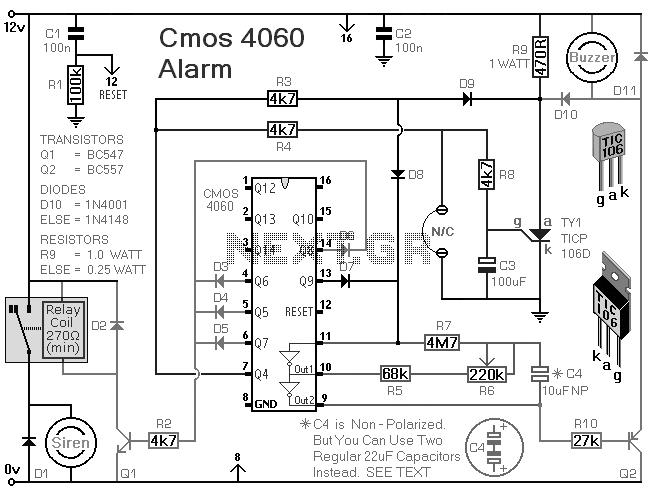
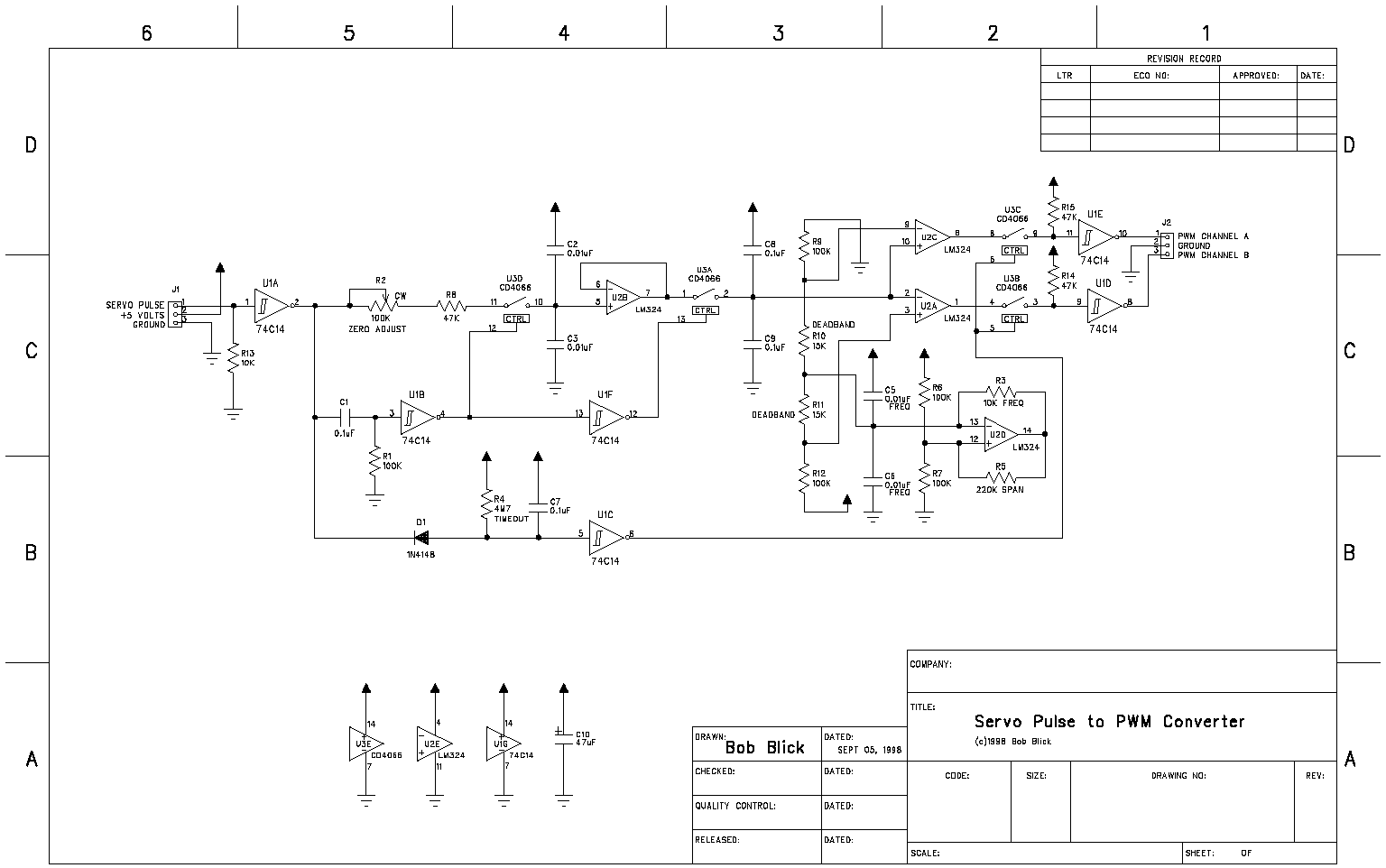
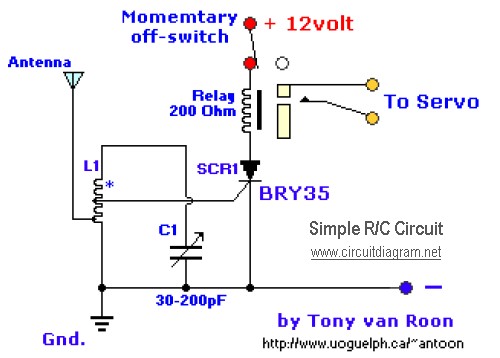
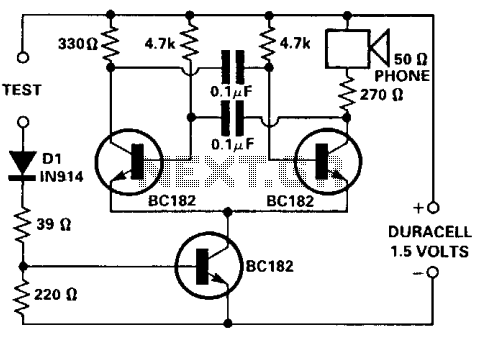
Simple Servo Testers
This is a simple servo tester designed to thoroughly evaluate the capabilities of nearly any modern servo. It features two pushbuttons, labeled CENTRE and SWEEP, along with a potentiometer that functions in the following manner:
The servo tester circuit is primarily composed of a microcontroller, which processes the input from the pushbuttons and the potentiometer, generating control signals for the servo motor. The CENTRE button is used to position the servo at its neutral point, typically at a 90-degree angle, which is crucial for ensuring that the servo operates correctly during testing. The SWEEP button allows the servo to move through its full range of motion, providing a comprehensive assessment of the servo's responsiveness and range.
The potentiometer is integrated into the circuit to allow for manual adjustment of the servo's position within its operational limits. By turning the potentiometer, the user can set the desired angle, which the microcontroller then translates into a corresponding pulse width modulation (PWM) signal sent to the servo. This signal controls the position of the servo horn accurately, enabling precise testing of the servo's performance.
Power supply considerations are essential for this circuit, as the servo tester should be powered by a stable voltage source compatible with the servo's operating voltage, typically ranging from 4.8V to 6V for most standard servos. Adequate decoupling capacitors should be placed near the power supply pins of the microcontroller to filter out noise and ensure stable operation.
Additionally, the circuit may include LED indicators to provide visual feedback on the operational status of the servo tester. These indicators can signal when the servo is in the center position or when it is actively sweeping, enhancing user experience and usability.
