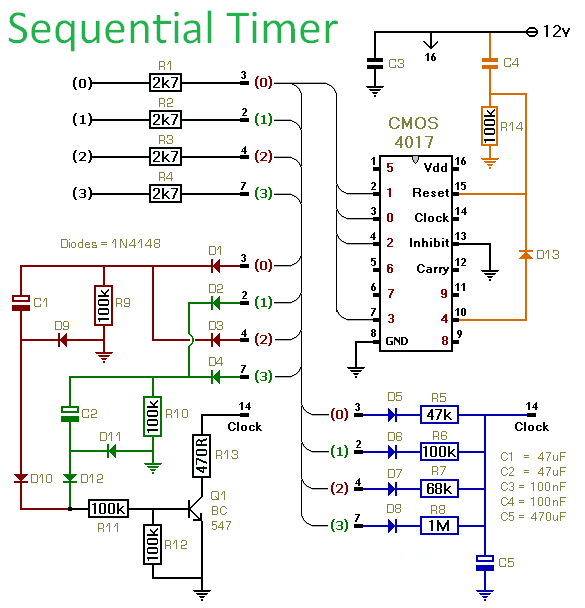
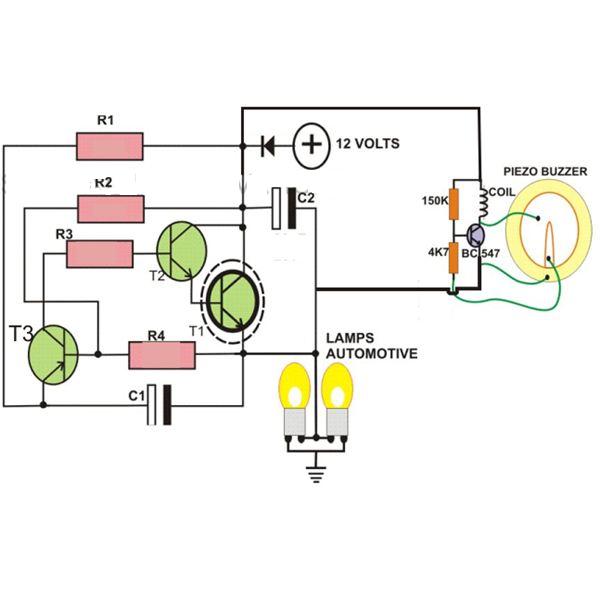
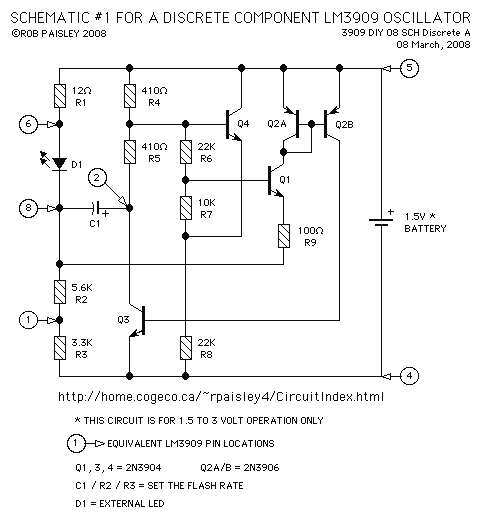
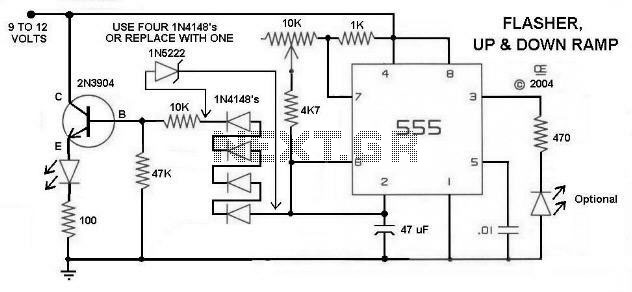
Sequential Flasher
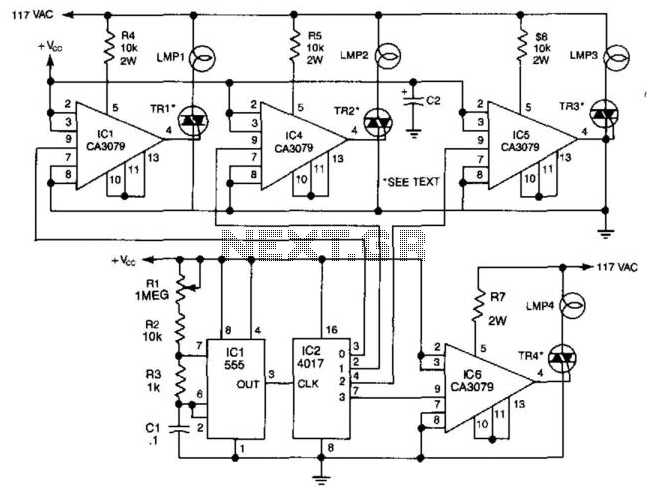
A 555 timer is used to drive a CMOS counter in this device, which employs an RCA CA3079 zero-voltage switch to control triacs TR1 through TR4. This circuit can be utilized for sequencing lamp displays, among other applications. Caution is advised as the CA3079s are connected to the 117-V line, along with the clock and counter circuit and their power supplies. It is important to exercise caution, ensure proper insulation, and adhere to safe construction practices.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a square wave output. This output serves as the clock signal for the CMOS counter, which counts the pulses produced by the 555 timer. The RCA CA3079 zero-voltage switch is employed to control the operation of the triacs, which in turn manage the power delivered to the connected loads, such as lamps. The triacs TR1 through TR4 are arranged in a manner that allows for sequential activation, enabling various lamp display patterns.
The circuit design should ensure that the 555 timer is powered adequately, typically operating at a voltage between 4.5V and 15V, while the CMOS counter should be selected based on the required counting capacity and voltage compatibility. The CA3079, designed for switching applications, provides the necessary isolation and control for the high voltage line, ensuring that the low-voltage components of the timer and counter are protected.
To implement this circuit safely, it is crucial to use components rated for the voltages involved, particularly the CA3079 and the triacs, which must handle the 117-V AC line. Proper insulation of all connections, especially those interfacing with high voltage, is essential to prevent accidental electric shock or circuit failure. Additionally, using heat sinks with the triacs may be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring reliability and longevity of the components.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical application of timer and counter technology in controlling high-voltage loads, suitable for decorative lighting and similar uses, while emphasizing the importance of safety in high-voltage electronics. Using a 555 timer to drive a CMOS counter, this device uses RCA CA3079 zero-voltage switch to control triacs TR1 through TR4. This circuit can be used to sequence lamp displays, etc. Caution: The CA3079s are connected to the 117-V line, as is the clock and counter circuit and their power supplies. Use caution, good insulation, and safe construction practices.
