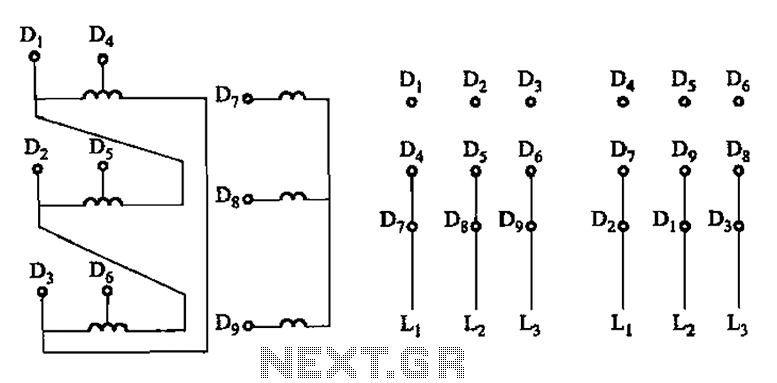
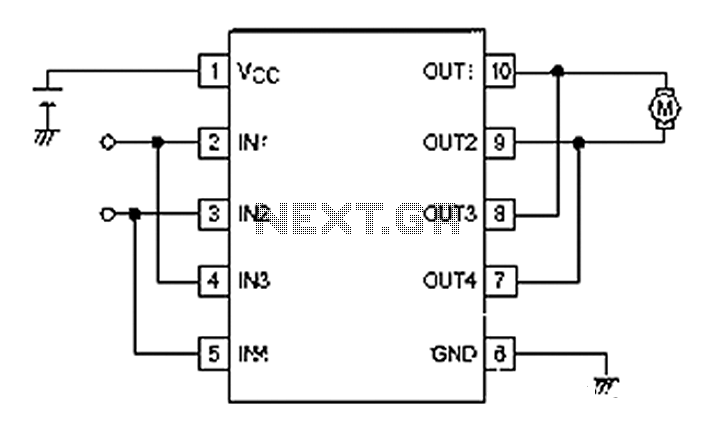
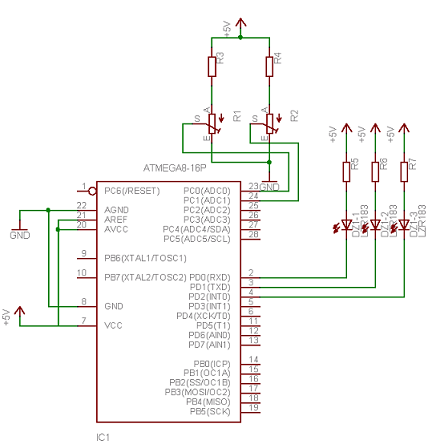
Servo Motor System Controller
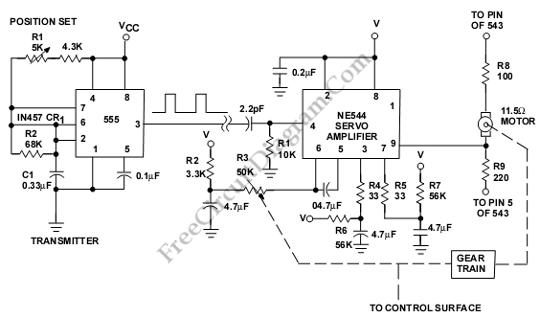
This is a servo system controller circuit designed for remote control of a servo motor. The circuit utilizes a 555 timer and requires only six additional components.
The servo system controller circuit operates by generating a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal, which is essential for controlling the position of the servo motor. The 555 timer, configured in astable mode, produces a continuous square wave output. The frequency and duty cycle of this output can be adjusted by varying the values of the resistors and capacitors connected to the timer.
To implement this circuit, the following components are typically required: a 555 timer IC, two resistors, one variable resistor (potentiometer), one capacitor, and a diode. The resistors determine the frequency of the PWM signal, while the potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the duty cycle, thereby controlling the angle of the servo motor. The capacitor smooths the output signal, ensuring stable operation.
The output from the 555 timer is fed into the control pin of the servo motor. The servo motor interprets the width of the PWM signal to adjust its position accordingly. By changing the duty cycle, the angle of the servo can be modified, allowing for precise control in various applications, such as robotics, automation systems, and remote-controlled devices.
This circuit is advantageous due to its simplicity, low cost, and the minimal number of additional components required, making it suitable for hobbyist projects and educational purposes in understanding basic servo control mechanisms.This is a Servo System Controller circuit. This circuit is used to control a servo motor remotely. This circuit uses the 555 and requires only six extra. 🔗 External reference
The servo system controller circuit operates by generating a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal, which is essential for controlling the position of the servo motor. The 555 timer, configured in astable mode, produces a continuous square wave output. The frequency and duty cycle of this output can be adjusted by varying the values of the resistors and capacitors connected to the timer.
To implement this circuit, the following components are typically required: a 555 timer IC, two resistors, one variable resistor (potentiometer), one capacitor, and a diode. The resistors determine the frequency of the PWM signal, while the potentiometer allows for fine-tuning of the duty cycle, thereby controlling the angle of the servo motor. The capacitor smooths the output signal, ensuring stable operation.
The output from the 555 timer is fed into the control pin of the servo motor. The servo motor interprets the width of the PWM signal to adjust its position accordingly. By changing the duty cycle, the angle of the servo can be modified, allowing for precise control in various applications, such as robotics, automation systems, and remote-controlled devices.
This circuit is advantageous due to its simplicity, low cost, and the minimal number of additional components required, making it suitable for hobbyist projects and educational purposes in understanding basic servo control mechanisms.This is a Servo System Controller circuit. This circuit is used to control a servo motor remotely. This circuit uses the 555 and requires only six extra. 🔗 External reference