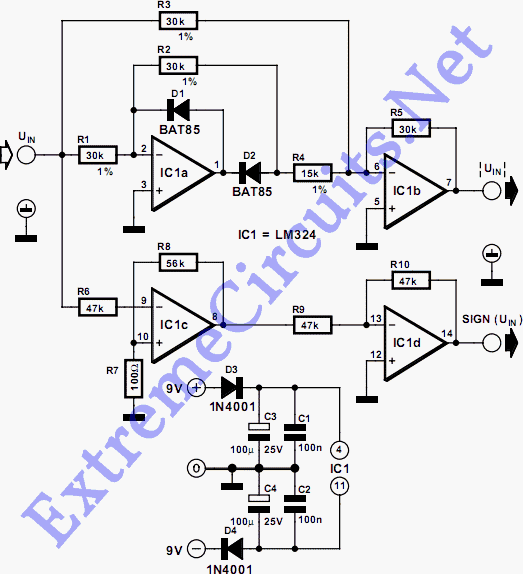
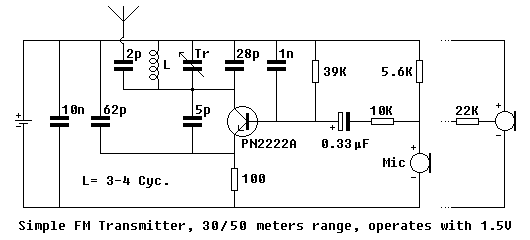
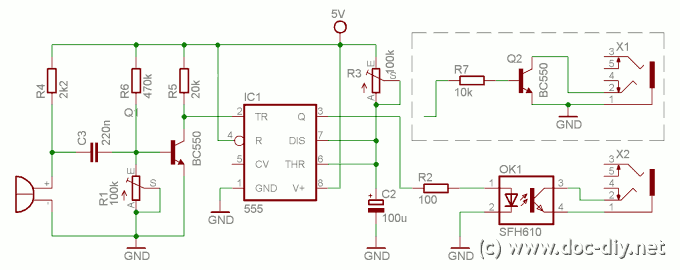
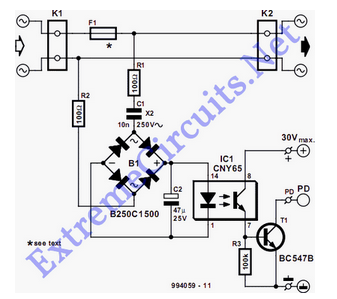
Simple RF Detector for 2 m
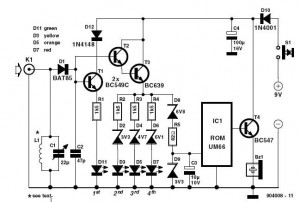
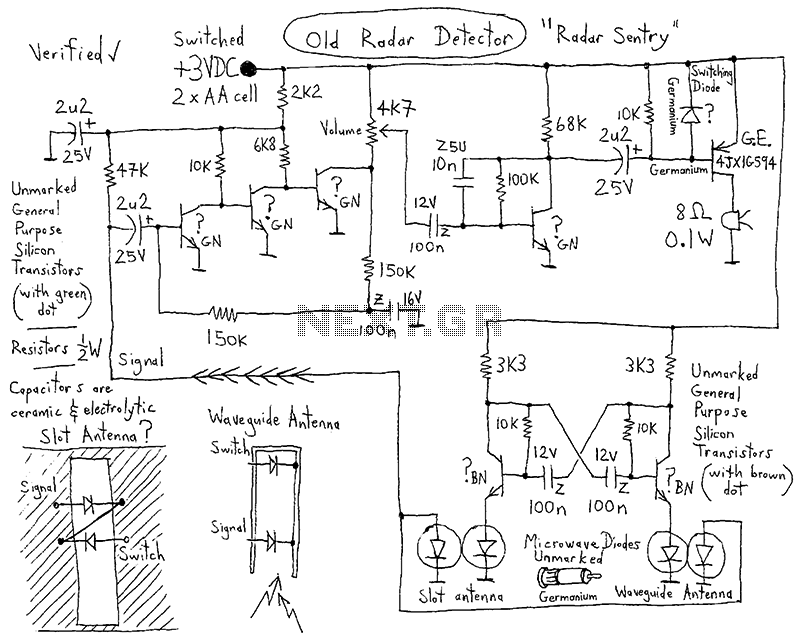
This simple circuit helps detect RF radiation leaking from transmitters, improper joints, broken cables, or equipment with inadequate RF shielding.
This circuit is designed to identify and measure radio frequency (RF) radiation emissions, which can indicate issues such as faulty connections, damaged cables, or insufficient shielding in electronic devices. The core component of the circuit is a sensitive RF detector, typically implemented using a diode or a specialized RF sensor module.
The circuit operates by capturing the RF signals present in the environment and converting them into a measurable voltage output. This output can then be displayed on an analog or digital meter, allowing the user to assess the level of RF radiation.
To enhance the sensitivity and accuracy of the measurements, the circuit may include additional components such as amplifiers, filters, and capacitors. An operational amplifier can be used to boost the signal strength, while a band-pass filter can help isolate the frequency range of interest, eliminating unwanted noise from other sources.
Furthermore, the design may incorporate a microcontroller to process the detected signals, providing a more sophisticated analysis of the RF emissions. The microcontroller can be programmed to trigger alarms or visual indicators when radiation levels exceed predefined thresholds, making the circuit not only a diagnostic tool but also a safety device.
Power supply considerations are also crucial; the circuit can be powered by batteries for portability or connected to a stable power source for continuous monitoring. Proper grounding and shielding techniques should be employed in the circuit layout to prevent interference and ensure accurate readings.
Overall, this RF radiation detection circuit serves as an essential tool for troubleshooting and maintaining the integrity of RF equipment, ensuring compliance with safety standards and optimal performance.This simple circuit helps you sniff out RF radiation leaking from your transmitter, improper joints, a broken cable or equipment with poor RF shielding. Th. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to identify and measure radio frequency (RF) radiation emissions, which can indicate issues such as faulty connections, damaged cables, or insufficient shielding in electronic devices. The core component of the circuit is a sensitive RF detector, typically implemented using a diode or a specialized RF sensor module.
The circuit operates by capturing the RF signals present in the environment and converting them into a measurable voltage output. This output can then be displayed on an analog or digital meter, allowing the user to assess the level of RF radiation.
To enhance the sensitivity and accuracy of the measurements, the circuit may include additional components such as amplifiers, filters, and capacitors. An operational amplifier can be used to boost the signal strength, while a band-pass filter can help isolate the frequency range of interest, eliminating unwanted noise from other sources.
Furthermore, the design may incorporate a microcontroller to process the detected signals, providing a more sophisticated analysis of the RF emissions. The microcontroller can be programmed to trigger alarms or visual indicators when radiation levels exceed predefined thresholds, making the circuit not only a diagnostic tool but also a safety device.
Power supply considerations are also crucial; the circuit can be powered by batteries for portability or connected to a stable power source for continuous monitoring. Proper grounding and shielding techniques should be employed in the circuit layout to prevent interference and ensure accurate readings.
Overall, this RF radiation detection circuit serves as an essential tool for troubleshooting and maintaining the integrity of RF equipment, ensuring compliance with safety standards and optimal performance.This simple circuit helps you sniff out RF radiation leaking from your transmitter, improper joints, a broken cable or equipment with poor RF shielding. Th. 🔗 External reference