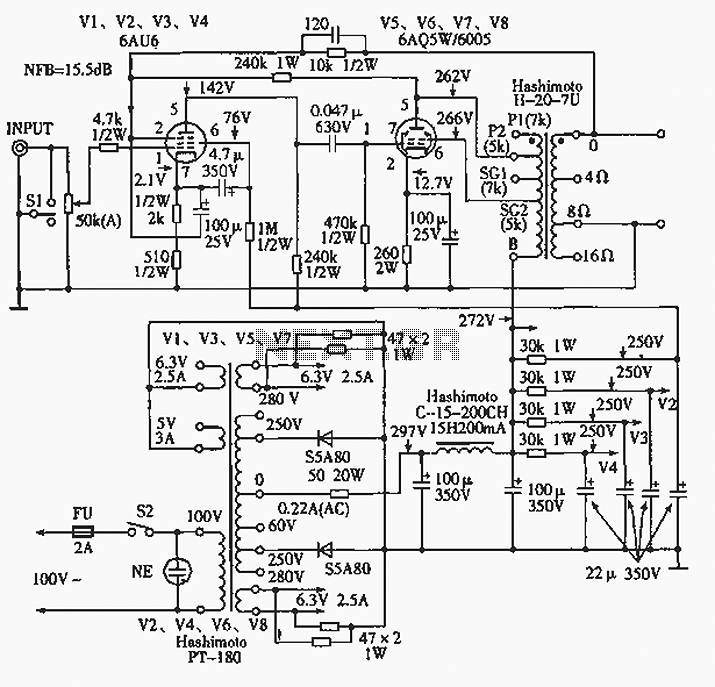
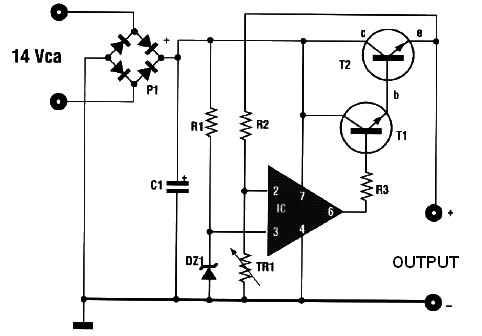
Single cell charger
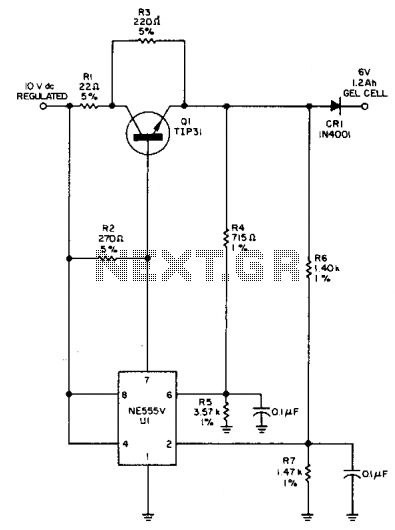
This circuit detects a full-charge state and automatically switches to a float condition—from 240 mA to 12 mA. The circuit uses the 555 timer.
The described circuit is designed to monitor the charging state of a battery and to transition between a high current charging mode and a low current float mode to maintain battery health and longevity. The 555 timer integrated circuit serves as the core component for timing and control functions.
In the charging phase, the circuit allows a current of 240 mA to flow into the battery. This is achieved by configuring the 555 timer in monostable or astable mode, depending on the desired timing characteristics. The output of the timer can control a transistor or a relay that connects the power supply to the battery.
Once the battery reaches a pre-set voltage level, indicating a full charge, the 555 timer detects this state through a voltage divider network connected to the battery terminals. Upon detection of the full charge, the timer output switches state, reducing the current to a float level of 12 mA. This transition is critical as it prevents overcharging, which can lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
The float state is maintained by adjusting the duty cycle of the 555 timer, ensuring that the battery remains topped off without excessive current flow. The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for reverse polarity protection and capacitors for smoothing voltage fluctuations.
Overall, this circuit effectively manages battery charging by utilizing the 555 timer's versatile timing capabilities, ensuring both efficient charging and safe maintenance of the battery's state of charge.This circuit detects a full-charge state and automatically switches to a float condition—from 240 mA to 12 mA. The circuit uses the 555 timer.
The described circuit is designed to monitor the charging state of a battery and to transition between a high current charging mode and a low current float mode to maintain battery health and longevity. The 555 timer integrated circuit serves as the core component for timing and control functions.
In the charging phase, the circuit allows a current of 240 mA to flow into the battery. This is achieved by configuring the 555 timer in monostable or astable mode, depending on the desired timing characteristics. The output of the timer can control a transistor or a relay that connects the power supply to the battery.
Once the battery reaches a pre-set voltage level, indicating a full charge, the 555 timer detects this state through a voltage divider network connected to the battery terminals. Upon detection of the full charge, the timer output switches state, reducing the current to a float level of 12 mA. This transition is critical as it prevents overcharging, which can lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
The float state is maintained by adjusting the duty cycle of the 555 timer, ensuring that the battery remains topped off without excessive current flow. The circuit may also include additional components such as diodes for reverse polarity protection and capacitors for smoothing voltage fluctuations.
Overall, this circuit effectively manages battery charging by utilizing the 555 timer's versatile timing capabilities, ensuring both efficient charging and safe maintenance of the battery's state of charge.This circuit detects a full-charge state and automatically switches to a float condition—from 240 mA to 12 mA. The circuit uses the 555 timer.
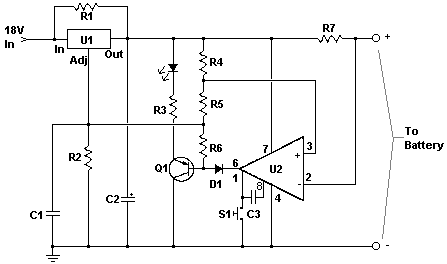

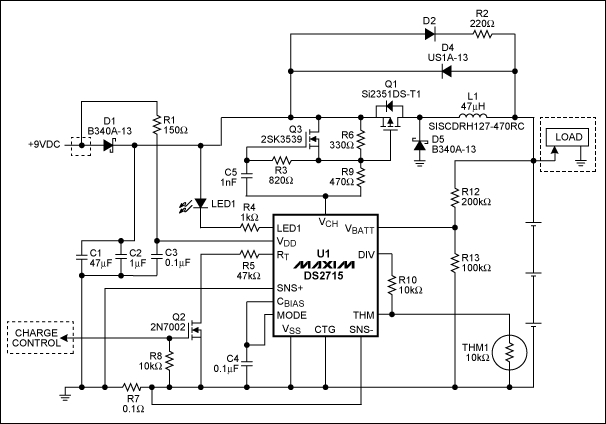
.jpg)