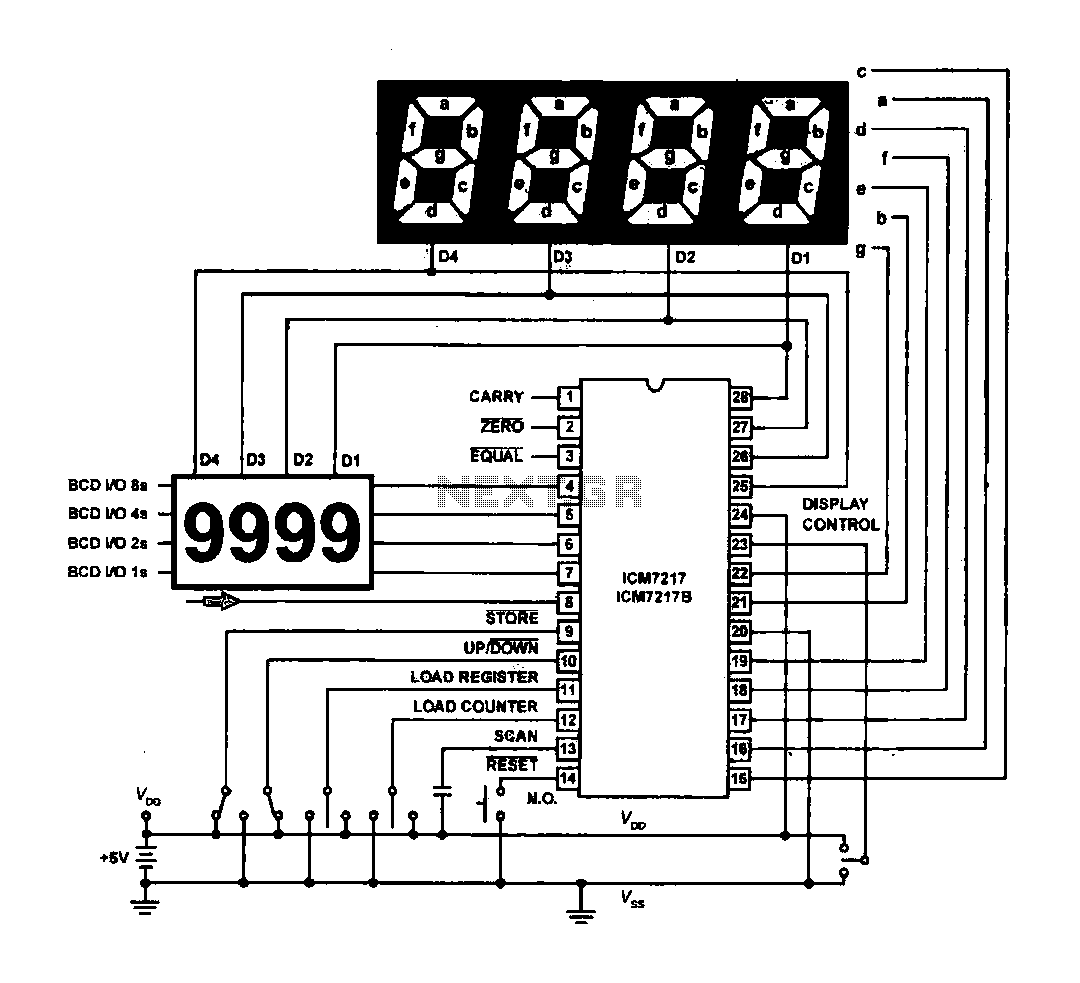
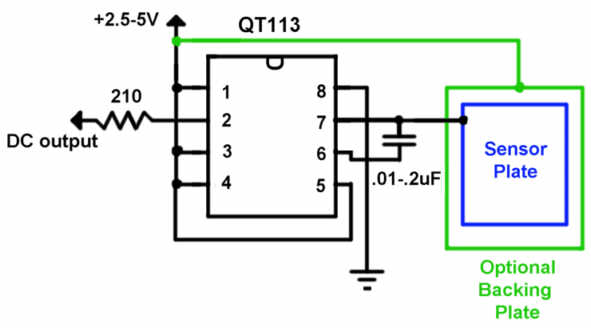
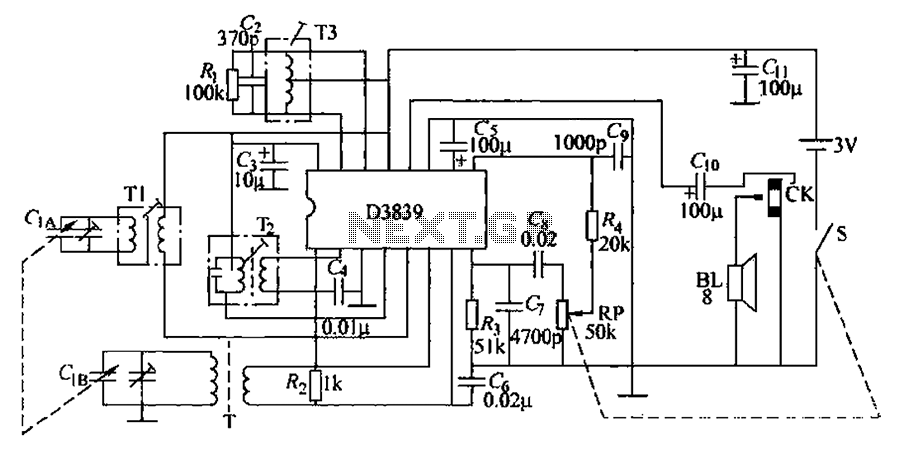
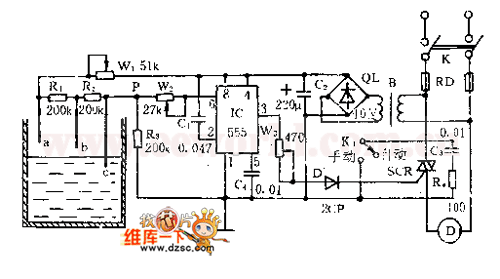
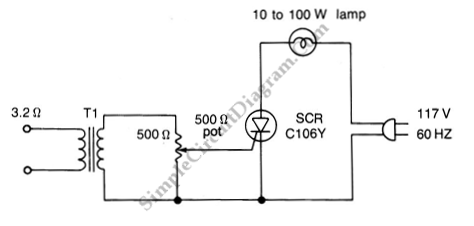
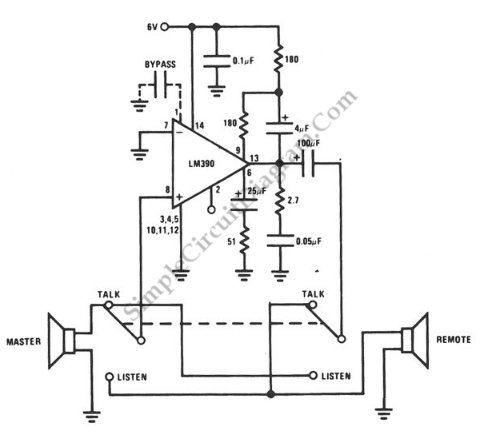
Simple PreAmp MIC Circuit
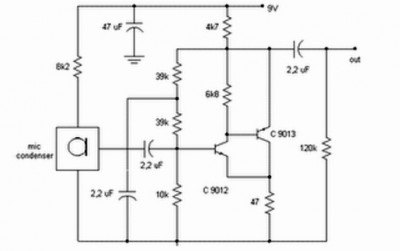
Preamp circuits are used in front of an RF oscillator to create an RF transmitter that is highly sensitive to sound. A microphone preamp must provide stable gain.
Preamp circuits play a crucial role in the functioning of RF transmitters by amplifying audio signals before they are modulated onto a radio frequency carrier. The primary function of a microphone preamp is to increase the amplitude of weak audio signals generated by microphones, ensuring that the subsequent RF circuitry receives a strong and clear input.
In designing a preamp circuit for an RF transmitter, several key components are typically included. These may consist of operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, capacitors, and sometimes inductors, depending on the required frequency response and gain characteristics. The op-amp serves as the core amplification element, where its gain can be adjusted through feedback resistors to achieve the desired level of amplification while maintaining low noise levels.
Stability in gain is critical for a microphone preamp, as variations can lead to distortion or loss of audio fidelity. To ensure stable gain across a range of input levels, the circuit may incorporate negative feedback mechanisms. Additionally, proper power supply decoupling is essential to minimize noise and interference, which can adversely affect the performance of the RF transmitter.
The preamp circuit should also be designed to handle the frequency response of the audio signals, typically ranging from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, while ensuring that the output signal is compatible with the RF oscillator's input requirements. Filtering components may be added to eliminate unwanted frequencies and improve the overall signal quality.
