SimpleCircuit IF Signal Generator
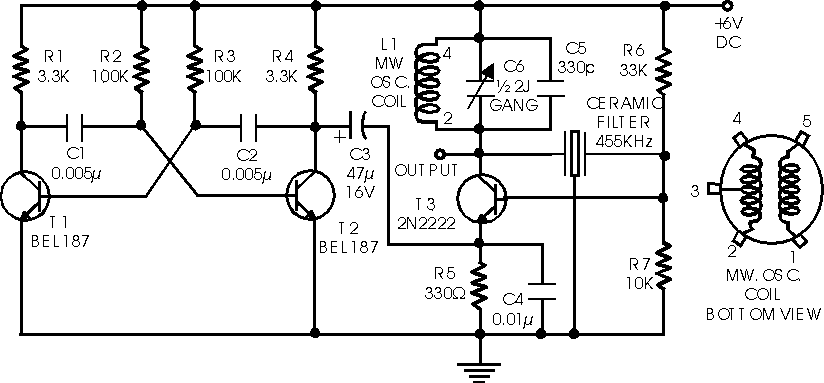
This is a range of IF signal circuits that may be of interest to radio hobbyists and professionals alike. Transistors T1 and T2 form an astable multivibrator oscillating in the audio frequency range of 1 to 2 kHz. An RF oscillator is built around transistor T3. A 455 kHz filter/resonator is used for stable reception. The audio frequency from the multivibrator is coupled from the collector of transistor T2 to the emitter of transistor T3 through capacitor C3. The tank circuit at the collector of transistor T3 is formed using a medium wave oscillator coil from a transistor radio, a fixed 100 pF capacitor C5, and half of a unit capacitor (C6). The oscillator frequency can be easily adjusted for any other medium frequency by using a filter or resonator of that frequency and by making appropriate changes in the tank circuit at the collector of transistor T3. Slight adjustments can be made by varying the values of resistors R6 and R7, if required.
The described circuit features a dual-stage configuration utilizing transistors T1 and T2 to create an astable multivibrator. This multivibrator generates a square wave signal with a frequency adjustable between 1 kHz and 2 kHz, making it suitable for audio applications. The output from the multivibrator is fed into the RF oscillator circuit, which is centered around transistor T3. This transistor operates as a high-frequency oscillator, producing a carrier frequency of 455 kHz, a standard frequency used in many radio applications.
Capacitor C3 serves as a coupling capacitor, allowing the audio frequency signal to pass while blocking any DC components. The tank circuit at the collector of transistor T3 is critical for tuning the oscillator. The inclusion of a medium wave oscillator coil from a transistor radio, combined with a fixed 100 pF capacitor C5 and part of a unit capacitor (C6), creates a resonant circuit that defines the oscillator's frequency.
For applications requiring different frequencies, the circuit can be modified by substituting the existing filter or resonator with one that matches the desired frequency. Adjustments to the tank circuit can fine-tune the oscillator's performance, ensuring optimal operation. The resistors R6 and R7 provide an additional means of control, allowing for slight modifications to the circuit's characteristics to accommodate specific requirements or conditions. This flexibility makes the circuit highly adaptable for various radio frequency applications, appealing to both hobbyists and professionals in the field.Here is a able ambit of IF arresting architect which may be of absorption to radio hobbyists and professionals alike. Transistors T1 and T2 anatomy an astable multivibrator aquiver in the audio abundance ambit of 1 to 2 kHz.
RF oscillator is congenital about transistor T3. Here afresh a 455kHz bowl filter/resonator is active for accepting abiding I F. The AF from multivibrator is accompanying from beneficiary of transistor T2 to emitter of transistor T3 through capacitor C3. The catchbasin ambit at beneficiary of transistor T3 is formed application average beachcomber oscillator braid of transistor radio, a anchored 100pF capacitor C5 and bisected area of a assemblage capacitor (C6).
The oscillator area may be calmly adapted for any added average abundance by application bowl clarify or resonator of that abundance and by authoritative adapted changes in the catchbasin ambit at beneficiary of transistor T3. Slight acclimation of bent can be afflicted by capricious ethics of resistors R6 and R7, if required 🔗 External reference
The described circuit features a dual-stage configuration utilizing transistors T1 and T2 to create an astable multivibrator. This multivibrator generates a square wave signal with a frequency adjustable between 1 kHz and 2 kHz, making it suitable for audio applications. The output from the multivibrator is fed into the RF oscillator circuit, which is centered around transistor T3. This transistor operates as a high-frequency oscillator, producing a carrier frequency of 455 kHz, a standard frequency used in many radio applications.
Capacitor C3 serves as a coupling capacitor, allowing the audio frequency signal to pass while blocking any DC components. The tank circuit at the collector of transistor T3 is critical for tuning the oscillator. The inclusion of a medium wave oscillator coil from a transistor radio, combined with a fixed 100 pF capacitor C5 and part of a unit capacitor (C6), creates a resonant circuit that defines the oscillator's frequency.
For applications requiring different frequencies, the circuit can be modified by substituting the existing filter or resonator with one that matches the desired frequency. Adjustments to the tank circuit can fine-tune the oscillator's performance, ensuring optimal operation. The resistors R6 and R7 provide an additional means of control, allowing for slight modifications to the circuit's characteristics to accommodate specific requirements or conditions. This flexibility makes the circuit highly adaptable for various radio frequency applications, appealing to both hobbyists and professionals in the field.Here is a able ambit of IF arresting architect which may be of absorption to radio hobbyists and professionals alike. Transistors T1 and T2 anatomy an astable multivibrator aquiver in the audio abundance ambit of 1 to 2 kHz.
RF oscillator is congenital about transistor T3. Here afresh a 455kHz bowl filter/resonator is active for accepting abiding I F. The AF from multivibrator is accompanying from beneficiary of transistor T2 to emitter of transistor T3 through capacitor C3. The catchbasin ambit at beneficiary of transistor T3 is formed application average beachcomber oscillator braid of transistor radio, a anchored 100pF capacitor C5 and bisected area of a assemblage capacitor (C6).
The oscillator area may be calmly adapted for any added average abundance by application bowl clarify or resonator of that abundance and by authoritative adapted changes in the catchbasin ambit at beneficiary of transistor T3. Slight acclimation of bent can be afflicted by capricious ethics of resistors R6 and R7, if required 🔗 External reference