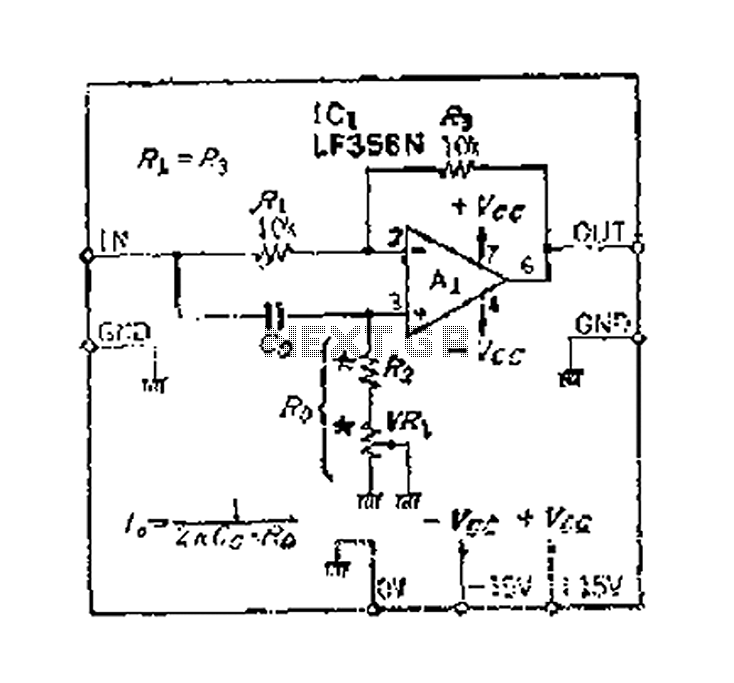
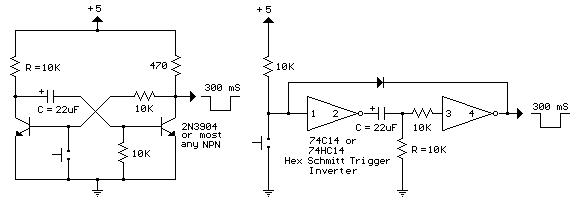
Simple phase detector
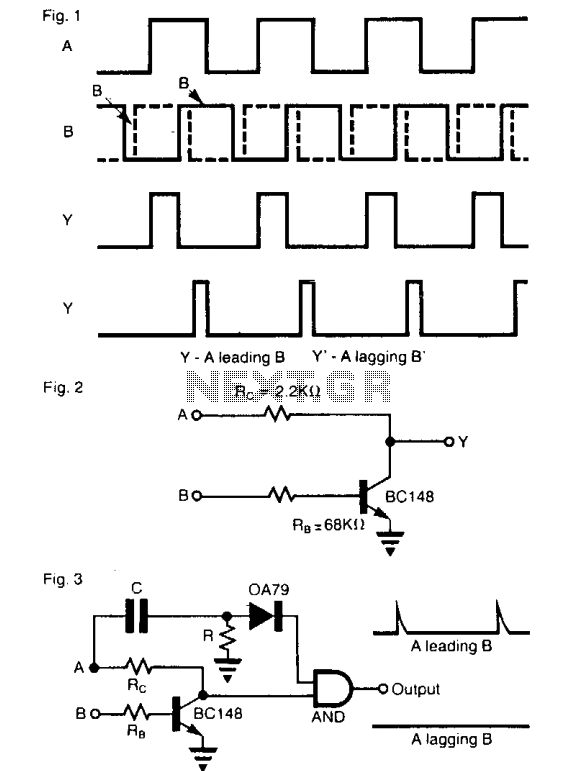
The operation of the circuit resembles that of an enabled inverter, where the output Y equals B when input A is high. If A is low, the output remains low, regardless of the state of B. When the signals A and B1 are connected to the inputs of this gate, the output Y generates a pulse train signal (denoted as Y or Yl) with a pulse duration corresponding to the phase difference between the two input signals. This circuit is suitable for measuring phase differences ranging from 0 to 180 degrees. Its functionality is comparable to that of circuits like the Exclusive OR gate, which are utilized for similar purposes. Additionally, this method allows for the determination of both leading and lagging positions of the signals using an AND gate. The phase difference, along with information about the leading and lagging aspects, provides comprehensive data about the phases of the two signals within a range of 0 to 360 degrees.
