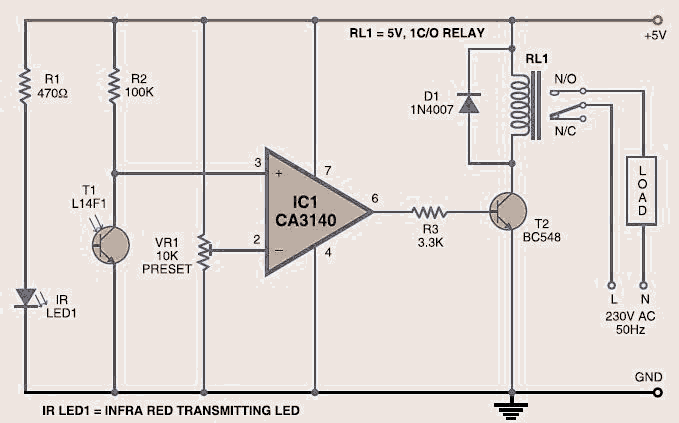
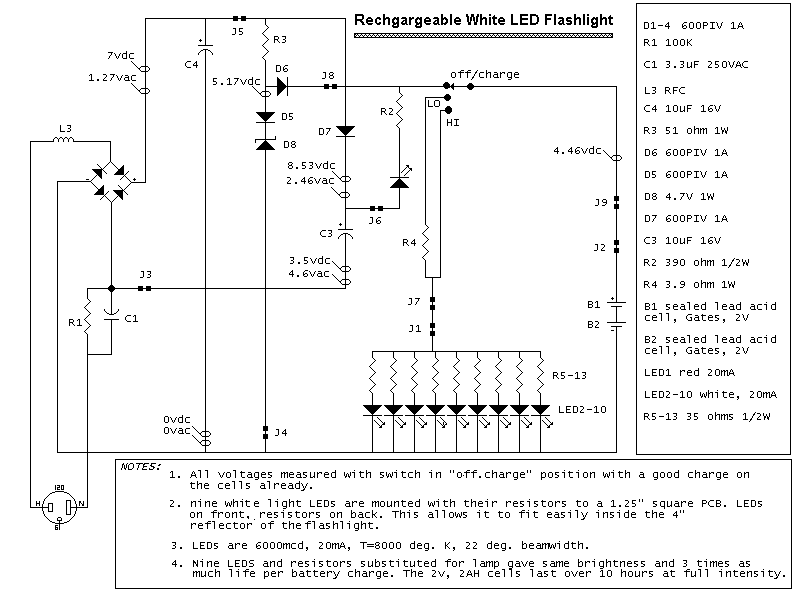
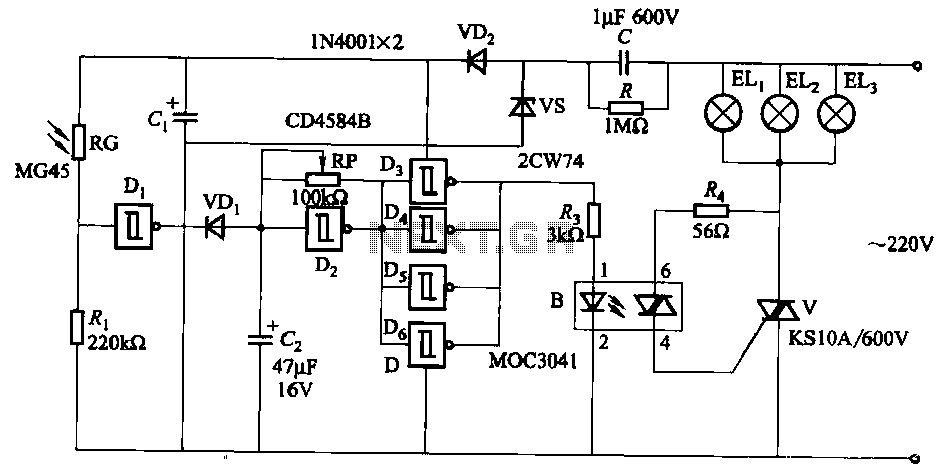
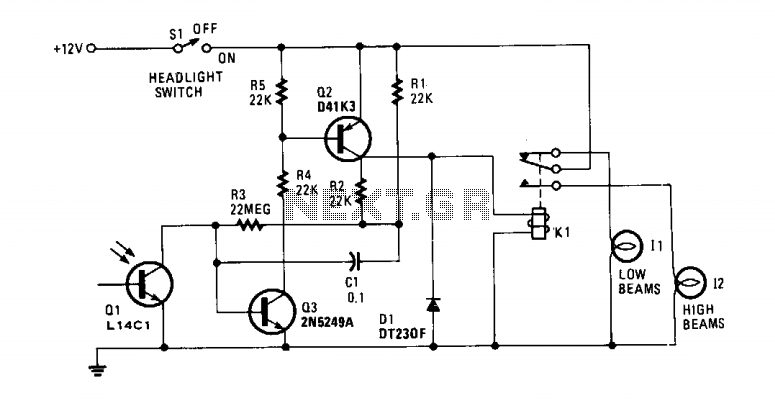
servo light dimmer

This dimmer is designed to control illumination effectively, with a power handling capacity that exceeds 1600 watts, significantly surpassing the typical 300-watt dimmers. The circuit utilizes a triac rated at 400 PIV and 8 amperes, while component VR1 allows for illumination adjustment. Resistors R2 and R3, along with capacitor C1, establish the minimum brightness level, which can be modified as desired.
The dimmer circuit operates by controlling the phase angle of the AC voltage supplied to the load, allowing for smooth dimming capabilities. The triac serves as the primary switching device, enabling the circuit to handle high power loads without overheating. When the circuit is powered, VR1 adjusts the gate trigger of the triac, thereby controlling the amount of voltage delivered to the load.
Resistors R2 and R3 are crucial for setting the reference voltage and current through the control circuit, which influences the minimum brightness level. The capacitor C1 works in conjunction with these resistors to filter and stabilize the voltage, ensuring a consistent performance across varying load conditions.
This dimmer is suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential lighting to commercial settings, where precise control over illumination is required. The ability to handle loads greater than 1600 watts makes it particularly advantageous for use with high-wattage lighting fixtures. Additionally, the adjustable minimum brightness feature allows for customized lighting environments, enhancing both functionality and user experience.
