Simple audio amplifier LM307 A741
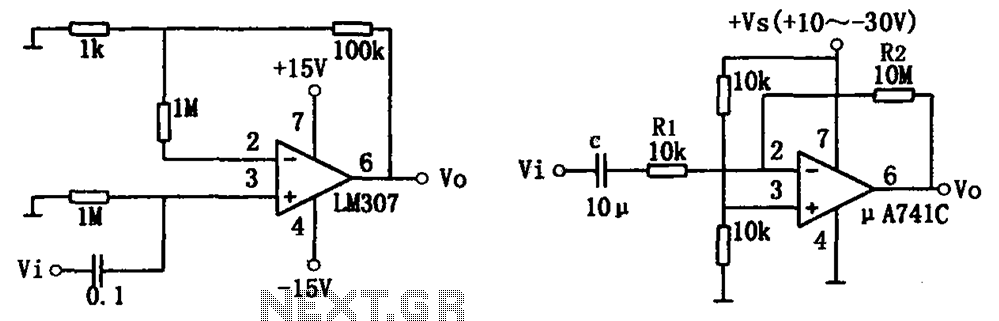
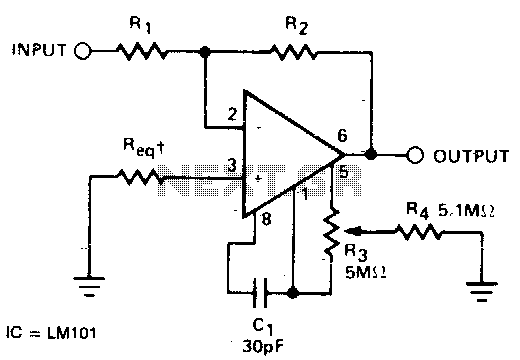
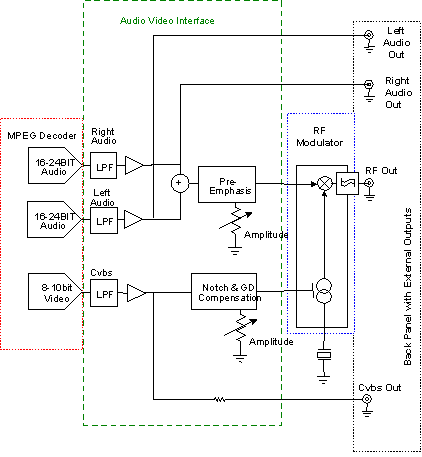
The simple audio amplifier circuit is illustrated in the figure. Utilizing an integrated op-amp configuration, this audio amplifier is stable and allows for easy negative feedback, facilitating the achievement of equalization characteristics. Additionally, the crosstalk between channels is minimal, making it straightforward to mix multiple input channels. Figure (a) displays a circuit that employs a dual power supply (Vs 15V), where the phase-inverting input terminal is grounded through a static balance resistance. The input signal (Vi) is introduced to the inverting input terminal of the LM307N via a 0.1 µF coupling capacitor. With an input resistance of approximately 1M, the equivalent load is light. The circuit offers a voltage gain of about 101 times and exhibits good dynamic characteristics. Figure (b) presents a circuit utilizing a single power supply. Since the DC level signal issue does not affect the AC amplifier, this power supply configuration is advantageous. In this setup, the audio signal is fed through a coupling capacitor (Ck) and resistor (R1) into the inverting input (pin 2) of the A741C. The circuit incorporates 100% negative feedback for the DC component (c DC component is effectively open), ensuring that the offset voltage remains unamplified. The voltage gain of the circuit is determined by the equation Av = -R2/R1, resulting in a gain of 1000 (or 60 dB). It is important to note that R1, R2, and capacitor C contribute to low-frequency attenuation and phase shift effects. Therefore, when dealing with low signal frequencies, it may be necessary to increase the capacitance of capacitor C.
This audio amplifier circuit is designed for versatility and efficiency in audio signal processing. The dual power supply configuration in Figure (a) allows for a stable operation with the LM307N op-amp, which is well-suited for audio applications due to its low noise and high gain characteristics. The use of a coupling capacitor (0.1 µF) ensures that only the AC components of the audio signal are amplified, while blocking any DC offset that could affect performance.
In contrast, the single power supply configuration in Figure (b) simplifies the power requirements, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The design effectively manages the DC offset through the implementation of negative feedback, ensuring that the amplifier maintains a linear response across the audio frequency range. The choice of feedback components (R1 and R2) is crucial, as they define the gain and frequency response of the amplifier. The gain equation highlights the inverse relationship between R1 and R2, allowing for precise control over amplification levels.
