Simple ni-cad battery charger
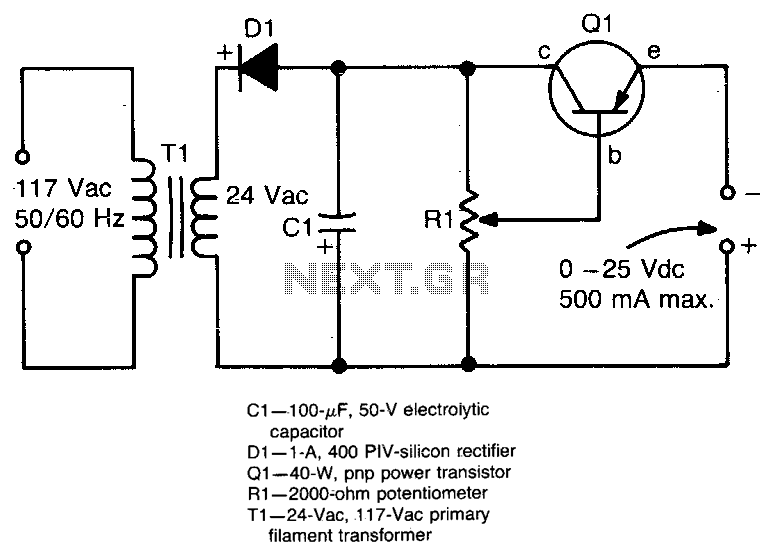
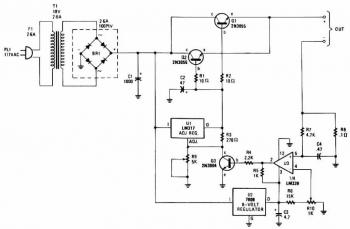
This circuit provides an adjustable output voltage of up to 35 V DC with a maximum output current of 50 mA. The transistor Q1 dissipates significant heat and must be mounted on a heatsink.
The circuit in question is designed to deliver a regulated output voltage that can be adjusted within the range of 0 to 35 volts DC, making it suitable for various applications requiring a stable power supply. The maximum output current is specified at 50 mA, indicating that the circuit is intended for low-power devices.
At the core of this circuit is transistor Q1, which plays a crucial role in voltage regulation. The choice of transistor is critical, as it must handle the power dissipation effectively. Given that Q1 dissipates considerable heat during operation, it is essential to attach it to a heatsink. The heatsink will aid in dissipating the heat generated, thereby preventing thermal overload and ensuring reliable operation.
The adjustable output voltage feature is typically achieved using a potentiometer or a variable resistor connected to the base of the transistor. This setup allows for fine-tuning the output voltage according to the specific requirements of the load. Additionally, the circuit may include feedback mechanisms to stabilize the output voltage against fluctuations in load current or input voltage.
To ensure optimal performance, it is recommended to use a transistor with a suitable power rating and thermal resistance. The heatsink should be chosen based on the thermal characteristics of the transistor and the expected ambient temperature to maintain safe operating conditions.
Overall, this circuit is a versatile solution for applications needing adjustable voltage levels, with careful consideration of thermal management to enhance reliability and efficiency.This circuit provides an adjustable output voltage up to 35 Vdc and maximum output current of 50 mA Transistor Ql dissipates quite a bit of heat and must be mounted on a heatsink.
The circuit in question is designed to deliver a regulated output voltage that can be adjusted within the range of 0 to 35 volts DC, making it suitable for various applications requiring a stable power supply. The maximum output current is specified at 50 mA, indicating that the circuit is intended for low-power devices.
At the core of this circuit is transistor Q1, which plays a crucial role in voltage regulation. The choice of transistor is critical, as it must handle the power dissipation effectively. Given that Q1 dissipates considerable heat during operation, it is essential to attach it to a heatsink. The heatsink will aid in dissipating the heat generated, thereby preventing thermal overload and ensuring reliable operation.
The adjustable output voltage feature is typically achieved using a potentiometer or a variable resistor connected to the base of the transistor. This setup allows for fine-tuning the output voltage according to the specific requirements of the load. Additionally, the circuit may include feedback mechanisms to stabilize the output voltage against fluctuations in load current or input voltage.
To ensure optimal performance, it is recommended to use a transistor with a suitable power rating and thermal resistance. The heatsink should be chosen based on the thermal characteristics of the transistor and the expected ambient temperature to maintain safe operating conditions.
Overall, this circuit is a versatile solution for applications needing adjustable voltage levels, with careful consideration of thermal management to enhance reliability and efficiency.This circuit provides an adjustable output voltage up to 35 Vdc and maximum output current of 50 mA Transistor Ql dissipates quite a bit of heat and must be mounted on a heatsink.