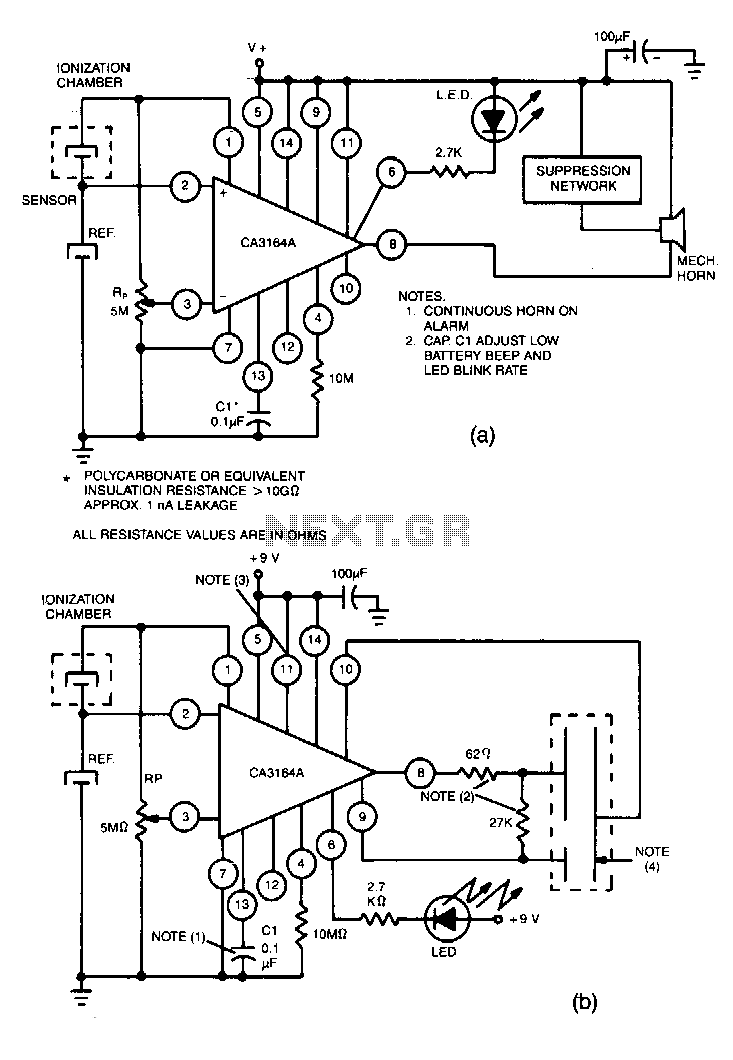
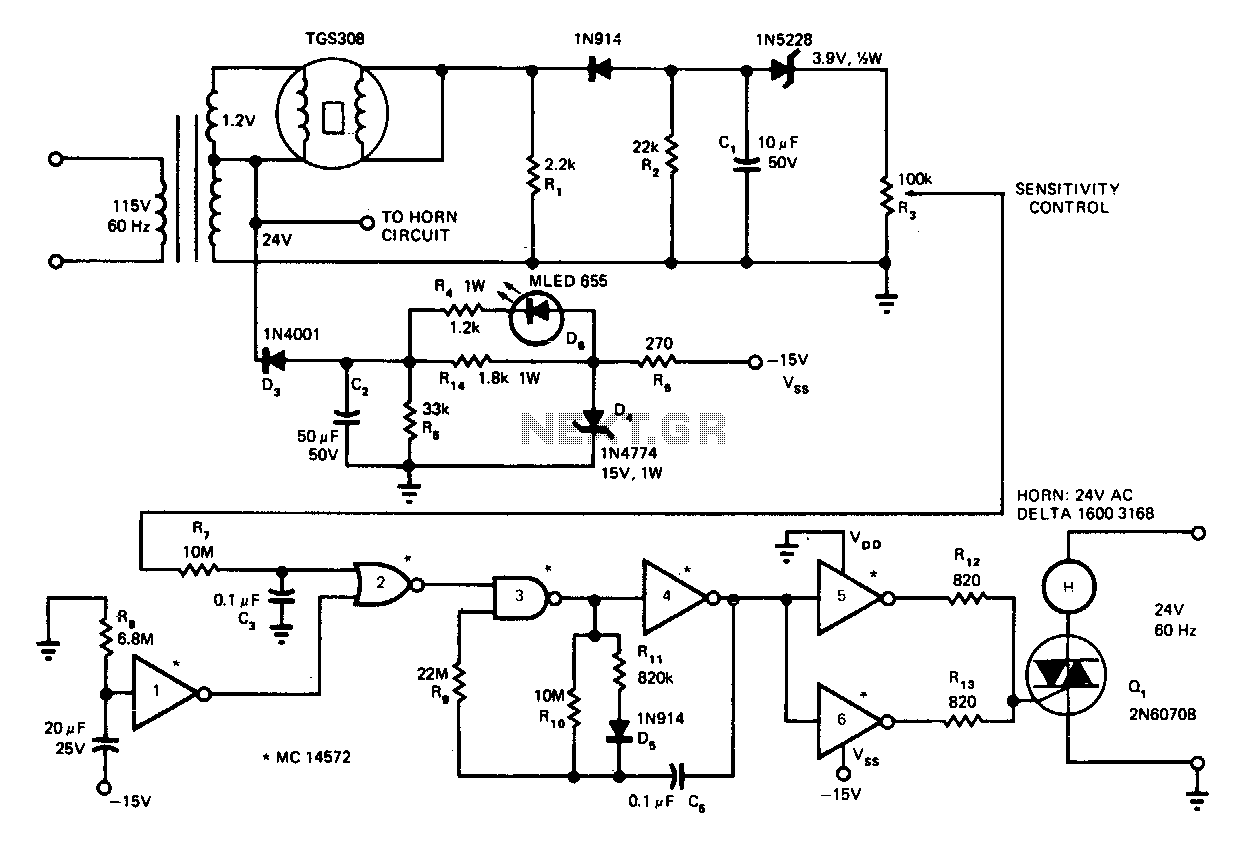
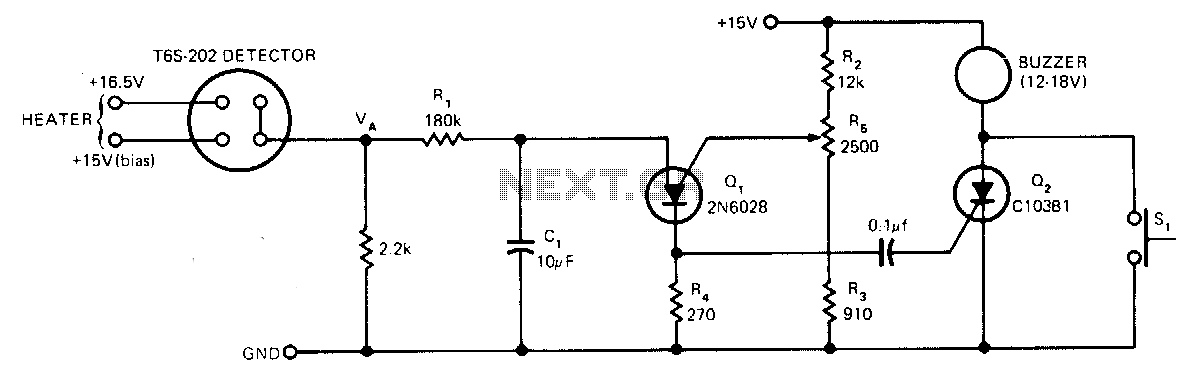
Smoke-detector
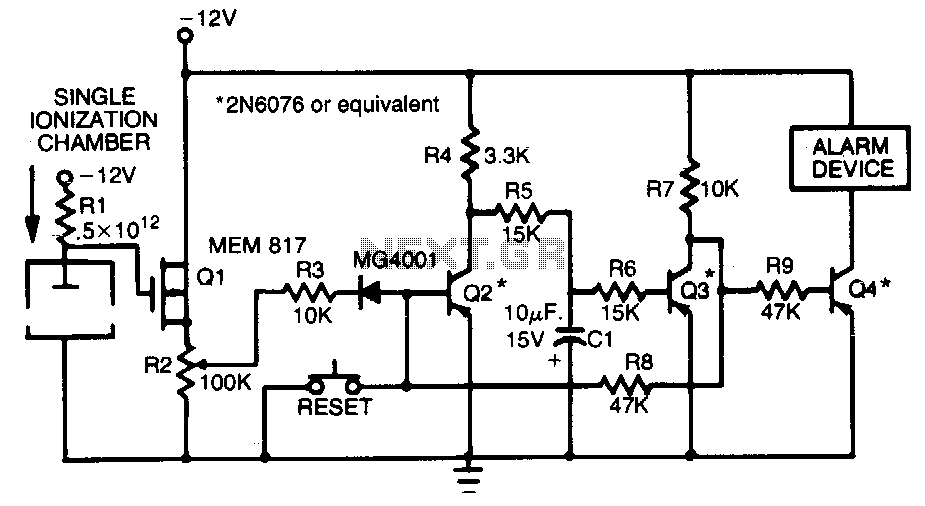
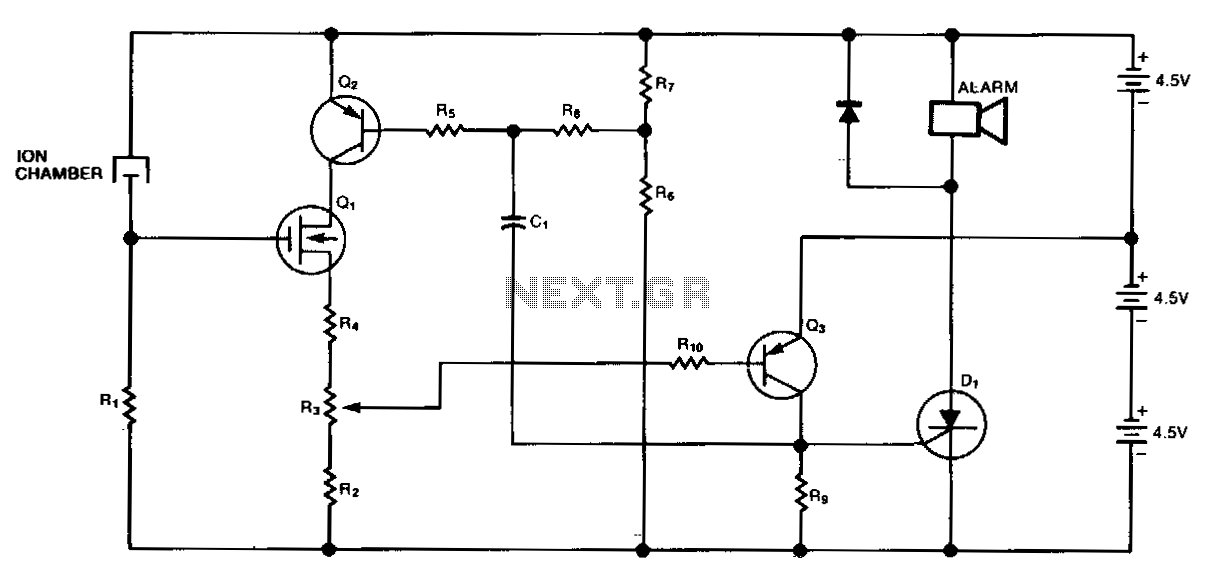
This smoke detector employs a MEM 817 p-channel enhancement mode MOSFET as its buffer amplifier. The sensor operates on the principle that the current decreases when smoke enters the chamber, leading to a negative voltage change at the gate of the buffer MOSFET. Quiescent voltage levels at the output of the chamber range from approximately -4 V to -6 V, with smoke detection resulting in a voltage change of about -4 V. The MOSFET is configured as a source follower.
The smoke detector circuit utilizes the MEM 817 p-channel enhancement mode MOSFET, which serves as a buffer amplifier to enhance the sensitivity and response time of the smoke detection mechanism. The core operation involves a sensing chamber where smoke particles reduce the ionization current, resulting in a measurable change in voltage.
When smoke enters the detection chamber, the ionization current decreases, which is reflected as a negative voltage at the gate terminal of the MOSFET. The buffer configuration allows for a high input impedance, ensuring that the sensing chamber is not loaded down by the subsequent circuitry. The source follower configuration of the MOSFET allows for the output voltage to closely track the gate voltage, providing a stable and reliable output signal that can be further processed or interfaced with alarm systems.
