small bare bone arduino bluduino
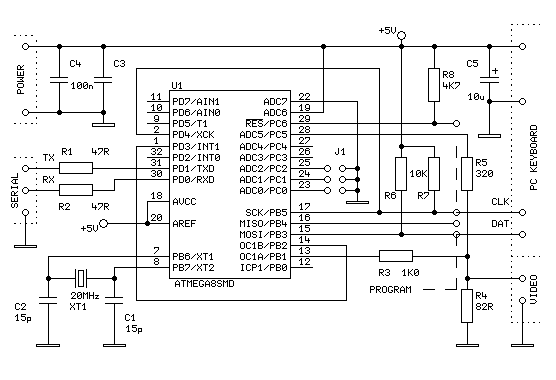
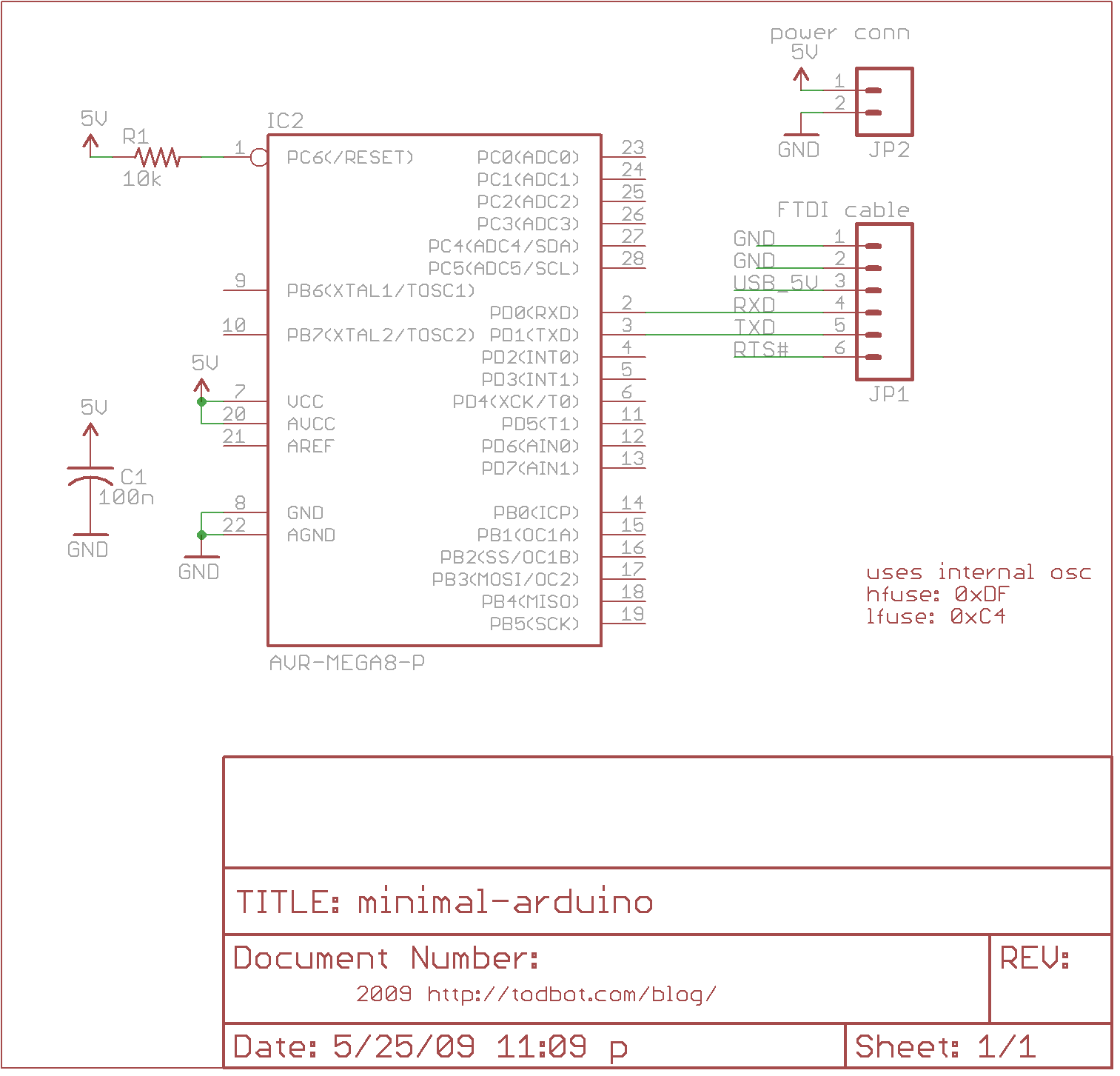
There are many bare-bones Arduinos available on the internet. Most of them are assembled on a solderless breadboard and utilize an ATmega168 (or ATmega328) microcontroller with an Arduino bootloader, a resonator (which may have built-in capacitors or require two external capacitors), and a resistor. Here is a quickly drawn Eagle schematic diagram. This represents a truly bare-bones Arduino, which means that...
