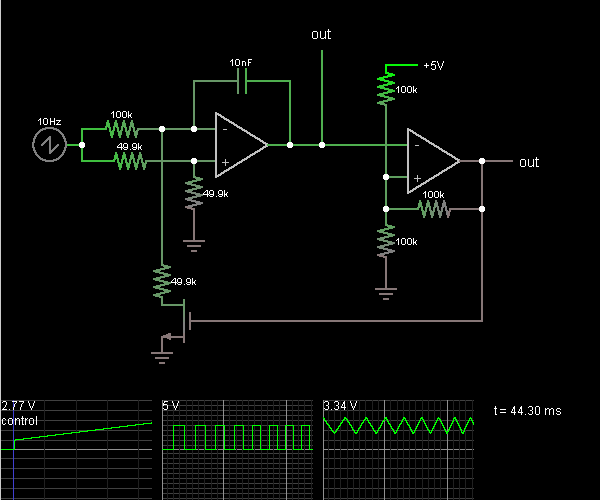
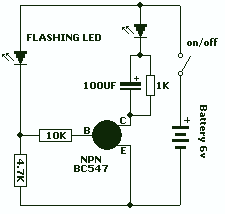
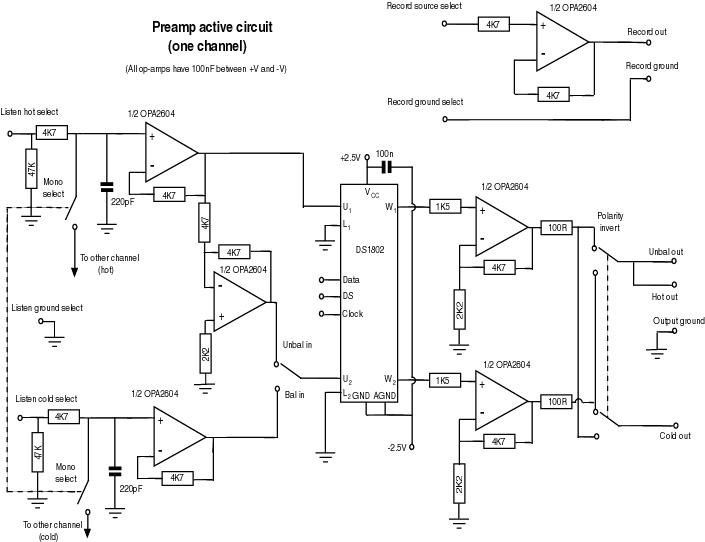
Simple LED Tester
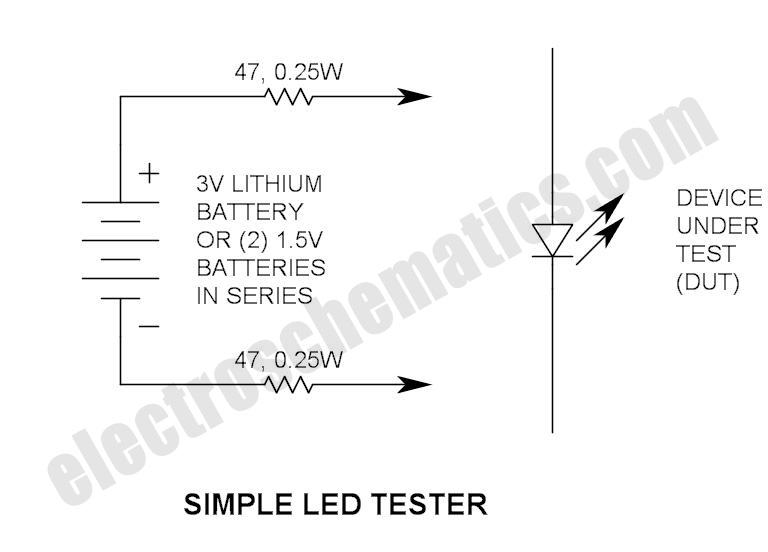
Do not let its extreme simplicity deceive you — this device is useful! Many have been made over the years, and some have even been given away as gifts. Yes, multimeter...
A multimeter is an essential instrument in electronics, used for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. Its design typically includes a digital or analog display, a rotary switch for selecting measurement modes, and input jacks for connecting test leads. The device can measure direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) voltage, making it versatile for various applications.
In a typical multimeter circuit, the core components include an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital displays, operational amplifiers for signal conditioning, and resistors for current measurement. The rotary switch allows users to select different measurement functions, which connects the appropriate circuitry to the display. The test leads, usually color-coded red for positive and black for negative, connect to the circuit under test.
For enhanced functionality, some multimeters incorporate features such as continuity testing, diode testing, and temperature measurement. These additional capabilities are achieved through specialized circuitry and sensors. The inclusion of a microcontroller can further expand the device's features, allowing for data logging and advanced computations.
The simplicity of a multimeter belies its utility in both professional and hobbyist applications. It is a fundamental tool for troubleshooting electrical issues, verifying circuit functionality, and conducting experiments in electronics.Do not let its extreme simplicity deceive you — this thing is useful! I have made many over the years and have even given some away as gifts. Yes multimete.. 🔗 External reference
A multimeter is an essential instrument in electronics, used for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. Its design typically includes a digital or analog display, a rotary switch for selecting measurement modes, and input jacks for connecting test leads. The device can measure direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) voltage, making it versatile for various applications.
In a typical multimeter circuit, the core components include an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for digital displays, operational amplifiers for signal conditioning, and resistors for current measurement. The rotary switch allows users to select different measurement functions, which connects the appropriate circuitry to the display. The test leads, usually color-coded red for positive and black for negative, connect to the circuit under test.
For enhanced functionality, some multimeters incorporate features such as continuity testing, diode testing, and temperature measurement. These additional capabilities are achieved through specialized circuitry and sensors. The inclusion of a microcontroller can further expand the device's features, allowing for data logging and advanced computations.
The simplicity of a multimeter belies its utility in both professional and hobbyist applications. It is a fundamental tool for troubleshooting electrical issues, verifying circuit functionality, and conducting experiments in electronics.Do not let its extreme simplicity deceive you — this thing is useful! I have made many over the years and have even given some away as gifts. Yes multimete.. 🔗 External reference

.jpg)