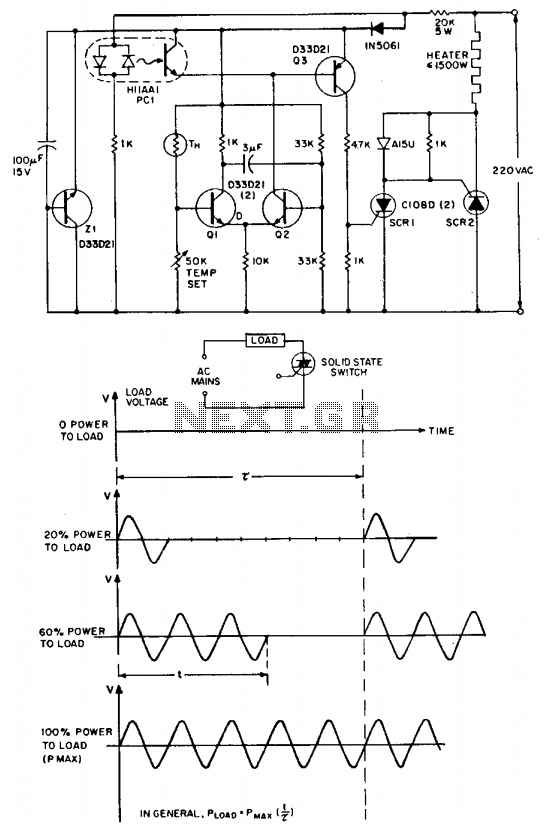
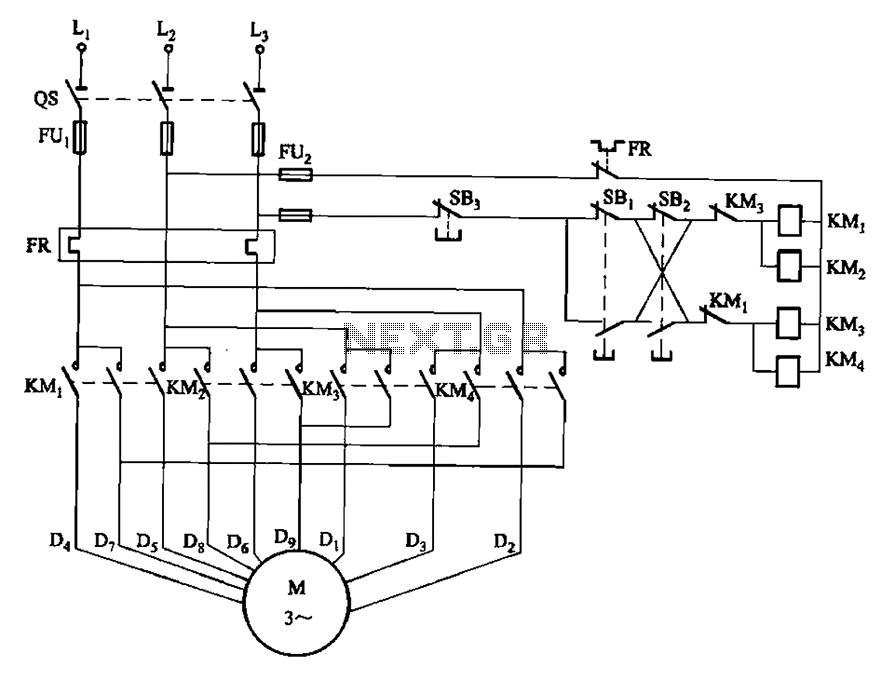
Series-Wound Direction And Speed Motor Control
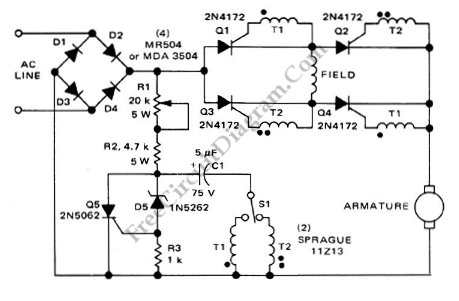
This is a motor controller circuit that controls the speed and direction of series-wound motors. This circuit employs silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR).
The motor controller circuit is designed to manage both the speed and direction of series-wound motors, which are commonly used in various applications due to their high starting torque and simplicity. The core component of this circuit is the silicon controlled rectifier (SCR), a semiconductor device that allows for the control of power delivery to the motor by adjusting the phase angle of the AC supply.
The operation of the circuit begins with the application of a control signal to the gate of the SCR. This signal turns the SCR on, allowing current to flow through the motor. By varying the timing of the gate signal, the effective voltage applied to the motor can be controlled, thereby regulating the motor's speed. This phase control technique is particularly effective for series-wound motors, as it takes advantage of their inherent characteristics.
Furthermore, the circuit can also be configured to reverse the direction of the motor. This is typically achieved by employing a relay or an additional set of SCRs that can switch the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor. By implementing this feature, the motor controller provides versatility for applications that require bidirectional movement.
In terms of design, the circuit may include additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, capacitors for filtering, and resistors for current limiting. A microcontroller may also be integrated to provide more sophisticated control algorithms, such as PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for smoother speed control and enhanced efficiency.
Overall, this motor controller circuit utilizing SCRs is a robust solution for applications requiring precise control over the operation of series-wound motors, making it suitable for industrial automation, robotics, and various other fields.This is a motor controller circuit that? control the speed? and direction of series-wound Motors. This circuit employs silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). 🔗 External reference
The motor controller circuit is designed to manage both the speed and direction of series-wound motors, which are commonly used in various applications due to their high starting torque and simplicity. The core component of this circuit is the silicon controlled rectifier (SCR), a semiconductor device that allows for the control of power delivery to the motor by adjusting the phase angle of the AC supply.
The operation of the circuit begins with the application of a control signal to the gate of the SCR. This signal turns the SCR on, allowing current to flow through the motor. By varying the timing of the gate signal, the effective voltage applied to the motor can be controlled, thereby regulating the motor's speed. This phase control technique is particularly effective for series-wound motors, as it takes advantage of their inherent characteristics.
Furthermore, the circuit can also be configured to reverse the direction of the motor. This is typically achieved by employing a relay or an additional set of SCRs that can switch the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor. By implementing this feature, the motor controller provides versatility for applications that require bidirectional movement.
In terms of design, the circuit may include additional components such as diodes for flyback protection, capacitors for filtering, and resistors for current limiting. A microcontroller may also be integrated to provide more sophisticated control algorithms, such as PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for smoother speed control and enhanced efficiency.
Overall, this motor controller circuit utilizing SCRs is a robust solution for applications requiring precise control over the operation of series-wound motors, making it suitable for industrial automation, robotics, and various other fields.This is a motor controller circuit that? control the speed? and direction of series-wound Motors. This circuit employs silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). 🔗 External reference