Overall, this simple servo tester serves as an invaluable tool for hobbyists and professionals alike, enabling the efficient evaluation and calibration of servo motors in various applications.This is a simple servo tester which will comprehensively test the capabilities of almost any modern servo. It has two pushbuttons, CENTRE and SWEEP and a potentiometer which works as follows: 🔗 External reference
The servo tester circuit is primarily composed of a microcontroller, which processes the input from the pushbuttons and the potentiometer, generating control signals for the servo motor. The CENTRE button is used to position the servo at its neutral point, typically at a 90-degree angle, which is crucial for ensuring that the servo operates correctly during testing. The SWEEP button allows the servo to move through its full range of motion, providing a comprehensive assessment of the servo's responsiveness and range.
The potentiometer is integrated into the circuit to allow for manual adjustment of the servo's position within its operational limits. By turning the potentiometer, the user can set the desired angle, which the microcontroller then translates into a corresponding pulse width modulation (PWM) signal sent to the servo. This signal controls the position of the servo horn accurately, enabling precise testing of the servo's performance.
Power supply considerations are essential for this circuit, as the servo tester should be powered by a stable voltage source compatible with the servo's operating voltage, typically ranging from 4.8V to 6V for most standard servos. Adequate decoupling capacitors should be placed near the power supply pins of the microcontroller to filter out noise and ensure stable operation.
Additionally, the circuit may include LED indicators to provide visual feedback on the operational status of the servo tester. These indicators can signal when the servo is in the center position or when it is actively sweeping, enhancing user experience and usability.
Overall, this simple servo tester serves as an invaluable tool for hobbyists and professionals alike, enabling the efficient evaluation and calibration of servo motors in various applications.This is a simple servo tester which will comprehensively test the capabilities of almost any modern servo. It has two pushbuttons, CENTRE and SWEEP and a potentiometer which works as follows: 🔗 External reference