The circuit functions as a phase detector, utilizing an enabled inverter configuration to ascertain the relationship between two input signals, A and B1. The inverter's output, Y, operates based on the logical state of input A. When A is high (logic 1), the output Y reflects the state of B, effectively enabling the transmission of B's logic level. Conversely, when A is low (logic 0), the output Y is forced to a low state (logic 0), rendering it independent of B's state.
Connecting the signals A and B1 to the inputs of the circuit results in the generation of a pulse train signal at the output. The duration of these pulses is directly related to the phase difference between the two input signals. This relationship allows the circuit to measure phase differences within a range of 0 to 180 degrees accurately. The output pulse train can be analyzed to determine the timing discrepancies between A and B1, facilitating phase measurements critical in various applications, including signal processing and communication systems.
Moreover, the circuit can be enhanced by incorporating an AND gate to further analyze the phase relationship. The leading and lagging positions of the signals can be identified, providing additional context to the phase measurement. By evaluating both the phase difference and the leading/lagging information, a complete understanding of the phase relationship between the two signals can be achieved, extending the measurement capabilities to a full 360-degree range. This comprehensive analysis is essential for applications requiring precise synchronization and timing between multiple signals.The operation of the circuit is like an enabled inverter, that is, the output Y = B provided A is high. If A is low, output is low (independent of the state of B). When the signals A and or B1 are connected to the inputs A and of this gate the output Y is a pulse train signal (shown a Y or Yl) which has a pulse duration equal to the phase difference between the two signals.
The circuit is directly suitable for phase difference measurement from zero to 180°. This performance is similar to the circuits like the Exclusive OR gate used for this purpose. With this method leading and lagging positions of the signals can also be found using an AND gate. Phase difference measured along with the leading and lagging information gives complete information about the phases of the two signals between zero and 360°.
The circuit functions as a phase detector, utilizing an enabled inverter configuration to ascertain the relationship between two input signals, A and B1. The inverter's output, Y, operates based on the logical state of input A. When A is high (logic 1), the output Y reflects the state of B, effectively enabling the transmission of B's logic level. Conversely, when A is low (logic 0), the output Y is forced to a low state (logic 0), rendering it independent of B's state.
Connecting the signals A and B1 to the inputs of the circuit results in the generation of a pulse train signal at the output. The duration of these pulses is directly related to the phase difference between the two input signals. This relationship allows the circuit to measure phase differences within a range of 0 to 180 degrees accurately. The output pulse train can be analyzed to determine the timing discrepancies between A and B1, facilitating phase measurements critical in various applications, including signal processing and communication systems.
Moreover, the circuit can be enhanced by incorporating an AND gate to further analyze the phase relationship. The leading and lagging positions of the signals can be identified, providing additional context to the phase measurement. By evaluating both the phase difference and the leading/lagging information, a complete understanding of the phase relationship between the two signals can be achieved, extending the measurement capabilities to a full 360-degree range. This comprehensive analysis is essential for applications requiring precise synchronization and timing between multiple signals.The operation of the circuit is like an enabled inverter, that is, the output Y = B provided A is high. If A is low, output is low (independent of the state of B). When the signals A and or B1 are connected to the inputs A and of this gate the output Y is a pulse train signal (shown a Y or Yl) which has a pulse duration equal to the phase difference between the two signals.
The circuit is directly suitable for phase difference measurement from zero to 180°. This performance is similar to the circuits like the Exclusive OR gate used for this purpose. With this method leading and lagging positions of the signals can also be found using an AND gate. Phase difference measured along with the leading and lagging information gives complete information about the phases of the two signals between zero and 360°.