Simple Microphone Preamp
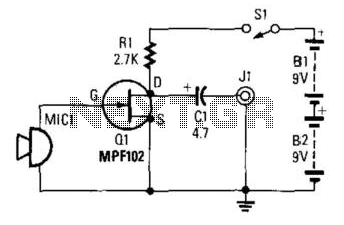
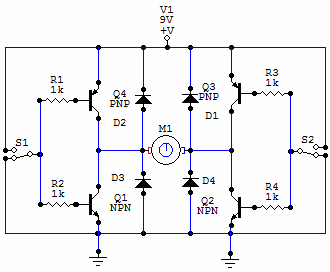
This preamplifier utilizes a small dynamic microphone connected to the gate of Q1. R1 acts as a load resistor. The audio output is taken from the negative side of C1 to ground. The output voltage will range between 10 and 100 mVpp, depending on the specifications of the microphone.
The described preamplifier circuit is designed to amplify low-level audio signals generated by a small dynamic microphone. The microphone serves as the input transducer, converting sound waves into electrical signals. The gate of Q1, which is typically a field-effect transistor (FET), is the primary amplification component in this configuration.
R1, the load resistor, plays a crucial role in setting the operating point of the transistor and determining the gain of the amplifier. The value of R1 can be selected based on the desired output characteristics and the specific microphone being used. The audio signal is extracted from the negative terminal of capacitor C1, which serves to block any DC component from the output, allowing only the AC audio signal to pass through to subsequent stages of processing or amplification.
The output voltage range of 10 to 100 mVpp indicates the circuit's sensitivity to variations in microphone performance, as different microphones will produce varying output levels based on their design and acoustic environment. This preamp circuit is suitable for applications where low-level audio signals need to be amplified for further processing, such as in audio recording systems, public address systems, or any application requiring sound capture and amplification.
Overall, this preamplifier design emphasizes simplicity and efficiency, making it an effective choice for integrating small dynamic microphones into larger audio systems. Proper attention to component selection and circuit layout will enhance performance and reliability in practical applications. This preamp uses a small dynamic microphone coupled to the gate of Ql. R1 is a load resistor. Audio is taken out b etween the negative side of CI and ground. Output will be between 10 and 100 mVpp, depending on the microphone.
The described preamplifier circuit is designed to amplify low-level audio signals generated by a small dynamic microphone. The microphone serves as the input transducer, converting sound waves into electrical signals. The gate of Q1, which is typically a field-effect transistor (FET), is the primary amplification component in this configuration.
R1, the load resistor, plays a crucial role in setting the operating point of the transistor and determining the gain of the amplifier. The value of R1 can be selected based on the desired output characteristics and the specific microphone being used. The audio signal is extracted from the negative terminal of capacitor C1, which serves to block any DC component from the output, allowing only the AC audio signal to pass through to subsequent stages of processing or amplification.
The output voltage range of 10 to 100 mVpp indicates the circuit's sensitivity to variations in microphone performance, as different microphones will produce varying output levels based on their design and acoustic environment. This preamp circuit is suitable for applications where low-level audio signals need to be amplified for further processing, such as in audio recording systems, public address systems, or any application requiring sound capture and amplification.
Overall, this preamplifier design emphasizes simplicity and efficiency, making it an effective choice for integrating small dynamic microphones into larger audio systems. Proper attention to component selection and circuit layout will enhance performance and reliability in practical applications. This preamp uses a small dynamic microphone coupled to the gate of Ql. R1 is a load resistor. Audio is taken out b etween the negative side of CI and ground. Output will be between 10 and 100 mVpp, depending on the microphone.