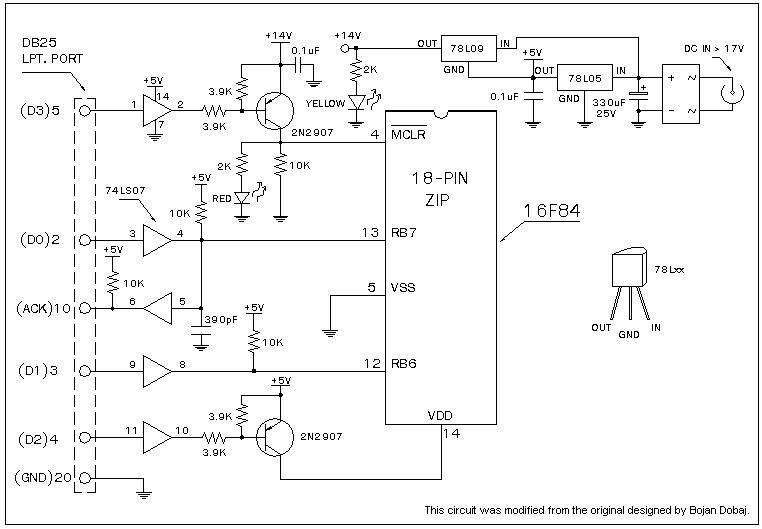
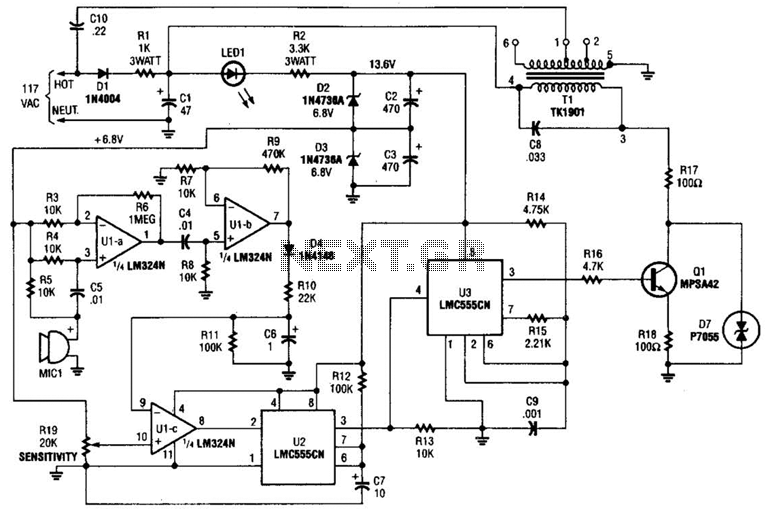
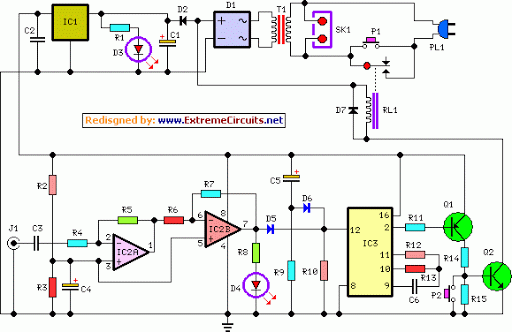
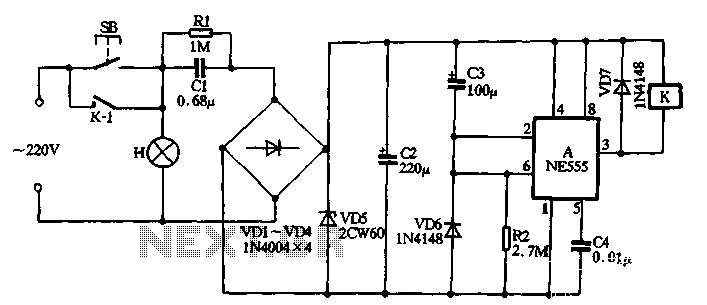
Simple Triac Circuit Circuit
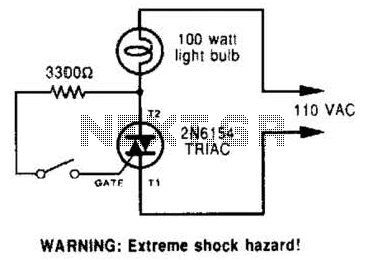
A triac can be utilized as a line-operated AC power switch that directly controls lamps, heaters, or motors. A brief current pulse into the gate activates the triac, and it remains on until the main current reverses.
A triac, or triode for alternating current, is a semiconductor device that functions as a switch for AC power applications. It is capable of controlling the flow of electrical power to various loads such as lamps, heaters, and motors. The operation of a triac is based on its ability to conduct current in both directions, making it suitable for AC circuits.
To activate a triac, a small current pulse is applied to its gate terminal. This pulse allows the triac to enter a conductive state, enabling current to flow from the anode to the cathode. Once activated, the triac remains in this conducting state as long as the current flowing through it exceeds a certain threshold, known as the holding current. This characteristic allows the triac to effectively control power delivery to the load.
An essential feature of triacs is their ability to turn off when the main current reverses. In AC applications, this typically occurs at the zero-crossing point of the voltage waveform. As the current approaches zero, the triac ceases to conduct, effectively turning off the power to the connected load. This property makes triacs advantageous for applications requiring on/off control of AC devices without the need for mechanical switching.
In practical applications, triacs are often used in conjunction with optoisolators or microcontrollers to provide isolation and control. The gate drive circuit can be designed to ensure that the pulse applied to the gate is sufficient to trigger the triac while also protecting it from overcurrent conditions. Additionally, snubber circuits may be implemented to protect the triac from voltage spikes that can occur when switching inductive loads.
Overall, triacs serve as efficient and reliable components in AC power control systems, enabling precise management of electrical energy in various applications. A triac can be used as a line-operated ac power switch that can directly control lamps, heaters, or motors. A brief and small current pulse into the gate turns the triac on; it remains on until the main current reverses.
A triac, or triode for alternating current, is a semiconductor device that functions as a switch for AC power applications. It is capable of controlling the flow of electrical power to various loads such as lamps, heaters, and motors. The operation of a triac is based on its ability to conduct current in both directions, making it suitable for AC circuits.
To activate a triac, a small current pulse is applied to its gate terminal. This pulse allows the triac to enter a conductive state, enabling current to flow from the anode to the cathode. Once activated, the triac remains in this conducting state as long as the current flowing through it exceeds a certain threshold, known as the holding current. This characteristic allows the triac to effectively control power delivery to the load.
An essential feature of triacs is their ability to turn off when the main current reverses. In AC applications, this typically occurs at the zero-crossing point of the voltage waveform. As the current approaches zero, the triac ceases to conduct, effectively turning off the power to the connected load. This property makes triacs advantageous for applications requiring on/off control of AC devices without the need for mechanical switching.
In practical applications, triacs are often used in conjunction with optoisolators or microcontrollers to provide isolation and control. The gate drive circuit can be designed to ensure that the pulse applied to the gate is sufficient to trigger the triac while also protecting it from overcurrent conditions. Additionally, snubber circuits may be implemented to protect the triac from voltage spikes that can occur when switching inductive loads.
Overall, triacs serve as efficient and reliable components in AC power control systems, enabling precise management of electrical energy in various applications. A triac can be used as a line-operated ac power switch that can directly control lamps, heaters, or motors. A brief and small current pulse into the gate turns the triac on; it remains on until the main current reverses.