The circuit utilizes a 555 timer configured in astable mode to generate a square wave output. This output serves as the clock signal for the CMOS counter, which counts the pulses produced by the 555 timer. The RCA CA3079 zero-voltage switch is employed to control the operation of the triacs, which in turn manage the power delivered to the connected loads, such as lamps. The triacs TR1 through TR4 are arranged in a manner that allows for sequential activation, enabling various lamp display patterns.
The circuit design should ensure that the 555 timer is powered adequately, typically operating at a voltage between 4.5V and 15V, while the CMOS counter should be selected based on the required counting capacity and voltage compatibility. The CA3079, designed for switching applications, provides the necessary isolation and control for the high voltage line, ensuring that the low-voltage components of the timer and counter are protected.
To implement this circuit safely, it is crucial to use components rated for the voltages involved, particularly the CA3079 and the triacs, which must handle the 117-V AC line. Proper insulation of all connections, especially those interfacing with high voltage, is essential to prevent accidental electric shock or circuit failure. Additionally, using heat sinks with the triacs may be necessary to dissipate heat generated during operation, ensuring reliability and longevity of the components.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a practical application of timer and counter technology in controlling high-voltage loads, suitable for decorative lighting and similar uses, while emphasizing the importance of safety in high-voltage electronics. Using a 555 timer to drive a CMOS counter, this device uses RCA CA3079 zero-voltage switch to control triacs TR1 through TR4. This circuit can be used to sequence lamp displays, etc. Caution: The CA3079s are connected to the 117-V line, as is the clock and counter circuit and their power supplies. Use caution, good insulation, and safe construction practices.