The quiescent voltage levels of -4 V to -6 V at the output indicate the baseline operational state of the smoke detector. Upon detection of smoke, the output voltage will shift significantly, indicating an alarm condition. This voltage shift is critical for triggering alarm circuits, which can be designed to activate sound alarms or visual indicators, ensuring prompt response to smoke detection.
In practical applications, additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the circuit to filter noise and stabilize the operation of the MOSFET, enhancing the overall reliability of the smoke detector. The careful design of this circuit is essential for ensuring that it meets safety standards and performs effectively in real-world environments.This smoke detector uses a MEM 817 p-channel enhancement mode MOSFET as its buffer amplifier. Operation of the sensor is based on a decrease in the current when smoke enters the chamber, thereby causing a negative voltage excursion at the gate of the buffer MOSFET. Quiescent voltage values at the output of the chamber vary from about -4 V to -6 V, and detection of smoke will result in an excursion of about -4 V. The MOSFET is connected as a source follower. 🔗 External reference
The smoke detector circuit utilizes the MEM 817 p-channel enhancement mode MOSFET, which serves as a buffer amplifier to enhance the sensitivity and response time of the smoke detection mechanism. The core operation involves a sensing chamber where smoke particles reduce the ionization current, resulting in a measurable change in voltage.
When smoke enters the detection chamber, the ionization current decreases, which is reflected as a negative voltage at the gate terminal of the MOSFET. The buffer configuration allows for a high input impedance, ensuring that the sensing chamber is not loaded down by the subsequent circuitry. The source follower configuration of the MOSFET allows for the output voltage to closely track the gate voltage, providing a stable and reliable output signal that can be further processed or interfaced with alarm systems.
The quiescent voltage levels of -4 V to -6 V at the output indicate the baseline operational state of the smoke detector. Upon detection of smoke, the output voltage will shift significantly, indicating an alarm condition. This voltage shift is critical for triggering alarm circuits, which can be designed to activate sound alarms or visual indicators, ensuring prompt response to smoke detection.
In practical applications, additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the circuit to filter noise and stabilize the operation of the MOSFET, enhancing the overall reliability of the smoke detector. The careful design of this circuit is essential for ensuring that it meets safety standards and performs effectively in real-world environments.This smoke detector uses a MEM 817 p-channel enhancement mode MOSFET as its buffer amplifier. Operation of the sensor is based on a decrease in the current when smoke enters the chamber, thereby causing a negative voltage excursion at the gate of the buffer MOSFET. Quiescent voltage values at the output of the chamber vary from about -4 V to -6 V, and detection of smoke will result in an excursion of about -4 V. The MOSFET is connected as a source follower. 🔗 External reference