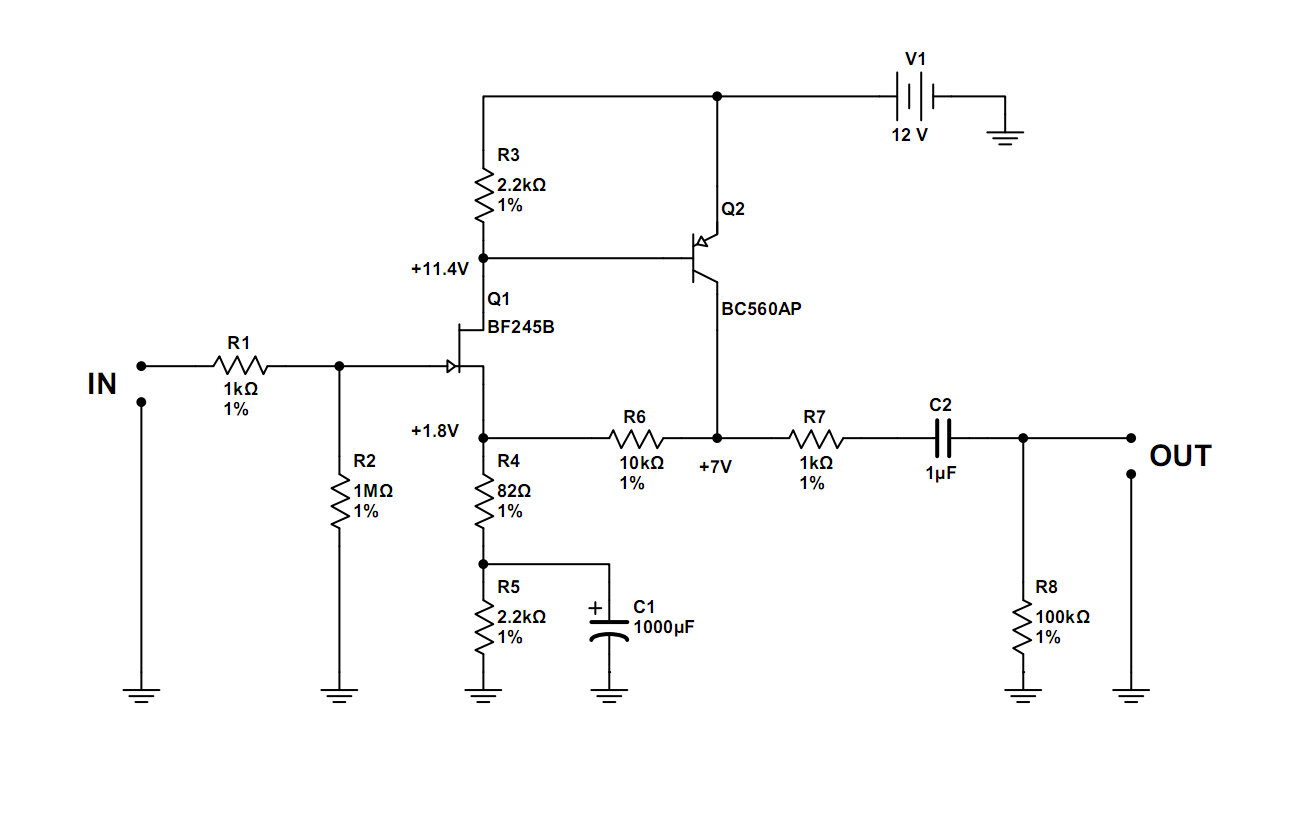
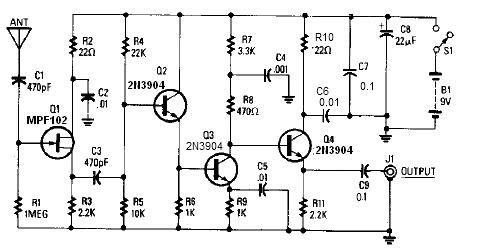
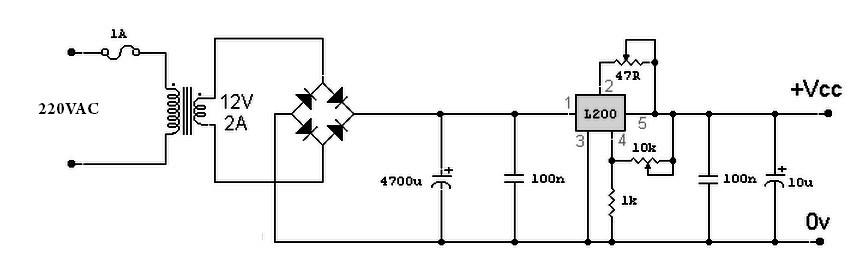
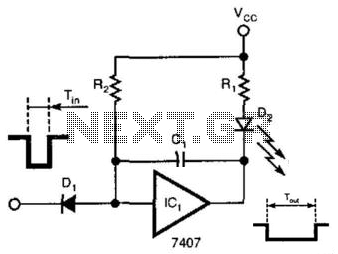
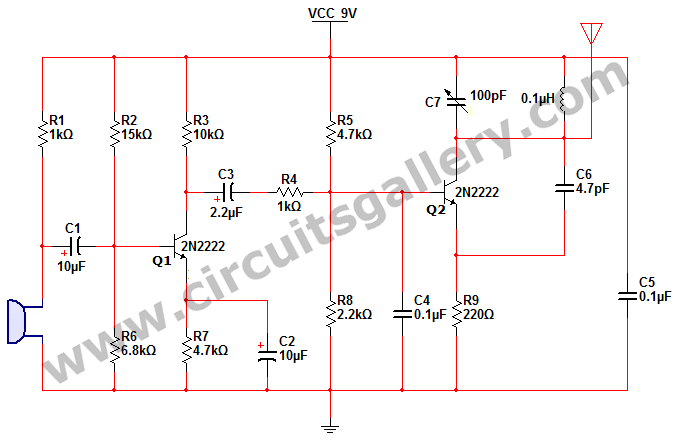
Simple quality-oriented PA 02

The differential input stage utilizes the integrated differential transistors 2SC1583 and 2SA798, with the amplified signal directed to the power amplifier tubes VT5 and VT6. The performance of the charge directly influences the overall performance of the power amplifier circuit. The design incorporates the charge difference of the 2SC1583 and 2SA798 to enhance the stability of the circuit and achieve superior sound quality. The transistors 2SK134 and 2SJ49 are well-regarded in the audio industry for their warm and delicate sound characteristics. This amplifier appeals to enthusiasts who appreciate the unique auditory qualities provided by these components, ensuring an exceptional sound experience.