Overall, this dimmer circuit represents a robust solution for effective illumination control, combining high power capacity with versatile adjustment features.And this is exactly what this dimmer does. One plus point is that it has a power handling capacity exceeding 1600 watts, far exceeding the ordinary 300 watt types. Any type of 400 PIV, 8 ampere triac may be used in the circuit VR1 provides illumination control. R2, R3 and C1 set the minimum brightness level which can however be altered. 🔗 External reference
The dimmer circuit operates by controlling the phase angle of the AC voltage supplied to the load, allowing for smooth dimming capabilities. The triac serves as the primary switching device, enabling the circuit to handle high power loads without overheating. When the circuit is powered, VR1 adjusts the gate trigger of the triac, thereby controlling the amount of voltage delivered to the load.
Resistors R2 and R3 are crucial for setting the reference voltage and current through the control circuit, which influences the minimum brightness level. The capacitor C1 works in conjunction with these resistors to filter and stabilize the voltage, ensuring a consistent performance across varying load conditions.
This dimmer is suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential lighting to commercial settings, where precise control over illumination is required. The ability to handle loads greater than 1600 watts makes it particularly advantageous for use with high-wattage lighting fixtures. Additionally, the adjustable minimum brightness feature allows for customized lighting environments, enhancing both functionality and user experience.
Overall, this dimmer circuit represents a robust solution for effective illumination control, combining high power capacity with versatile adjustment features.And this is exactly what this dimmer does. One plus point is that it has a power handling capacity exceeding 1600 watts, far exceeding the ordinary 300 watt types. Any type of 400 PIV, 8 ampere triac may be used in the circuit VR1 provides illumination control. R2, R3 and C1 set the minimum brightness level which can however be altered. 🔗 External reference