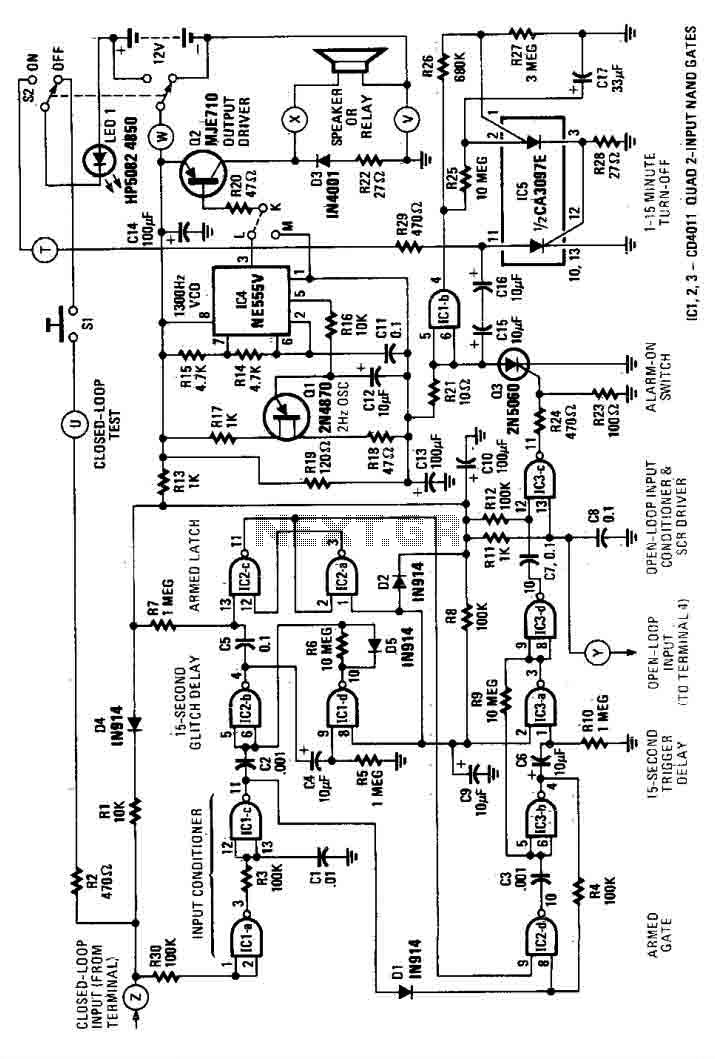
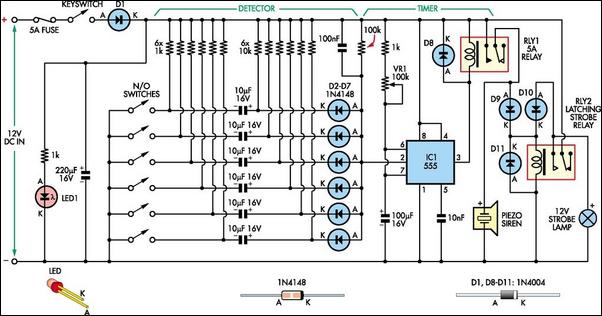
Simple Utility Mixer
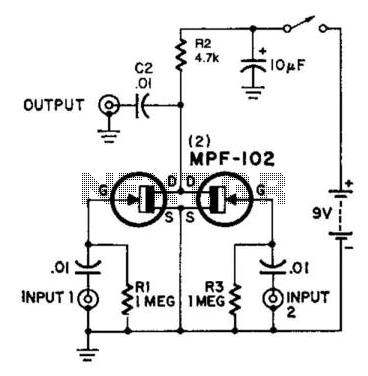
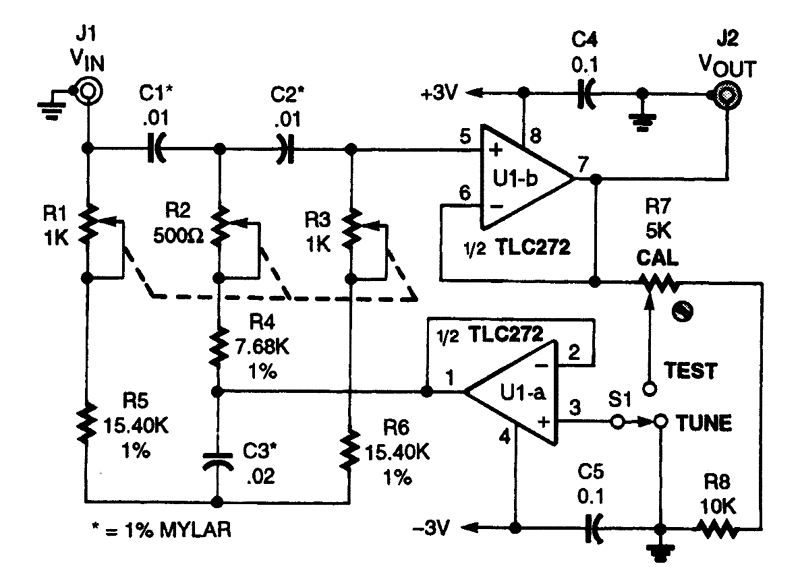
Here is an interesting mixer circuit. With it, signals from audio to high-frequency RF can be effectively combined. Additionally, this circuit provides some gain with a low noise figure. The inputs can accommodate nearly any level or impedance, and the low-impedance output can drive most tuned circuits or transistors. The device consists of two similar FET amplifier stages with a common load resistor (R2). Each FET generates a signal across this resistor, leading to a form of cancellation and resulting in a difference signal. To achieve less gain, R2 can be reduced to 220 ohms. This modification will not affect the mixing capability.