The differential input stage is a critical component in the design of high-fidelity audio amplifiers. It employs the 2SC1583 and 2SA798 transistors, which are known for their excellent charge handling capabilities. These transistors are configured to amplify the input audio signal while minimizing noise and distortion. The output from this stage is fed into the power amplifier tubes, specifically VT5 and VT6, which further amplify the signal for driving loudspeakers.
The choice of transistors in the differential stage is pivotal, as their charge performance dictates the overall efficacy of the amplifier circuit. By utilizing the charge difference between the 2SC1583 and 2SA798, the circuit achieves enhanced stability, which is essential for maintaining sound quality across various operating conditions. This design approach not only improves linearity but also contributes to a more dynamic response, allowing for the reproduction of a wider range of audio frequencies with clarity.
Furthermore, the inclusion of the 2SK134 and 2SJ49 transistors in the amplifier circuit is a testament to the design's focus on sound quality. These components are celebrated in the audio community for their ability to produce a warm and nuanced sound profile, which is often sought after by audiophiles. The synergy between these transistors and the overall circuit design ensures that the amplifier delivers a rich listening experience, characterized by depth and detail.
In summary, the differential input stage, combined with carefully selected power amplifier tubes and transistors, forms the backbone of a high-quality audio amplifier. This configuration not only enhances the stability and performance of the amplifier but also ensures that the sound produced is both warm and engaging, appealing to those who appreciate the finer nuances of audio reproduction.Differential input stage uses the integrated differential charge 2SC15 8 3 and 2SA798, the amplified signal is VT3.VT4 direct anyone to the power amplifier tubes VT5, VT6. Poor charge performance directly determines the performance of the entire power amplifier circuit, so the machine using the difference in charge of loading 2SC1583 and 2SA798, to improve the stability of the machine, and get good sound quality 2SK134,2SJ49 audio industry can be described as the old pine here, the tube is known to sound warm and delicate, with a tube and charm. So for this Xiao Jin rang interested in fancy vines have lovers taste, use this tube, but also to ensure that this amp sounds such as sound quality
The differential input stage is a critical component in the design of high-fidelity audio amplifiers. It employs the 2SC1583 and 2SA798 transistors, which are known for their excellent charge handling capabilities. These transistors are configured to amplify the input audio signal while minimizing noise and distortion. The output from this stage is fed into the power amplifier tubes, specifically VT5 and VT6, which further amplify the signal for driving loudspeakers.
The choice of transistors in the differential stage is pivotal, as their charge performance dictates the overall efficacy of the amplifier circuit. By utilizing the charge difference between the 2SC1583 and 2SA798, the circuit achieves enhanced stability, which is essential for maintaining sound quality across various operating conditions. This design approach not only improves linearity but also contributes to a more dynamic response, allowing for the reproduction of a wider range of audio frequencies with clarity.
Furthermore, the inclusion of the 2SK134 and 2SJ49 transistors in the amplifier circuit is a testament to the design's focus on sound quality. These components are celebrated in the audio community for their ability to produce a warm and nuanced sound profile, which is often sought after by audiophiles. The synergy between these transistors and the overall circuit design ensures that the amplifier delivers a rich listening experience, characterized by depth and detail.
In summary, the differential input stage, combined with carefully selected power amplifier tubes and transistors, forms the backbone of a high-quality audio amplifier. This configuration not only enhances the stability and performance of the amplifier but also ensures that the sound produced is both warm and engaging, appealing to those who appreciate the finer nuances of audio reproduction.Differential input stage uses the integrated differential charge 2SC15 8 3 and 2SA798, the amplified signal is VT3.VT4 direct anyone to the power amplifier tubes VT5, VT6. Poor charge performance directly determines the performance of the entire power amplifier circuit, so the machine using the difference in charge of loading 2SC1583 and 2SA798, to improve the stability of the machine, and get good sound quality 2SK134,2SJ49 audio industry can be described as the old pine here, the tube is known to sound warm and delicate, with a tube and charm. So for this Xiao Jin rang interested in fancy vines have lovers taste, use this tube, but also to ensure that this amp sounds such as sound quality