Moreover, the low-frequency characteristics of the circuit can be tailored by adjusting the values of R1, R2, and the coupling capacitor C, which can be particularly beneficial in applications requiring specific equalization or filtering of audio signals. The design also minimizes crosstalk, enhancing the quality of mixed audio inputs and ensuring a clearer output.
Overall, this simple audio amplifier circuit is a robust solution for various audio applications, providing stable amplification with minimal interference and the flexibility to accommodate different signal conditions. As shown in FIG simple audio amplifier circuit. Using the integrated op-amp configuration of audio amplifier is stable, easy to negative feedback, so it is easy to get equaliza tion characteristics. In addition, crosstalk between channels is small, it is also very easy to mix multiple input channels. Figure (a) shows a circuit using a dual power supply (Vs 15V), with the phase-inverting input terminal, respectively, to ground the static balance resistance, the input signal Vi by the 0.1 F coupling capacitor into LM307N-inverting input terminal (Cited 3 feet).
The signal source, the input resistance of about 1M, and therefore the equivalent load is light. The circuit voltage is about 101 times magnification, and has good dynamic characteristics. Figure (b) shows a circuit using a single power supply, because the DC level signal problem does not exist in the AC amplifier, so this power supply is desirable. In this circuit, the audio signal via a coupling capacitor C K and resistor R1 fed, A741C inverting input (pin 2).
The figure shows that the circuit for DC component is introduced 100% negative feedback (c DC component is quite open), so the offset voltage without amplification. The voltage of the circuit magnification: Av -R2/R1 -1000 (ie 60dB). It should be emphasized that: R1, R2 and capacitor C having low frequency attenuation and phase shift effect, when the signal frequency is low, may be appropriate to increase the capacitance C of capacity.
This audio amplifier circuit is designed for versatility and efficiency in audio signal processing. The dual power supply configuration in Figure (a) allows for a stable operation with the LM307N op-amp, which is well-suited for audio applications due to its low noise and high gain characteristics. The use of a coupling capacitor (0.1 µF) ensures that only the AC components of the audio signal are amplified, while blocking any DC offset that could affect performance.
In contrast, the single power supply configuration in Figure (b) simplifies the power requirements, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. The design effectively manages the DC offset through the implementation of negative feedback, ensuring that the amplifier maintains a linear response across the audio frequency range. The choice of feedback components (R1 and R2) is crucial, as they define the gain and frequency response of the amplifier. The gain equation highlights the inverse relationship between R1 and R2, allowing for precise control over amplification levels.
Moreover, the low-frequency characteristics of the circuit can be tailored by adjusting the values of R1, R2, and the coupling capacitor C, which can be particularly beneficial in applications requiring specific equalization or filtering of audio signals. The design also minimizes crosstalk, enhancing the quality of mixed audio inputs and ensuring a clearer output.
Overall, this simple audio amplifier circuit is a robust solution for various audio applications, providing stable amplification with minimal interference and the flexibility to accommodate different signal conditions. As shown in FIG simple audio amplifier circuit. Using the integrated op-amp configuration of audio amplifier is stable, easy to negative feedback, so it is easy to get equaliza tion characteristics. In addition, crosstalk between channels is small, it is also very easy to mix multiple input channels. Figure (a) shows a circuit using a dual power supply (Vs 15V), with the phase-inverting input terminal, respectively, to ground the static balance resistance, the input signal Vi by the 0.1 F coupling capacitor into LM307N-inverting input terminal (Cited 3 feet).
The signal source, the input resistance of about 1M, and therefore the equivalent load is light. The circuit voltage is about 101 times magnification, and has good dynamic characteristics. Figure (b) shows a circuit using a single power supply, because the DC level signal problem does not exist in the AC amplifier, so this power supply is desirable. In this circuit, the audio signal via a coupling capacitor C K and resistor R1 fed, A741C inverting input (pin 2).
The figure shows that the circuit for DC component is introduced 100% negative feedback (c DC component is quite open), so the offset voltage without amplification. The voltage of the circuit magnification: Av -R2/R1 -1000 (ie 60dB). It should be emphasized that: R1, R2 and capacitor C having low frequency attenuation and phase shift effect, when the signal frequency is low, may be appropriate to increase the capacitance C of capacity.