The described mixer circuit is designed to combine various signal types, ranging from audio frequencies to high-frequency radio frequency (RF) signals. The circuit operates using two Field Effect Transistor (FET) amplifier stages, which are configured to work together with a shared load resistor, denoted as R2. This configuration is crucial for the mixing process, as each FET amplifies its respective input signal, which is then developed across the common load resistor.
The unique aspect of this circuit is its ability to produce a difference signal due to the cancellation effect that occurs when the two amplified signals interact at the load resistor. This principle is fundamental in many RF applications, where mixing different frequencies is essential for modulation and demodulation processes.
The flexibility of the circuit is noteworthy, as it can handle a wide range of input levels and impedances, making it versatile for various applications. The low-impedance output is particularly advantageous, allowing the circuit to drive most tuned circuits or transistors without significant signal degradation.
For users seeking to adjust the gain of the circuit, it is recommended to modify the value of the load resistor R2. By reducing R2 to 220 ohms, the gain can be decreased without compromising the mixer’s fundamental mixing capabilities. This adjustment allows for greater control over the output signal, catering to specific application requirements while maintaining the integrity of the mixing function. Overall, this mixer circuit represents a robust solution for combining signals across a broad frequency spectrum while ensuring low noise and effective gain characteristics. Here"s an interesting mixer circuit. With it you can effectively combine signals from audio to high-fre-quency RF. Als o, as a special bonus, this circuit will provide some gain at a low noise figure. The inputs can be of almost any level or impedance, and the output (low-Z) will drive most tuned circuits or transistors. Basically, the device consists of two similar FET amplifier stages with a common load resistor (R2). Each FET develops a signal across this resistor, a form of cancellation occurs, and a difference signal results.
If you want less gain, try reducing R2 to 2 200-. This modification will not affect the mixing ability.
The described mixer circuit is designed to combine various signal types, ranging from audio frequencies to high-frequency radio frequency (RF) signals. The circuit operates using two Field Effect Transistor (FET) amplifier stages, which are configured to work together with a shared load resistor, denoted as R2. This configuration is crucial for the mixing process, as each FET amplifies its respective input signal, which is then developed across the common load resistor.
The unique aspect of this circuit is its ability to produce a difference signal due to the cancellation effect that occurs when the two amplified signals interact at the load resistor. This principle is fundamental in many RF applications, where mixing different frequencies is essential for modulation and demodulation processes.
The flexibility of the circuit is noteworthy, as it can handle a wide range of input levels and impedances, making it versatile for various applications. The low-impedance output is particularly advantageous, allowing the circuit to drive most tuned circuits or transistors without significant signal degradation.
For users seeking to adjust the gain of the circuit, it is recommended to modify the value of the load resistor R2. By reducing R2 to 220 ohms, the gain can be decreased without compromising the mixer’s fundamental mixing capabilities. This adjustment allows for greater control over the output signal, catering to specific application requirements while maintaining the integrity of the mixing function. Overall, this mixer circuit represents a robust solution for combining signals across a broad frequency spectrum while ensuring low noise and effective gain characteristics. Here"s an interesting mixer circuit. With it you can effectively combine signals from audio to high-fre-quency RF. Als o, as a special bonus, this circuit will provide some gain at a low noise figure. The inputs can be of almost any level or impedance, and the output (low-Z) will drive most tuned circuits or transistors. Basically, the device consists of two similar FET amplifier stages with a common load resistor (R2). Each FET develops a signal across this resistor, a form of cancellation occurs, and a difference signal results.
If you want less gain, try reducing R2 to 2 200-. This modification will not affect the mixing ability.