Smart Audio Alert Device (SAAD)
This is a senior project from Stony Brook University, designed and implemented by Tak-Fung Yip and Franklin Delgado, with consultation from Professor Milutin Stanac.
The senior project from Stony Brook University represents a collaborative effort in the field of electronics engineering. The project was developed by students Tak-Fung Yip and Franklin Delgado, under the guidance of Professor Milutin Stanac. The initiative likely encompasses a range of components, including circuit design, system integration, and potentially software development, aimed at addressing specific engineering challenges or demonstrating innovative solutions.
The project may involve the creation of a prototype that utilizes various electronic components such as microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators. These elements can be integrated to form a cohesive system that performs designated tasks, showcasing the application of theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios. The involvement of a faculty advisor suggests a structured approach, ensuring adherence to academic standards and the incorporation of best practices in engineering design.
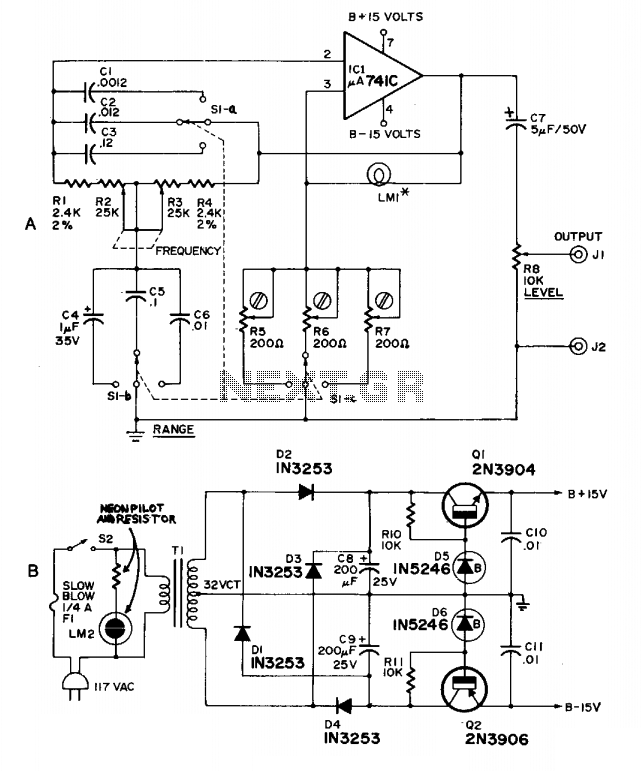
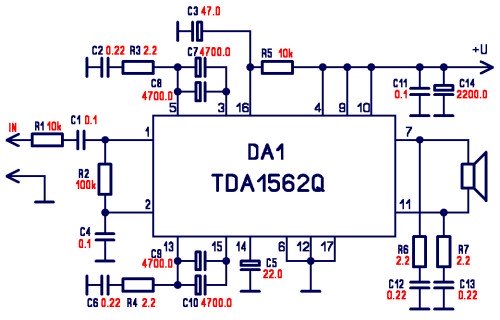
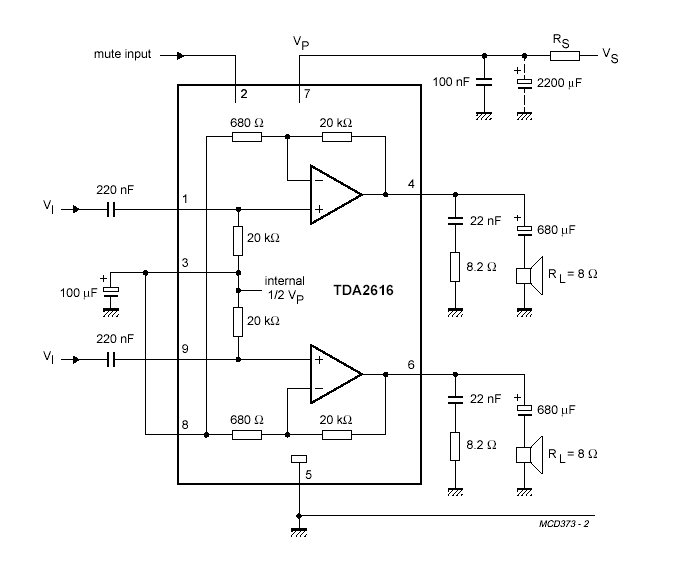
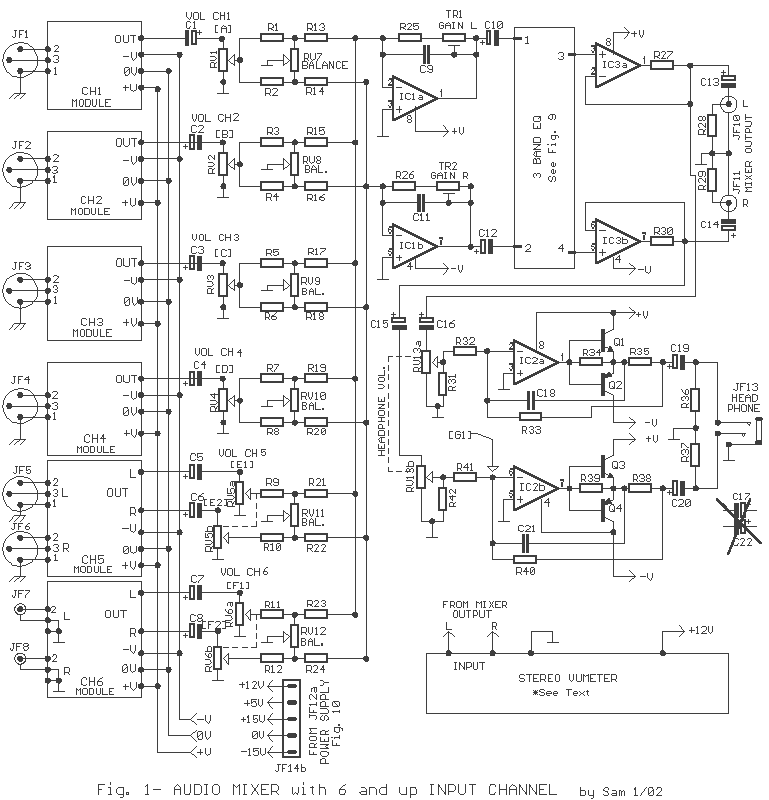