In summary, the design of a preamp circuit for an RF transmitter involves careful consideration of component selection, gain stability, and frequency response to achieve optimal performance in sound sensitivity and clarity.preamp circuits use infront an RF oscilator to make an RF transmitter that is very sensitive to sound. A microphone preamp must provide stable gain. 🔗 External reference
Preamp circuits play a crucial role in the functioning of RF transmitters by amplifying audio signals before they are modulated onto a radio frequency carrier. The primary function of a microphone preamp is to increase the amplitude of weak audio signals generated by microphones, ensuring that the subsequent RF circuitry receives a strong and clear input.
In designing a preamp circuit for an RF transmitter, several key components are typically included. These may consist of operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, capacitors, and sometimes inductors, depending on the required frequency response and gain characteristics. The op-amp serves as the core amplification element, where its gain can be adjusted through feedback resistors to achieve the desired level of amplification while maintaining low noise levels.
Stability in gain is critical for a microphone preamp, as variations can lead to distortion or loss of audio fidelity. To ensure stable gain across a range of input levels, the circuit may incorporate negative feedback mechanisms. Additionally, proper power supply decoupling is essential to minimize noise and interference, which can adversely affect the performance of the RF transmitter.
The preamp circuit should also be designed to handle the frequency response of the audio signals, typically ranging from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, while ensuring that the output signal is compatible with the RF oscillator's input requirements. Filtering components may be added to eliminate unwanted frequencies and improve the overall signal quality.
In summary, the design of a preamp circuit for an RF transmitter involves careful consideration of component selection, gain stability, and frequency response to achieve optimal performance in sound sensitivity and clarity.preamp circuits use infront an RF oscilator to make an RF transmitter that is very sensitive to sound. A microphone preamp must provide stable gain. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713