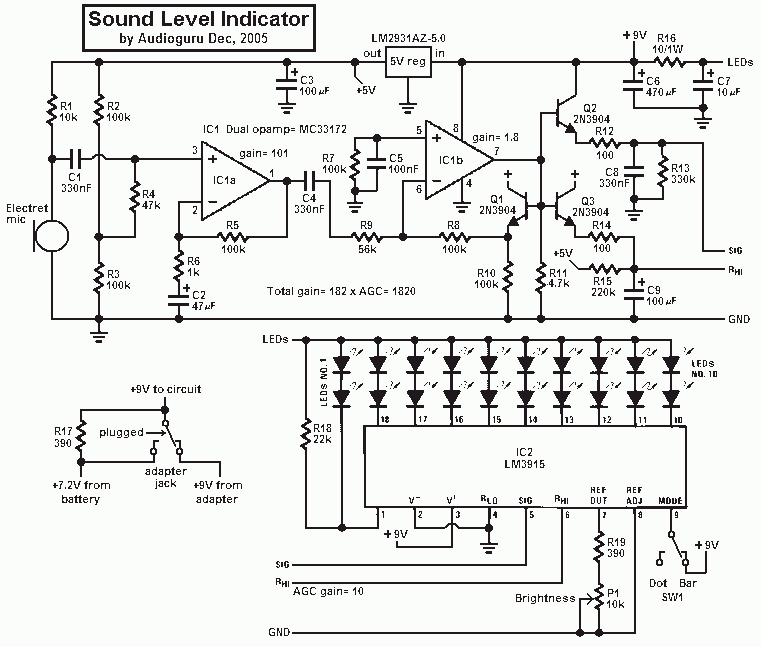
Sight n sound metronome
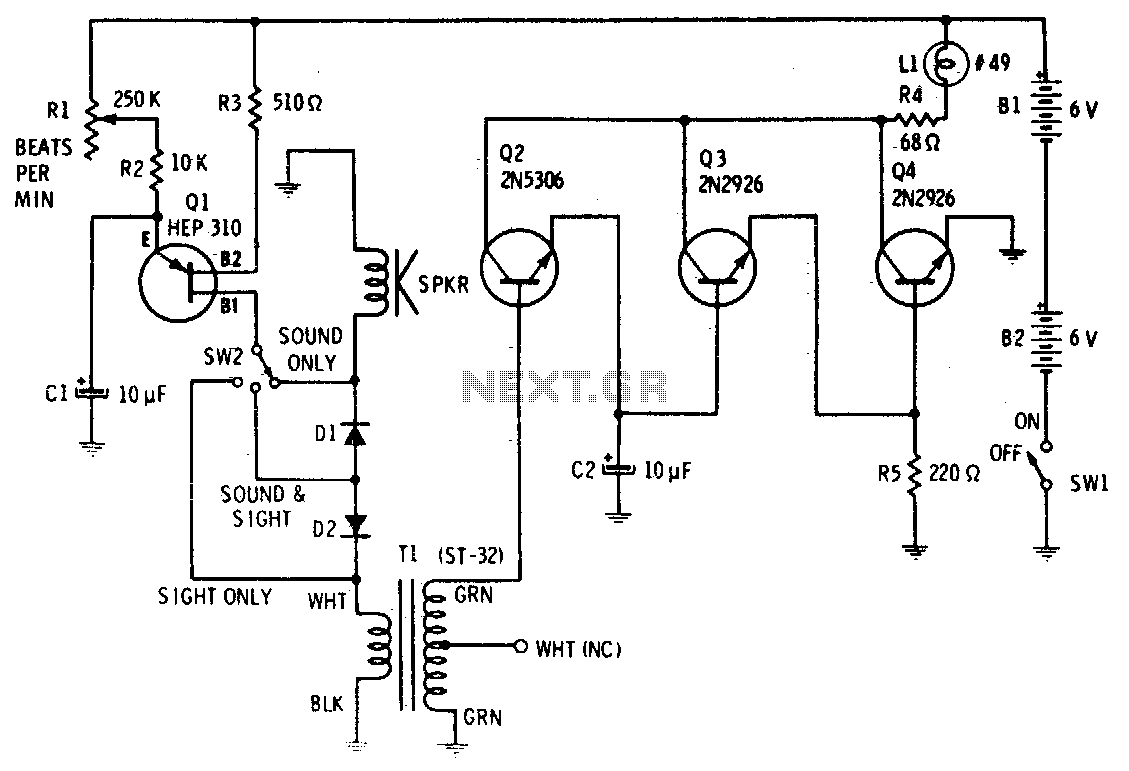
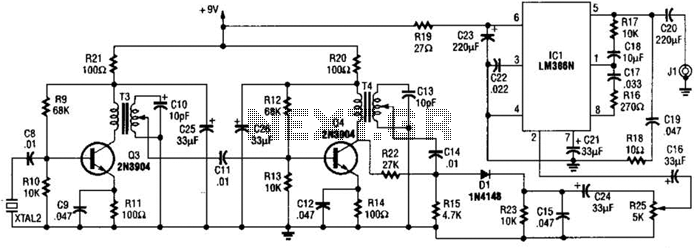
Precise, adjustable control of beats per minute ranges from a slow tempo of 18 to a rapid tempo of 500. These beats are generated acoustically through a speaker, accompanied by a light that flashes in synchronization. When switch SW1 is closed, capacitor C1 begins to charge through resistors R1 and R2. Eventually, C1 reaches a voltage that activates the emitter of a unijunction transistor, which discharges the energy stored in C1 into an 8-ohm speaker. To produce a distinct "plop" sound, brief pulses across the secondary of transformer T2 drive transistor Q2 into conduction. The additional gain provided by transistors Q3 and Q4 is sufficient to briefly switch relay LI on and off as the pulse wave passes. Capacitor C2 slightly stretches the pulse to counteract the thermal inertia of the lamp, resulting in a bright flash.