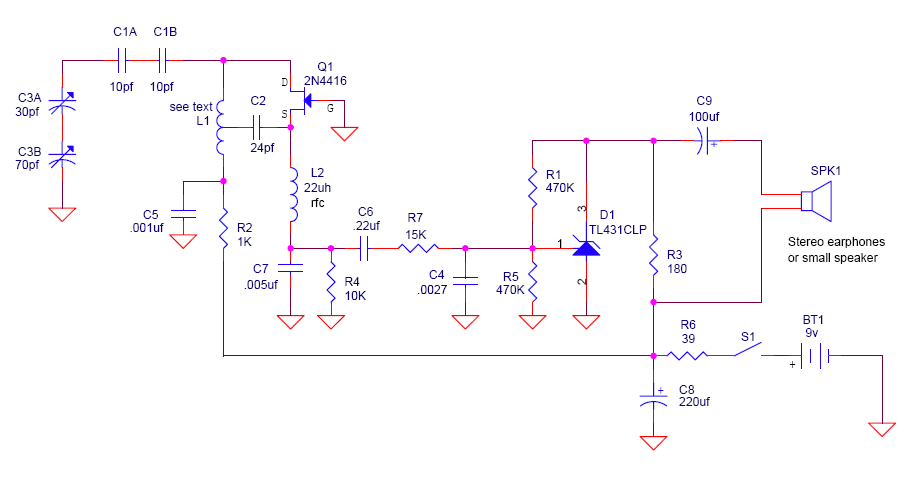
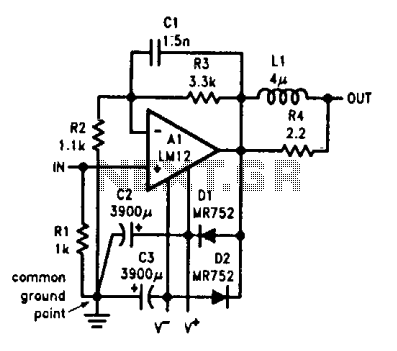
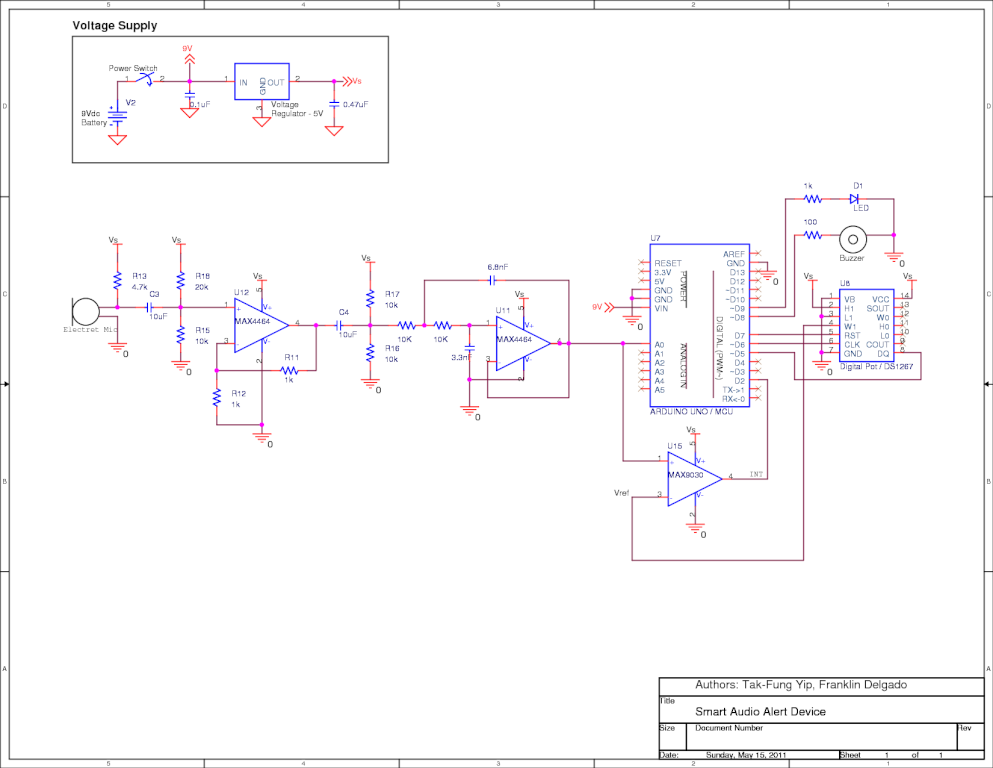
Moreover, the project may include a detailed schematic representation, illustrating the interconnections between components and the flow of signals within the system. Such a schematic would typically feature power supply arrangements, input/output interfaces, and any necessary signal conditioning circuits. The design process would involve iterative testing and refinement, focusing on optimizing performance, reliability, and usability.
In conclusion, this senior project not only reflects the students' engineering capabilities but also serves as a valuable educational experience, preparing them for future challenges in the electronics domain.This is a senior project from Stony Brook University, which is designed and implemented by Tak-Fung Yip, Franklin Delgado, and consulted by professor Milutin Stanac.. 🔗 External reference
The senior project from Stony Brook University represents a collaborative effort in the field of electronics engineering. The project was developed by students Tak-Fung Yip and Franklin Delgado, under the guidance of Professor Milutin Stanac. The initiative likely encompasses a range of components, including circuit design, system integration, and potentially software development, aimed at addressing specific engineering challenges or demonstrating innovative solutions.
The project may involve the creation of a prototype that utilizes various electronic components such as microcontrollers, sensors, and actuators. These elements can be integrated to form a cohesive system that performs designated tasks, showcasing the application of theoretical knowledge in practical scenarios. The involvement of a faculty advisor suggests a structured approach, ensuring adherence to academic standards and the incorporation of best practices in engineering design.
Moreover, the project may include a detailed schematic representation, illustrating the interconnections between components and the flow of signals within the system. Such a schematic would typically feature power supply arrangements, input/output interfaces, and any necessary signal conditioning circuits. The design process would involve iterative testing and refinement, focusing on optimizing performance, reliability, and usability.
In conclusion, this senior project not only reflects the students' engineering capabilities but also serves as a valuable educational experience, preparing them for future challenges in the electronics domain.This is a senior project from Stony Brook University, which is designed and implemented by Tak-Fung Yip, Franklin Delgado, and consulted by professor Milutin Stanac.. 🔗 External reference