stage (VT1) is a common-emitter amplifier circuit for input signals, the second stage is an emitter-follower circuit (VT2). The transistor VT2 operates at low current because of the hi gh resistance of the resistor R5. The process of AM demodulation occurs at the lower bend of the volt-ampere curve. A high linearity of demodulation provided by the deep negative feedback in the emitter-follower circuit. 🔗 External reference
The envelope detector circuit described employs two transistors to achieve effective AM signal demodulation. The first stage, VT1, is configured as a common-emitter amplifier, which amplifies the incoming AM signal. This stage is critical for enhancing weak signals, allowing for better detection of the envelope of the modulated waveform. The common-emitter configuration is known for providing significant voltage gain, which is essential when dealing with low-level AM signals.
Following the amplification stage, the second transistor, VT2, is configured as an emitter-follower. This configuration is characterized by its high input impedance and low output impedance, which effectively isolates the first stage from the load. The low current operation of VT2, facilitated by the high resistance of resistor R5, is crucial in minimizing power consumption while maintaining performance. This low current operation also helps to reduce thermal noise, further enhancing the sensitivity of the envelope detector.
The demodulation process occurs at the lower bend of the volt-ampere curve, a region that allows for optimal linearity in signal processing. The deep negative feedback employed in the emitter-follower stage significantly contributes to the high linearity of the demodulated output. This feedback mechanism helps to stabilize the gain and improve the overall fidelity of the detected audio signal.
In summary, this envelope detector circuit leverages the strengths of both common-emitter and emitter-follower configurations to achieve precise AM signal demodulation, making it suitable for applications requiring high sensitivity and linear detection of modulated signals.This is a very sensitive envelope detector for AM radio. The circuit (see Fig. 1) provides linear detection of weak signals with modulation depth of 80. 85% The first stage (VT1) is a common-emitter amplifier circuit for input signals, the second stage is an emitter-follower circuit (VT2). The transistor VT2 operates at low current because of the hi gh resistance of the resistor R5. The process of AM demodulation occurs at the lower bend of the volt-ampere curve. A high linearity of demodulation provided by the deep negative feedback in the emitter-follower circuit. 🔗 External reference