The circuit described operates as a beat generator with adjustable tempo, utilizing a unijunction transistor for pulse generation and a speaker for sound output. The primary component responsible for controlling the beat rate is capacitor C1, which charges through the resistors R1 and R2 when the switch SW1 is engaged. The charging process determines the timing of the pulse output, which can be adjusted to achieve a range of tempos.
Once the voltage across C1 reaches a specific threshold, it activates the unijunction transistor, allowing the stored energy to be discharged into the connected speaker. This discharge creates an audible sound, characterized by a "plop" as the energy is released. The transformer T2 plays a crucial role in shaping the pulse waveform, ensuring that it is suitable for driving the subsequent transistor Q2. This transistor amplifies the pulse signal, providing enough current to actuate the relay LI.
Transistors Q3 and Q4 serve to further amplify the signal, ensuring that the relay is effectively switched on and off in response to the pulse waveform. This switching action can be critical for applications that require precise timing or control, such as in light flashing or other timing-dependent circuits. The inclusion of capacitor C2 is significant as it mitigates the effects of thermal inertia in the lamp, allowing for a more pronounced flash when the relay is activated. This design highlights the interplay between various components to achieve a cohesive and responsive electronic system.Precise, adjustable control of beats per minute from a largo of 18 to a frenzied, high presto of 500, These beats are produced acoustically through a speaker. A light flashes at the same rate. When SW1 is closed, CI begins to charge through Rl and R2. Cl will eventually reach a voltage at which the emitter of unijunction transistor is switched on, "dumping" the energy stored in Cl into an 8 ohm speaker.
To produce a distinct "plop", brief pulses across T2 secondary drive Q2 into conduction The extra gain of Q3 and Q4 are sufficient to briefly switch LI on, then o£f; as the pulse wave pas-ses. Capacitor C2 "stretches" the puise slightly to overcome the thermal inertia of the lamp, so that a bright flash occurs,.
The circuit described operates as a beat generator with adjustable tempo, utilizing a unijunction transistor for pulse generation and a speaker for sound output. The primary component responsible for controlling the beat rate is capacitor C1, which charges through the resistors R1 and R2 when the switch SW1 is engaged. The charging process determines the timing of the pulse output, which can be adjusted to achieve a range of tempos.
Once the voltage across C1 reaches a specific threshold, it activates the unijunction transistor, allowing the stored energy to be discharged into the connected speaker. This discharge creates an audible sound, characterized by a "plop" as the energy is released. The transformer T2 plays a crucial role in shaping the pulse waveform, ensuring that it is suitable for driving the subsequent transistor Q2. This transistor amplifies the pulse signal, providing enough current to actuate the relay LI.
Transistors Q3 and Q4 serve to further amplify the signal, ensuring that the relay is effectively switched on and off in response to the pulse waveform. This switching action can be critical for applications that require precise timing or control, such as in light flashing or other timing-dependent circuits. The inclusion of capacitor C2 is significant as it mitigates the effects of thermal inertia in the lamp, allowing for a more pronounced flash when the relay is activated. This design highlights the interplay between various components to achieve a cohesive and responsive electronic system.Precise, adjustable control of beats per minute from a largo of 18 to a frenzied, high presto of 500, These beats are produced acoustically through a speaker. A light flashes at the same rate. When SW1 is closed, CI begins to charge through Rl and R2. Cl will eventually reach a voltage at which the emitter of unijunction transistor is switched on, "dumping" the energy stored in Cl into an 8 ohm speaker.
To produce a distinct "plop", brief pulses across T2 secondary drive Q2 into conduction The extra gain of Q3 and Q4 are sufficient to briefly switch LI on, then o£f; as the pulse wave pas-ses. Capacitor C2 "stretches" the puise slightly to overcome the thermal inertia of the lamp, so that a bright flash occurs,.