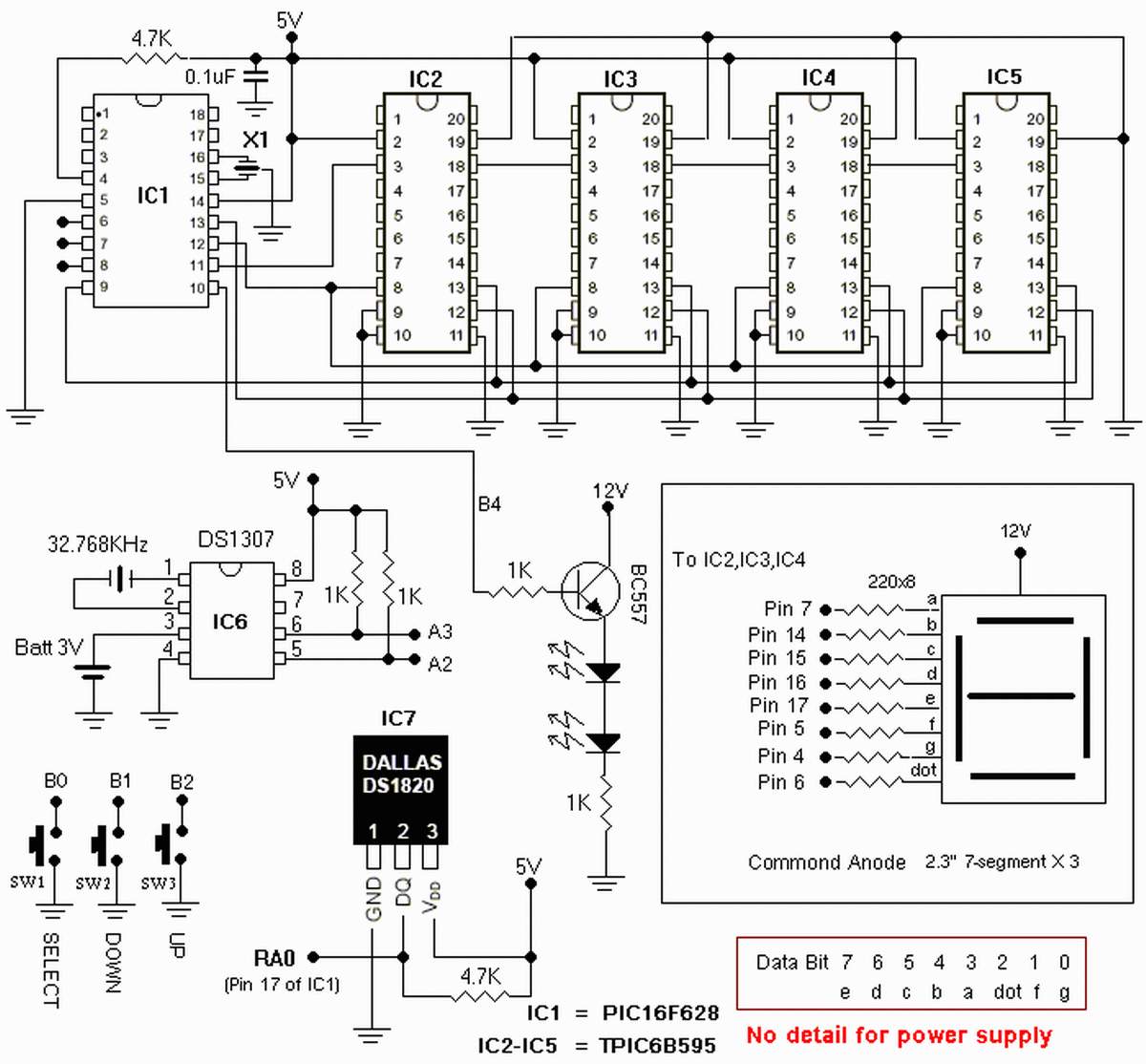
Simple Audio Test Oscillator Circuit
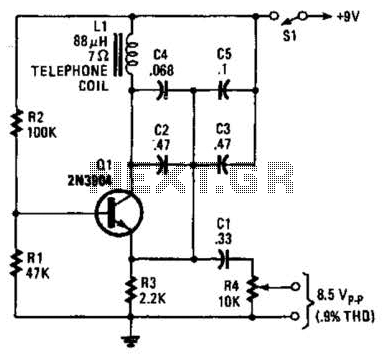
An 88 mH surplus telephone toroidal coil is utilized in a 1 kHz oscillator. It can provide up to 8 V peak-to-peak into a high-impedance load. The total harmonic distortion (THD) is 0.9%.
The circuit employs an 88 mH toroidal coil, which serves as a crucial inductor in the oscillator design. This inductor is characterized by its compact form factor and efficient magnetic properties, making it suitable for high-frequency applications. The oscillator operates at a frequency of 1 kHz, a common frequency for various signal generation tasks, including audio applications and timing circuits.
The output voltage capability of up to 8 V peak-to-peak indicates that the oscillator can drive a high-impedance load effectively, which is essential for interfacing with other electronic components or systems that require a stable voltage level. The high-impedance load ensures minimal current draw, allowing for efficient operation of the oscillator circuit.
The total harmonic distortion (THD) of 0.9% suggests that the output waveform is relatively clean, with minimal distortion introduced by the oscillator. This level of THD is acceptable for many applications, where fidelity of the signal is important, such as in audio systems or precision timing applications.
For implementation, the oscillator circuit can be constructed using additional components such as capacitors for tuning, transistors or operational amplifiers for signal amplification, and resistors for biasing. The toroidal coil's inductance plays a vital role in determining the oscillation frequency alongside the capacitive elements in the circuit. Proper layout and component selection are crucial to minimize parasitic effects and maintain the desired performance characteristics. An 88-mH surplus telephone toroidal coil is used in a 1-kHz oscillator. Up to 8 V p-p into a high-Z load is available. THD is 0.9%.
The circuit employs an 88 mH toroidal coil, which serves as a crucial inductor in the oscillator design. This inductor is characterized by its compact form factor and efficient magnetic properties, making it suitable for high-frequency applications. The oscillator operates at a frequency of 1 kHz, a common frequency for various signal generation tasks, including audio applications and timing circuits.
The output voltage capability of up to 8 V peak-to-peak indicates that the oscillator can drive a high-impedance load effectively, which is essential for interfacing with other electronic components or systems that require a stable voltage level. The high-impedance load ensures minimal current draw, allowing for efficient operation of the oscillator circuit.
The total harmonic distortion (THD) of 0.9% suggests that the output waveform is relatively clean, with minimal distortion introduced by the oscillator. This level of THD is acceptable for many applications, where fidelity of the signal is important, such as in audio systems or precision timing applications.
For implementation, the oscillator circuit can be constructed using additional components such as capacitors for tuning, transistors or operational amplifiers for signal amplification, and resistors for biasing. The toroidal coil's inductance plays a vital role in determining the oscillation frequency alongside the capacitive elements in the circuit. Proper layout and component selection are crucial to minimize parasitic effects and maintain the desired performance characteristics. An 88-mH surplus telephone toroidal coil is used in a 1-kHz oscillator. Up to 8 V p-p into a high-Z load is available. THD is 0.9%.