The bare-bones Arduino is a minimalistic version of the standard Arduino boards, designed for users who need a compact, cost-effective solution for their projects. The schematic typically includes the following essential components:
1. **Microcontroller**: The core of the circuit is the ATmega168 or ATmega328 microcontroller. This device is responsible for executing the program code and controlling the entire system. It features a range of digital input/output pins, analog inputs, and communication interfaces, making it versatile for various applications.
2. **Bootloader**: The Arduino bootloader is pre-installed on the microcontroller, allowing users to upload code directly via a serial interface without needing an external programmer. This feature simplifies the programming process and enables rapid prototyping.
3. **Resonator**: A resonator (or crystal oscillator) is included to provide a stable clock signal for the microcontroller. This component is crucial for ensuring accurate timing and reliable operation of the microcontroller. Depending on the design, it may include built-in capacitors or require the addition of two external capacitors to function correctly.
4. **Resistor**: A pull-up or pull-down resistor may be included in the circuit to ensure that the microcontroller's input pins are at a defined logic level when not actively driven. This is important for preventing floating inputs, which can lead to unpredictable behavior.
5. **Power Supply**: The schematic will also indicate how the circuit is powered, which typically involves connecting to a USB power source or a battery. Voltage regulation may be necessary if the supply voltage exceeds the acceptable range for the microcontroller.
6. **Breadboard Layout**: The use of a solderless breadboard allows for easy assembly and modification of the circuit. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for prototyping and testing different configurations without the need for soldering.
The bare-bones Arduino design is particularly advantageous for applications where space and cost are critical factors, such as in embedded systems or DIY electronics projects. By focusing on essential components and omitting unnecessary features, this design allows users to create custom solutions tailored to their specific needs.There are many `bare bone` Arduinos you can find from internet. Most of them are on a solderless breadboard with a ATmega168 (or 328) chip with Arduino bootloader, a resonator (with built-in capacitors or needs 2 capacitors), a resistor.Here is a quick drawn Eagle schematic diagram. This is truely `bare bone` Arduino which means that.. 🔗 External reference
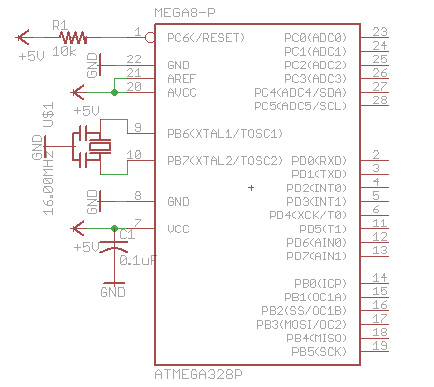
The bare-bones Arduino is a minimalistic version of the standard Arduino boards, designed for users who need a compact, cost-effective solution for their projects. The schematic typically includes the following essential components:
1. **Microcontroller**: The core of the circuit is the ATmega168 or ATmega328 microcontroller. This device is responsible for executing the program code and controlling the entire system. It features a range of digital input/output pins, analog inputs, and communication interfaces, making it versatile for various applications.
2. **Bootloader**: The Arduino bootloader is pre-installed on the microcontroller, allowing users to upload code directly via a serial interface without needing an external programmer. This feature simplifies the programming process and enables rapid prototyping.
3. **Resonator**: A resonator (or crystal oscillator) is included to provide a stable clock signal for the microcontroller. This component is crucial for ensuring accurate timing and reliable operation of the microcontroller. Depending on the design, it may include built-in capacitors or require the addition of two external capacitors to function correctly.
4. **Resistor**: A pull-up or pull-down resistor may be included in the circuit to ensure that the microcontroller's input pins are at a defined logic level when not actively driven. This is important for preventing floating inputs, which can lead to unpredictable behavior.
5. **Power Supply**: The schematic will also indicate how the circuit is powered, which typically involves connecting to a USB power source or a battery. Voltage regulation may be necessary if the supply voltage exceeds the acceptable range for the microcontroller.
6. **Breadboard Layout**: The use of a solderless breadboard allows for easy assembly and modification of the circuit. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for prototyping and testing different configurations without the need for soldering.
The bare-bones Arduino design is particularly advantageous for applications where space and cost are critical factors, such as in embedded systems or DIY electronics projects. By focusing on essential components and omitting unnecessary features, this design allows users to create custom solutions tailored to their specific needs.There are many `bare bone` Arduinos you can find from internet. Most of them are on a solderless breadboard with a ATmega168 (or 328) chip with Arduino bootloader, a resonator (with built-in capacitors or needs 2 capacitors), a resistor.Here is a quick drawn Eagle schematic diagram. This is truely `bare bone` Arduino which means that.. 🔗 External reference